R is a programming language for statistical computing and data visualization, maintained by The R Project with over 20,000 packages available through CRAN. RStudio is an IDE that adds syntax highlighting, debugging tools, and a visual interface for managing plots and packages. This guide covers installing both on Fedora, managing R packages through CRAN and the cran2copr repository, and removing them when no longer needed.
Choose Your Installation Approach
Fedora provides R through its default repositories, making installation straightforward with DNF. However, RStudio Desktop is not available in the Fedora repos and must be downloaded directly from Posit’s download page. The table below summarizes your options.
| Component | Installation Method | Version | Updates |
|---|---|---|---|
| R Language | Fedora Repos (DNF) | Latest stable | Automatic via dnf upgrade |
| RStudio Desktop | Posit RPM Download | Latest stable | Manual (script below) |
| R Packages (Fedora) | DNF from official repos | 500+ packages | Automatic via dnf upgrade |
| R Packages (cran2copr) | DNF via COPR | Additional packages | Automatic via dnf upgrade |
| R Packages (CRAN) | R console install.packages() | Full CRAN library | Manual via R console |
For most users, the DNF method for R is recommended because it integrates with Fedora’s package management and receives security updates automatically. Install RStudio separately using the official RPM from Posit if you need an IDE.
Update Your Fedora System
Before installing new software, refresh your package database and apply any pending updates. This step ensures you install the latest available versions and avoid dependency conflicts.
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshIf kernels or core libraries update, consider rebooting before continuing. This step typically takes a few minutes depending on how recently you last updated.
Install R from Fedora Repositories
Fedora packages R and its development libraries in the default repositories. You can install just the core R language, or add development headers for compiling R packages from source.
Option 1: Install Core R Language
For most data analysis work, the base R package provides everything you need. In particular, this installation includes the R interpreter, base libraries, and standard datasets.
sudo dnf install RThe R metapackage pulls in R-core (the interpreter) and R-core-devel (headers for compiling packages). After installation completes, verify R is accessible:
R --versionExpected output:
R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31) -- "[Not] Part in a Rumble" Copyright (C) 2025 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform: x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu
Option 2: Install R with Full Development Support
If you plan to compile R packages that depend on external libraries, Java integration, or mathematical functions, you should install the complete development stack:
sudo dnf install R-core R-core-devel R-java R-java-devel libRmath libRmath-develSpecifically, this command installs:
- R-core: The R interpreter, base libraries, and standard datasets.
- R-core-devel: Header files needed to compile R packages from source.
- R-java / R-java-devel: Java integration for R packages that use rJava or similar bridges.
- libRmath / libRmath-devel: Standalone mathematical library for applications that need R’s statistical functions without the full interpreter.
Additionally, some CRAN packages require additional system libraries for compilation. If you encounter errors when installing packages like httr, xml2, or textshaping, install these common dependencies:
sudo dnf install libcurl-devel openssl-devel harfbuzz-devel fribidi-devel freetype-devel libpng-devel libjpeg-turbo-devel libxml2-develIn essence, these libraries provide SSL/TLS support, XML parsing, font rendering, and image processing capabilities that many R packages depend on during compilation.
Install RStudio Desktop
RStudio Desktop is not available in the Fedora repositories. Posit (the company that develops RStudio) distributes official RPM packages for Fedora and other Red Hat-based distributions, so you need to download the package manually and install it with DNF.
Download and Install RStudio
First, ensure R is installed on your system. RStudio requires R to function, and DNF will warn you if R is missing when you attempt installation.
sudo dnf install RNext, download the latest RStudio Desktop RPM from the Posit download page. You can use curl to download directly to your current directory:
curl -LO https://download1.rstudio.org/electron/rhel9/x86_64/rstudio-2025.09.2-418-x86_64.rpmThe version number in the URL above reflects the current release at the time of writing. Check the Posit download page for the latest version and update the URL accordingly. Posit builds the Fedora/RHEL RPM against RHEL 9, which is compatible with current Fedora releases.
Once downloaded, install the RPM using DNF. This approach automatically resolves and installs any missing dependencies:
sudo dnf install ./rstudio-2025.09.2-418-x86_64.rpmAfter installation completes, you can remove the downloaded RPM file:
rm rstudio-2025.09.2-418-x86_64.rpmLaunch RStudio
You can start RStudio from the terminal:
rstudioAlternatively, open RStudio from the GNOME desktop by searching for “RStudio” in Activities. The application appears in your Applications menu after installation.
