This guide shows you how to install NVIDIA drivers on Rocky Linux so you can use hardware-accelerated graphics, CUDA workloads, and graphics processing unit (GPU) compute for gaming, visualization, machine learning, and scientific simulations. The steps use NVIDIA’s official CUDA repository to deliver current driver releases with direct vendor support.
By the end, you will have working NVIDIA drivers with GPU acceleration enabled, verified through nvidia-smi. The instructions cover both the proprietary drivers and the open kernel modules, with guidance on choosing the right flavor for your GPU.
These steps apply to Rocky Linux 10, 9, and 8. Rocky 9 and 8 use NVIDIA’s DNF (Dandified Yum) module streams for driver selection, while Rocky 10 installs drivers as standard packages because the CUDA repository does not provide driver modules on RHEL/Rocky 10. Follow the version-labeled sections when commands differ.
Install NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
The workflow below starts with choosing a driver flavor, then prepares your system, enables the required repositories, installs dependencies and the driver, and verifies everything with nvidia-smi.
Choose Your NVIDIA Driver Option for Rocky Linux
NVIDIA provides both proprietary drivers and open kernel modules in the CUDA repository. Use the table below to pick the best fit before installing.
| Feature | Proprietary drivers | Open kernel modules |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel module type | Closed-source NVIDIA kernel modules | Open-source kernel modules with NVIDIA user-space libraries |
| GPU architecture support | Maxwell, Pascal, Volta, Turing, and later | Turing and newer only (required for Blackwell and later) |
| Feature coverage | Full feature set and widest compatibility | May have limitations on some features or workloads |
| Recommended for | Most desktops, workstations, and mixed-GPU systems | Turing-and-newer systems that require open modules |
Recommended for most users: Install the proprietary drivers for the widest hardware support and the fewest surprises. Use the open kernel modules only if your GPU is Turing or newer and you specifically need the open-source kernel flavor.
NVIDIA is switching the default driver flavor to the open kernel modules starting with the R560 driver series. The open modules are recommended for Turing, Ampere, Ada, and Hopper GPUs, while Blackwell and newer GPUs require them. Maxwell, Pascal, and Volta GPUs are not compatible with the open modules, so use the proprietary drivers for those cards.
If you are not sure which architecture your GPU uses, capture the PCI ID with lspci -nn and compare it against NVIDIA’s open kernel module compatibility list (the table includes PCI Device IDs for supported GPUs) before choosing a flavor.
Prepare Your System for NVIDIA Driver Installation
Update Rocky Linux Packages
Update your existing packages to avoid conflicts from outdated libraries or kernel mismatches. The following command refreshes the repository metadata and upgrades all installed packages:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshIf this process updates the kernel, reboot your system before continuing. The NVIDIA driver installer needs kernel headers that match your running kernel, so a reboot ensures consistency.
Identify Your Graphics Card
Confirm that your system has an NVIDIA GPU and note the model and PCI ID for driver compatibility. The lspci command lists all PCI devices, and grep filters for VGA or 3D controllers (see our grep command guide if you want more filtering options):
lspci -nn | grep -E "VGA|3D"For example, this output shows an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650:
03:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation TU117 [GeForce GTX 1650] [10DE:1F82] (rev a1)
If your GPU is not supported by the current branch, use NVIDIA’s legacy GPU list and the NVIDIA Unix driver archive to identify the correct driver branch for your hardware.
If lspci is missing, install the pciutils package first:
sudo dnf install pciutils -yThe -y flag automatically answers yes to prompts. Remove it if you want to review the package list before installing.
Check Secure Boot Status
Check your Secure Boot status. Secure Boot can prevent unsigned kernel modules from loading, which affects NVIDIA driver installation. Use the mokutil command to check:
mokutil --sb-stateIf the command is missing, install mokutil first:
sudo dnf install mokutil -yWhen Secure Boot is enabled, you will see:
SecureBoot enabled
Alternatively, when Secure Boot is disabled:
SecureBoot disabled
With Secure Boot enabled, you will need to sign the NVIDIA kernel module or import the Machine Owner Key (MOK) after installation. The troubleshooting section below covers this process.
Install EPEL and Enable Required Repositories
The NVIDIA driver installation requires packages from EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux), including dkms (Dynamic Kernel Module Support) for kernel module builds on Rocky Linux 10, 9, and 8. CRB (CodeReady Builder) or PowerTools is disabled by default and is only needed if a dependency install complains about missing packages.
