BalenaEtcher provides a reliable way to create bootable USB drives and flash SD cards from ISO, IMG, and other disk image formats. Specifically, whether you need to install a new Linux distribution, create a recovery drive, or prepare installation media for another computer, balenaEtcher handles the process. Furthermore, it includes built-in validation to ensure your bootable media works correctly on the first boot.
By the end of this guide, you will have balenaEtcher installed on your Debian system, ready to flash disk images to USB drives and SD cards. The installation uses the official .deb package from the balenaEtcher GitHub releases, which provides the latest stable version with all dependencies automatically resolved.
Update Debian Before Installing balenaEtcher
First, update your Debian system to ensure all existing packages are current. This step essentially helps avoid dependency conflicts during the balenaEtcher installation.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeConsequently, this command refreshes your package database and upgrades any outdated packages to their latest versions.
Additionally, install wget if it is not already present on your system. Minimal Debian installations may not include this tool by default:
sudo apt install wgetInstall balenaEtcher via .deb Package
BalenaEtcher distributes official .deb packages through their GitHub releases page. Notably, this method provides the latest stable version and handles dependency resolution automatically.
Download the balenaEtcher Package
The following command automatically fetches the latest balenaEtcher release from GitHub and downloads the .deb package:
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/balena-io/etcher/releases/latest | grep -oP '"browser_download_url": "\K[^"]+amd64[^"]*\.deb(?=")' | xargs wgetThis command uses the GitHub API to find the latest release, extracts the .deb download URL, and passes it to wget. Consequently, you will always download the current version without manually checking version numbers.
Once the download completes, you will see output similar to:
balena-etcher_2.x.x_amd64.deb 100%[=============================================>] 118.14M 12.5MB/s in 9.8s
Install the Downloaded Package
Next, install the downloaded .deb package using APT, which automatically resolves and installs any missing dependencies:
sudo apt install ./balena-etcher*.debThe ./ prefix explicitly tells APT to install from a local file rather than searching the repositories. Moreover, APT handles all required dependencies automatically, eliminating the need for separate dpkg and fix-broken commands. The wildcard pattern matches whatever version was downloaded.
Verify the Installation
After the installation completes, confirm that balenaEtcher installed correctly by checking the package status:
dpkg -l balena-etcherExpected output confirming successful installation:
Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold | Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend |/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad) ||/ Name Version Architecture Description +++-==============-============-============-=========================================== ii balena-etcher 2.x.x amd64 Flash OS images to SD cards and USB drives
Debian users might recall the previously available hosted APT repository for balenaEtcher. However, this repository is now deprecated and no longer receives updates. Therefore, future installations and updates require downloading the .deb package directly from GitHub as shown in this guide.
Launch balenaEtcher
After installation completes, you can launch balenaEtcher using either the terminal or the graphical application menu. Typically, most desktop users prefer the menu method.
Launch from Terminal
To start balenaEtcher from the command line, run:
balena-etcherSubsequently, the application window opens, displaying the three-step flashing interface: select image, select target drive, and flash.
Launch from Applications Menu
However, for users who prefer the graphical interface, balenaEtcher appears in your application menu after installation:
- Click on the “Activities” button in the top left corner of your screen.
- Select “Show Applications” to display all installed applications.
- Search for “balenaEtcher” or scroll through the application list to find it.
- Click the balenaEtcher icon to launch the application.