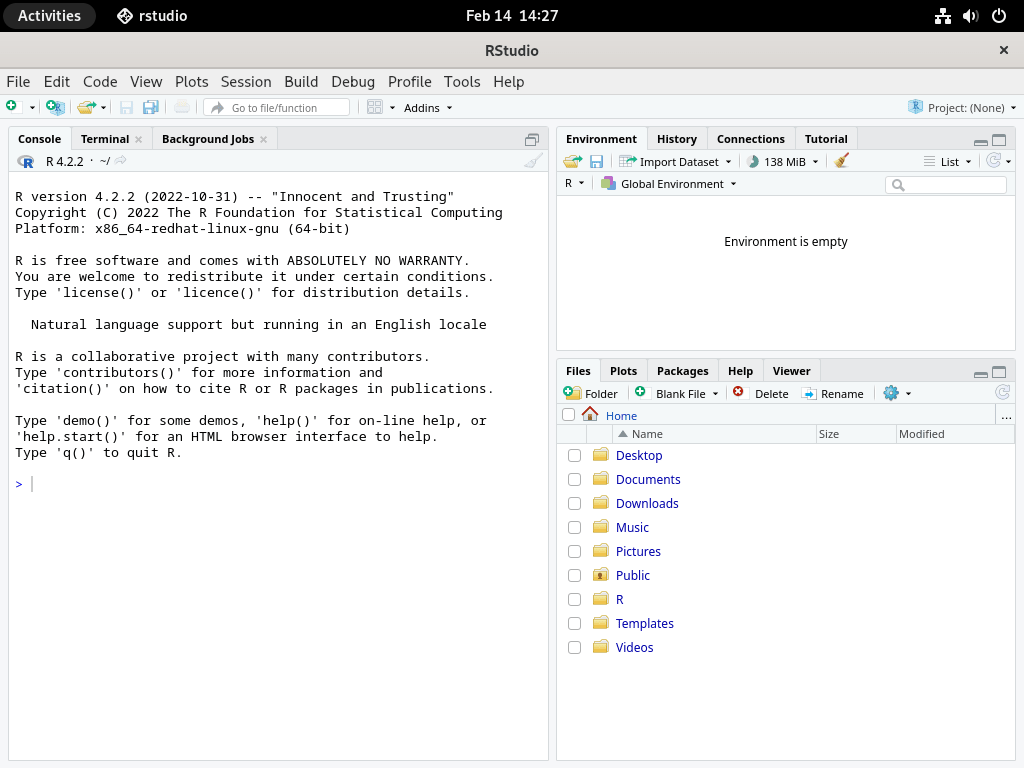
When RStudio launches, it automatically detects your R installation and opens an integrated R console. The interface includes panels for script editing, console output, environment variables, and plot visualization.
Update RStudio
RStudio does not include automatic updates or a DNF repository. To update, download and install the latest RPM, which replaces the existing version. The following script automates this by fetching the latest version from GitHub:
#!/bin/bash
# Fetch the latest RStudio version tag from GitHub
LATEST=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/rstudio/rstudio/tags | grep -o '"name": "v[^"]*"' | head -1 | sed 's/"name": "v//;s/"//')
if [ -z "$LATEST" ]; then
echo "Failed to fetch latest version"
exit 1
fi
# Convert version format: 2025.09.2+418 -> 2025.09.2-418
VERSION=$(echo "$LATEST" | tr '+' '-')
RPM="rstudio-${VERSION}-x86_64.rpm"
URL="https://download1.rstudio.org/electron/rhel9/x86_64/${RPM}"
echo "Downloading RStudio $VERSION..."
curl -LO "$URL" && sudo dnf install "./${RPM}" && rm "${RPM}"Save this script as update-rstudio.sh and run it with bash update-rstudio.sh whenever you want to check for updates.
Verify the R Installation
After installing R, confirm it works correctly by starting an interactive R session and running a simple command.
Start the R Console
To start, launch the R interpreter from your terminal:
RYou will see the R startup banner and an interactive prompt:
R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31) -- "[Not] Part in a Rumble" Copyright (C) 2025 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform: x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details. Natural language support but running in an English locale R is a collaborative project with many contributors. Type 'contributors()' for more information and 'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications. Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or 'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help. Type 'q()' to quit R. >
Test Basic Functionality
Then, run a simple calculation to verify the interpreter works:
print("Hello from R!")Expected output:
[1] "Hello from R!"
Exit the R Console
To leave the R session and return to your shell, type:
q()R will ask whether to save your workspace image. Type n to exit without saving, or y to preserve your session data (variables, history) for next time. For quick testing, declining to save is usually appropriate.
Install R Packages from CRAN
CRAN hosts over 20,000 R packages for statistics, machine learning, data visualization, and specialized domains. Because these packages extend R’s capabilities, you install them directly from the R console using the install.packages() function.
Install a Package
Start R and install a package by name. This example installs ggplot2, one of the most popular data visualization libraries:
RThen, inside the R console:
install.packages("ggplot2")When you run this command, R downloads the package from a CRAN mirror and compiles it if necessary. If prompted to select a mirror, choose one geographically close to you. Additionally, the first installation on a fresh system may prompt you to create a personal library directory since installing to the system library requires root privileges.