Rocky Linux 10
On Rocky Linux 10, install the config-manager plugin used later to add the NVIDIA repository, then add EPEL:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -y
sudo dnf install epel-release -yRocky Linux 9
Similarly, Rocky Linux 9 provides EPEL through the extras repository. Install the config-manager plugin, then add EPEL:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -y
sudo dnf install epel-release -yRocky Linux 8
For version 8, the repository uses the name PowerTools instead of CRB. Install the plugin, then add EPEL:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -y
sudo dnf install epel-release -yFor more details on EPEL configuration and available packages, see our EPEL installation guide for Rocky Linux.
Keep EPEL enabled after installation so DKMS updates arrive alongside kernel updates.
Add the NVIDIA CUDA Repository
Add the NVIDIA CUDA repository. NVIDIA maintains official RPM repositories for RHEL and compatible distributions like Rocky Linux, and the CUDA Installation Guide for Linux documents the same repository layout used below.
Rocky Linux 10
For version 10, use the RHEL 10 repository:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel10/x86_64/cuda-rhel10.repoRocky Linux 9
On version 9, use the RHEL 9 repository:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel9/x86_64/cuda-rhel9.repoRocky Linux 8
Version 8 uses the RHEL 8 repository:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel8/x86_64/cuda-rhel8.repoOnce you add the repository, DNF will prompt you to import the NVIDIA GPG key during the first package installation. Type y to accept the key import.
Install Build Dependencies
With the repositories configured, install the kernel headers and development tools. The NVIDIA repository uses DKMS-based kmod packages on Rocky Linux 10, 9, and 8, so these dependencies are required for both proprietary and open kernel modules:
sudo dnf install kernel-headers kernel-devel gcc make dkms acpid libglvnd-glx libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-devel pkgconf-pkg-config -yThis command installs:
kernel-headersandkernel-devel– Required for DKMS to compile kernel modules (Rocky 8/9/10)gccandmake– Build toolchain for compilationdkms– Dynamic Kernel Module Support, rebuilds modules after kernel updates (Rocky 8/9/10)acpid– Power management daemon for GPU power eventslibglvnd-*– Vendor-neutral OpenGL dispatch librarypkgconf-pkg-config– Provides thepkg-configcommand used by build scripts
If the dependency install fails with missing packages, enable CRB or PowerTools for your release and rerun the dependency command:
Rocky Linux 10:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbRocky Linux 9:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbRocky Linux 8:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertoolsFor detailed information about kernel headers on Rocky Linux, see our kernel headers installation guide.
Install NVIDIA Drivers
Now you can install the NVIDIA drivers. Rocky Linux 9 and 8 use DNF module streams from the CUDA repository, while Rocky Linux 10 installs the driver as standard packages.
Rocky Linux 9 and 8: Module Installation
Rocky Linux 9 and 8 use DNF module streams to manage NVIDIA driver versions. The latest-dkms stream installs the newest driver with DKMS support for automatic kernel module rebuilding:
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:latest-dkms -yYou can view all available driver streams, including legacy branches for older GPUs:
sudo dnf module list nvidia-driverExample output (Rocky Linux 9; stream list changes as NVIDIA updates the repository):
Name Stream Profiles Summary nvidia-driver latest default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for latest branch nvidia-driver latest-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for latest-dkms branch nvidia-driver open-dkms [d] default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for open-dkms branch nvidia-driver 515 default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 515 branch nvidia-driver 515-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for 515-dkms branch nvidia-driver 515-open default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 515-open branch nvidia-driver 520 default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 520 branch nvidia-driver 520-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for 520-dkms branch nvidia-driver 520-open default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 520-open branch nvidia-driver 525 default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 525 branch nvidia-driver 525-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for 525-dkms branch nvidia-driver 525-open default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 525-open branch nvidia-driver 530 default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 530 branch nvidia-driver 530-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for 530-dkms branch nvidia-driver 530-open default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 530-open branch nvidia-driver 535 default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 535 branch nvidia-driver 535-dkms default [d], fm, ks Nvidia driver for 535-dkms branch nvidia-driver 535-open default [d], fm, ks, src Nvidia driver for 535-open branch
To use the open kernel modules, enable the open stream and install the nvidia-open meta package:
sudo dnf module enable nvidia-driver:open-dkms -y
sudo dnf install nvidia-open -yOpen kernel modules only support Turing-and-newer GPUs. Maxwell, Pascal, and Volta GPUs require the proprietary modules. If you run into stability issues, reset the module stream and reinstall the proprietary branch:
sudo dnf module reset nvidia-driver -y && sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:latest-dkms -y
Rocky Linux 10: Proprietary DKMS Packages
On Rocky Linux 10, install the proprietary stack as regular packages. This is the safest option for Maxwell, Pascal, or Volta GPUs and for mixed-GPU systems:
sudo dnf install kmod-nvidia-latest-dkms nvidia-driver nvidia-driver-libs nvidia-driver-cuda -yThis command installs the proprietary NVIDIA driver along with the CUDA integration libraries that provide nvidia-smi. Driver versions change frequently, so rely on the verification step below to confirm the exact version installed.