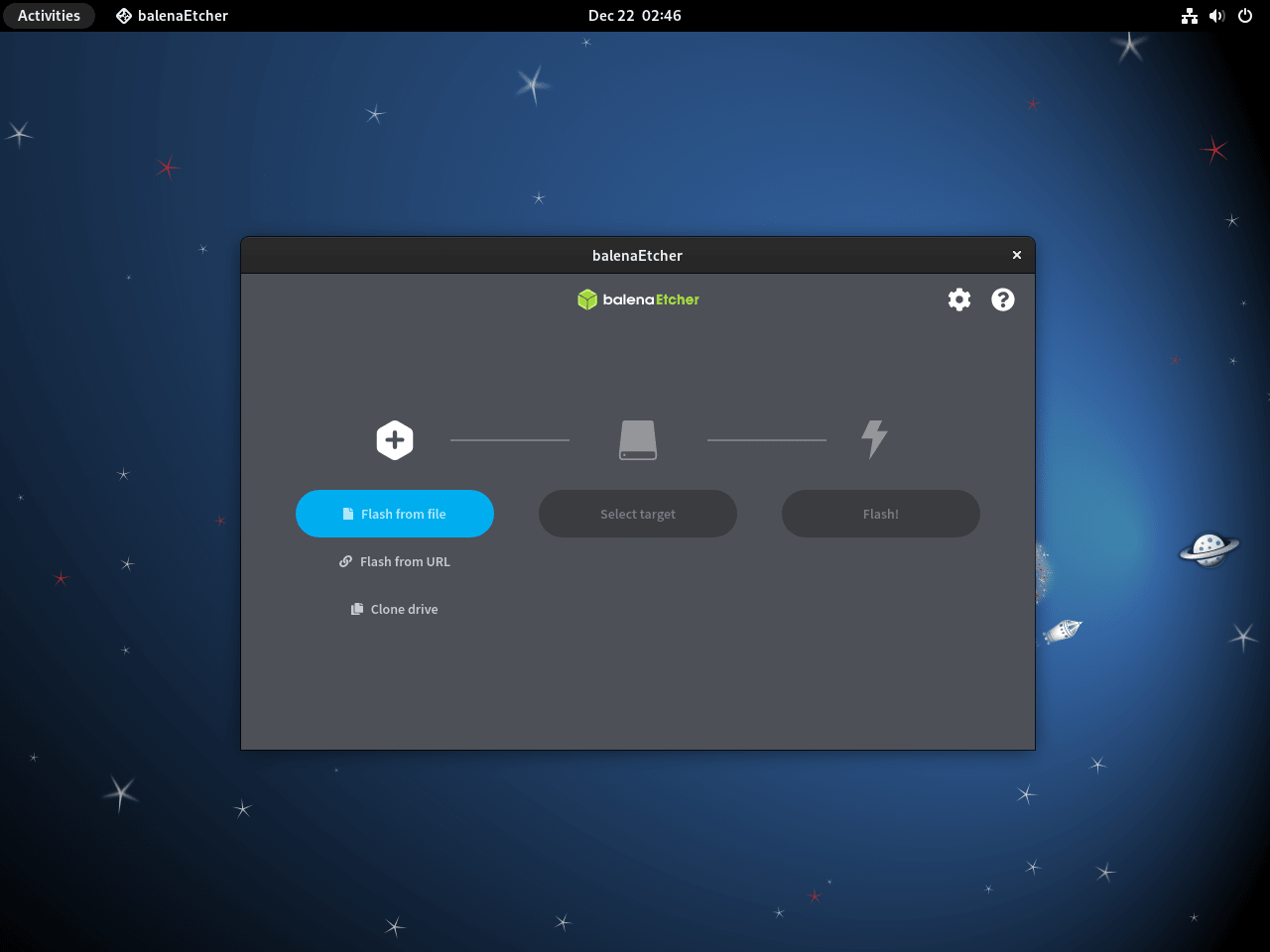
Troubleshoot balenaEtcher
Command Not Found After Installation
If you receive a “command not found” error when running balena-etcher, verify the package installed correctly:
dpkg -l | grep balenaExpected output confirming installation:
ii balena-etcher 2.x.x amd64 Flash OS images to SD cards and USB drives, safely and easily.
Conversely, if the package appears with status iU or iF instead of ii, dependencies are missing. Resolve this immediately by running:
sudo apt --fix-broken installPermission Denied When Flashing
If balenaEtcher fails to write to your USB drive with a permission error, ensure you have proper access to the device. Specifically, the application requires elevated privileges to write directly to block devices.
First, identify your target device:
lsblkExample output showing a USB drive at /dev/sdb:
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 238.5G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 512M 0 part /boot/efi └─sda2 8:2 0 238G 0 part / sdb 8:16 1 14.9G 0 disk └─sdb1 8:17 1 14.9G 0 part
Should the issue persist, try launching balenaEtcher with elevated privileges:
sudo balena-etcherApplication Fails to Start
If the application fails to start, check for error messages by running it from the terminal:
balena-etcher 2>&1 | head -20Common issues include missing GTK libraries or display server problems. Therefore, ensure your desktop environment is fully loaded before launching the application.
Remove balenaEtcher
To remove balenaEtcher from your Debian system, first uninstall the package and then clean up orphaned dependencies:
sudo apt remove balena-etcherNext, remove any packages that were installed as dependencies but are no longer needed:
sudo apt autoremoveRemove Configuration Files
BalenaEtcher stores user configuration in your home directory. If you want a complete removal, explicitly delete these files as well.
Warning: The following command permanently deletes balenaEtcher configuration files, including any saved preferences. This action cannot be undone.
rm -rf ~/.config/balenaEtcherAfter removal, verify the package is no longer installed:
dpkg -l | grep balenaFinally, no output confirms the package was successfully removed.
Conclusion
You now have balenaEtcher installed on Debian, ready to create bootable USB drives and flash SD cards from disk images. Additionally, the application validates written data automatically, ensuring your installation media works correctly. For future updates, satisfy dependencies by downloading the latest .deb package from the GitHub releases page and repeating the installation process.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>