Rocky Linux 10: Open Kernel Modules (Turing and Newer)
If you need the open kernel modules and your GPU is Turing or newer, install the nvidia-open meta package. This is required for Blackwell-class GPUs and aligns with NVIDIA’s default open-module choice starting with the R560 driver series.
sudo dnf install nvidia-open -yThe nvidia-open meta package should install nvidia-driver-cuda, which provides nvidia-smi. If nvidia-smi is missing, reinstall the CUDA integration package:
sudo dnf install nvidia-driver-cuda -yReboot to Load the Driver
Once the installation completes, reboot your system to load the NVIDIA kernel module and initialize the GPU:
sudo rebootVerify the Installation
Once your system reboots, confirm that the NVIDIA driver loaded correctly by running the nvidia-smi utility:
nvidia-smiA successful run prints a table with the driver version, GPU model, memory usage, and running processes. Example format (values vary):
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI XXX.XX.XX Driver Version: XXX.XX.XX CUDA Version: X.Y | |-------------------------------+----------------------+--------------------| | GPU Name | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | |===============================+======================+====================| | 0 NVIDIA GPU | 00000000:01:00.0 Off | N/A | +-------------------------------+----------------------+--------------------+
NVIDIA driver and CUDA versions change frequently. Your
nvidia-smioutput will show the current release installed from the NVIDIA repository.
If you want the NVIDIA Settings graphical user interface (GUI), install the package first:
sudo dnf install nvidia-settings -yThen launch the NVIDIA X Server Settings application for graphical configuration:
nvidia-settingsThis utility displays detailed GPU information, allows display configuration, and provides access to performance settings.
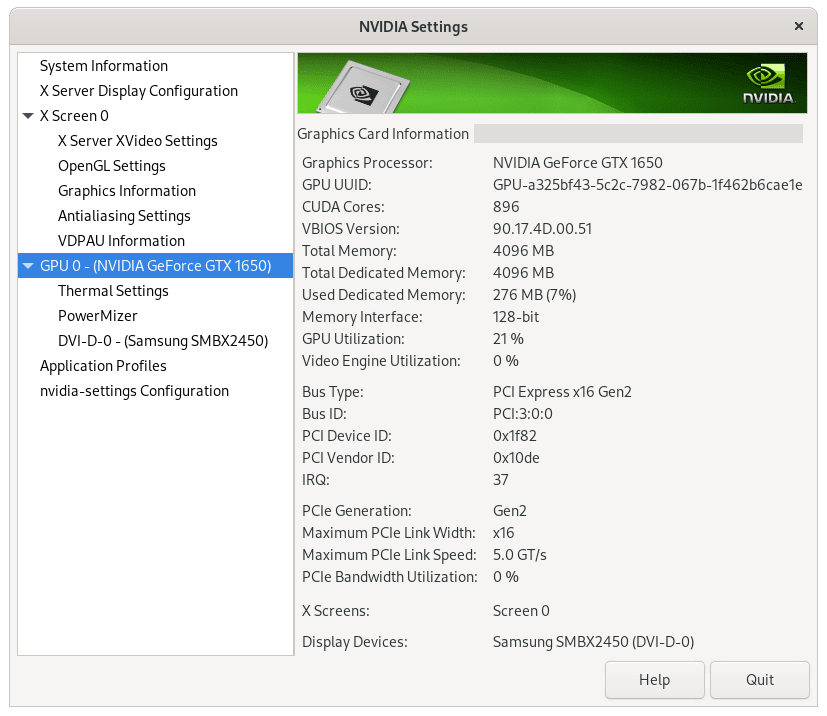
Rocky Linux 10 ships GNOME as Wayland-only. The
xorg-x11-server-Xorgandgnome-session-xsessionpackages are not available in the default repositories, so a GNOME Xorg session is not an option on Rocky 10.
Update NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
NVIDIA releases driver updates regularly with bug fixes, security patches, and new GPU support. To update your drivers, use the standard DNF upgrade command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThis command upgrades all packages including NVIDIA drivers when new versions become available in the repository. After updating, reboot to load the new kernel module.
On Rocky Linux 9 and 8, upgrades stay within your selected module stream. If you need a different branch, switch streams with the module list in the install section and reinstall the desired stream.
You can check your currently installed driver version with:
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=driver_version --format=csv,noheaderExample output:
XXX.XX.XX
Troubleshoot NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
NVIDIA driver installation can sometimes encounter issues related to Secure Boot, the Nouveau driver, or kernel module loading. The following sections cover common problems along with diagnostic commands and solutions.
Nouveau Driver Conflicts
The open-source Nouveau driver ships with Rocky Linux and loads automatically for NVIDIA GPUs. Because it conflicts with the proprietary NVIDIA driver, you must block it from loading.
Check if Nouveau is currently loaded:
lsmod | grep -i nouveau || echo "nouveau not loaded"When output appears, Nouveau is active. Example format (sizes vary):
nouveau <size> <used>
If you see nouveau not loaded, the module is already inactive and you can skip to the next section. Otherwise, create configuration files to block it from loading:
echo "blacklist nouveau" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
echo 'omit_drivers+=" nouveau "' | sudo tee /etc/dracut.conf.d/blacklist-nouveau.confRegenerate the initramfs to apply the block configuration:
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo depmod -aThen reboot and verify that Nouveau no longer loads:
sudo rebootAfter rebooting, run the check again. When you see nouveau not loaded, the block configuration is working correctly:
lsmod | grep -i nouveau || echo "nouveau not loaded"nouveau not loaded
Secure Boot Preventing Driver Loading
When Secure Boot is enabled, the NVIDIA kernel module may fail to load because the system does not recognize its signature. You will see errors like:
modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'nvidia': Key was rejected by service
Check whether the NVIDIA module loaded:
lsmod | grep nvidiaWhen the output is empty and Secure Boot is enabled, you need to import the Machine Owner Key (MOK) that DKMS uses to sign the module. Verify the DKMS public key exists:
ls -la /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubIf the file is missing, generate the key pair with DKMS:
sudo dkms generate_mokSigning key: /var/lib/dkms/mok.key Public certificate (MOK): /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub Certificate or key are missing, generating self signed certificate for MOK...
When the key exists, you will see output similar to this:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 832 Feb 4 23:26 /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub
Then import the key into the MOK database:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubThe command prompts you to create a one-time password. Remember this password because you will need it during the next step.
Reboot your system:
sudo rebootDuring boot, the MOK Manager utility appears. Select “Enroll MOK”, then “Continue”, then “Yes”. Enter the password you created earlier, and select “Reboot”.
Once the system boots, verify that the NVIDIA module loaded correctly:
lsmod | grep nvidiaWhen the driver loads successfully, you will see NVIDIA modules listed. Example format (sizes vary):
nvidia_drm <size> <used> nvidia_modeset <size> <used> nvidia_drm nvidia <size> <used> nvidia_modeset video <size> <used> nvidia_modeset
nvidia-smi Shows “No devices were found”
When nvidia-smi reports no devices, the kernel module may not have loaded, or there may be a hardware detection issue.
No devices were found
Check for NVIDIA-related errors in the system journal. These commands use tail to show the most recent entries, so see our tail command guide if you want to adjust the output length:
sudo journalctl -b | grep -i nvidia | tail -20Jan 08 11:22:14 rocky kernel: NVRM: No NVIDIA GPU found.
Verify whether the kernel module loaded:
lsmod | grep -i nvidia || echo "nvidia modules not loaded"nvidia modules not loaded
If you see nvidia modules not loaded, try loading the module manually:
sudo modprobe nvidiaWhen modprobe fails, check dmesg for errors:
dmesg | grep -i nvidia | tail -10[ 56.842] NVRM: No NVIDIA GPU found.
If the system reports “No NVIDIA GPU found” but lspci still lists the card, verify that your GPU is supported by the driver branch you installed. Older cards may require a legacy branch from NVIDIA’s legacy GPU list and the Unix driver archive.
After loading the module, rerun nvidia-smi. The standard GPU table output confirms the driver is active:
NVIDIA-SMI XXX.XX.XX
MOK Key Lost After Windows Update (Dual Boot)
On dual-boot systems, Windows updates can reset firmware settings and clear an enrolled MOK key. When this happens, the NVIDIA driver may stop loading and nvidia-smi will fail.
NVIDIA-SMI has failed because it couldn't communicate with the NVIDIA driver.
Confirm the NVIDIA module is not loading:
lsmod | grep -i nvidia || echo "nvidia modules not loaded"nvidia modules not loaded
Re-import the DKMS MOK key:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubSet a one-time password, reboot, and complete the MOK enrollment in the UEFI interface as described above. After rebooting, verify the driver is active:
nvidia-smiNVIDIA-SMI XXX.XX.XX
Remove NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
To remove the NVIDIA drivers and revert to the open-source Nouveau driver, follow the steps below for your Rocky Linux version.
Rocky Linux 9 and 8
Reset the module stream, then remove the proprietary driver packages:
sudo dnf module reset nvidia-driver -y
sudo dnf remove nvidia-driver* -yIf you installed the open kernel modules, remove the open packages as well:
sudo dnf remove nvidia-open kmod-nvidia-open-dkms -yThen clean up dependencies:
sudo dnf autoremove -yRocky Linux 10 (Proprietary DKMS Packages)
Remove the driver packages directly:
sudo dnf remove kmod-nvidia-latest-dkms nvidia-driver nvidia-driver-libs nvidia-driver-cuda -y
sudo dnf autoremove -yRocky Linux 10 (Open Kernel Modules)
Remove the open kernel module package and related driver packages:
sudo dnf remove nvidia-open kmod-nvidia-open-dkms nvidia-driver nvidia-driver-libs nvidia-driver-cuda -y
sudo dnf autoremove -yRe-enable Nouveau (Optional)
If you previously blocked Nouveau and want to restore it, remove the configuration files you created earlier:
sudo rm -f /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
sudo rm -f /etc/dracut.conf.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --forceRemove the NVIDIA Repository (Optional)
To fully clean up, remove the NVIDIA CUDA repository from your system:
sudo rm -f /etc/yum.repos.d/cuda-rhel*.repo
sudo dnf clean allReboot to complete the removal and load the Nouveau driver:
sudo rebootNVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux: Install the CUDA Toolkit (Optional)
If you plan to compile CUDA applications, install the CUDA compiler package from the NVIDIA repository. This keeps the install smaller than the full toolkit while still providing nvcc.
sudo dnf install cuda-nvcc-13-1 -yIf you need the full toolkit (libraries, profilers, Nsight tools), install
cuda-toolkit-13-1instead. It is a large download and does not add the NVIDIA driver, so complete the driver installation above first.
The nvcc binary is installed under /usr/local/cuda-*. Use the full path if it is not in your PATH:
/usr/local/cuda-13.1/bin/nvcc --versionnvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver Copyright (c) 2005-2025 NVIDIA Corporation Built on Tue_Dec_16_07:23:41_PM_PST_2025 Cuda compilation tools, release 13.1, V13.1.115 Build cuda_13.1.r13.1/compiler.37061995_0
CUDA toolkit versions update frequently. Your
nvccoutput will reflect the current toolkit version from the NVIDIA repository.
FAQ: NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
nvidia-smi is installed by the NVIDIA driver stack, so it works without the CUDA toolkit. To check for the toolkit, look for nvcc under /usr/local/cuda-*/bin or run nvcc --version if it is in your PATH.
Check the installed packages. Open modules install nvidia-open and kmod-nvidia-open-dkms, while the proprietary stack installs kmod-nvidia-latest-dkms. Use rpm -q nvidia-open kmod-nvidia-open-dkms and rpm -q kmod-nvidia-latest-dkms to see what is present.
Conclusion: NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux
You now have NVIDIA drivers installed on Rocky Linux, with DKMS handling kernel module rebuilds across Rocky 10, 9, and 8. The nvidia-smi utility confirms GPU detection and provides real-time monitoring of temperature, memory usage, and running processes. Use the NVIDIA Settings GUI for display tuning, and keep your drivers updated through standard DNF upgrades.