Load and Use a Package
After installation, load the package into your session:
library(ggplot2)Now you can use functions from ggplot2 in your R scripts and interactive sessions. However, each new R session requires reloading packages you want to use.
Update Installed Packages
Periodically, you should check for updates and upgrade all installed packages to their latest versions by running:
update.packages(ask = FALSE)The ask = FALSE argument skips confirmation prompts for each package. If you prefer to review updates before installing, omit this argument, and R will prompt you for each available update.
Alternatively, to reinstall a specific package to get its latest version, use install.packages() again:
install.packages("ggplot2")As a result, this command overwrites the existing installation with the newest version from CRAN.
Remove an R Package
To uninstall a package you no longer need:
remove.packages("package_name")Replace package_name with the actual package name. This removes only the specified package; dependencies installed alongside it remain in your library.
Install R Packages via DNF
Notably, Fedora includes over 500 R packages in its official repositories, covering popular libraries for data manipulation, visualization, and statistical modeling. Installing R packages through DNF offers faster installation (no compilation) and automatic updates through dnf upgrade.
Package names follow the pattern R-<packagename>. For example, to install ggplot2:
sudo dnf install R-ggplot2To discover available packages, search with:
dnf search R-*Expand Coverage with cran2copr
For R packages not in the official Fedora repositories, the cran2copr project provides additional pre-built RPMs. This community repository covers thousands of CRAN packages beyond what Fedora packages officially.
COPR (Community Projects) repositories are maintained by community members, not the Fedora Project. While cran2copr is widely used and actively maintained, packages do not undergo the same review process as official Fedora packages. Use community repositories at your discretion.
Enable the cran2copr Repository
Fedora 41 and later include the COPR plugin (dnf5-plugins) by default. If for some reason it is missing, install it first:
sudo dnf install 'dnf-command(copr)'Next, enable the cran2copr repository:
sudo dnf copr enable iucar/cranYou will see a notice that COPR repositories are community-maintained. Type y to confirm and proceed. Once enabled, the repository becomes available for package installation.
Install the COPR Manager (Optional)
Additionally, the cran2copr project provides an R package called CoprManager that integrates COPR installation into your R workflow. While optional, it allows you to install COPR packages from within R.
sudo dnf install R-CoprManagerInstall Additional Packages from cran2copr
After enabling the repository, packages from cran2copr install the same way as official Fedora packages. For example, to install a package not in the official repos:
sudo dnf install R-tidyverseAll R packages installed via DNF update automatically with your system:
sudo dnf upgradeNot every CRAN package is available through DNF (official repos or cran2copr). If a package you need is missing, install it from within R using install.packages().
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Package Compilation Fails with Missing Headers
Some R packages compile native code and require system libraries. If you see errors like “cannot find -lcurl” or “harfbuzz/hb.h: No such file or directory”, install the corresponding development packages:
sudo dnf install libcurl-devel openssl-devel harfbuzz-devel fribidi-devel freetype-devel libpng-devel libjpeg-turbo-devel libxml2-develAfter installing the missing libraries, retry the R package installation.
RStudio Fails to Launch
If RStudio crashes on startup or shows a blank window, check whether all dependencies installed correctly. Run RStudio from the terminal to see error messages:
rstudioCommon causes include missing Qt libraries or display server issues. On Wayland systems, RStudio should work without modification, but if you experience graphical glitches, setting the QT platform to xcb may help:
QT_QPA_PLATFORM=xcb rstudioR Cannot Find Installed Packages
If R reports “there is no package called…” for a package you installed, the library path may not include your user library. Check your library paths:
.libPaths()Packages installed as a regular user go to ~/R/x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu-library/4.5/ by default. Packages installed with sudo or via DNF go to the system library. Therefore, ensure the library containing your package appears in the output.
Remove R and RStudio
If you no longer need R or RStudio, you can uninstall them with DNF. Fortunately, removal is straightforward and does not affect other software on your system.
Remove R
First, remove R and its development packages:
sudo dnf remove R R-core R-core-devel R-java R-java-devel libRmath libRmath-develThen, clean up any orphaned dependencies that were installed alongside R:
sudo dnf autoremoveFinally, verify that R is no longer available on your system:
which RIf R was removed successfully, this command returns no output. Otherwise, it shows the path to the R binary.
Remove RStudio
To uninstall RStudio, run:
sudo dnf remove rstudioRemove User Configuration and Data
The following commands permanently delete R packages you installed in your home directory, RStudio configuration files, and any R workspace data. Back up anything you want to keep before proceeding.
R stores user-installed packages and history in your home directory:
rm -rf ~/R
rm -rf ~/.Rhistory ~/.Rprofile ~/.RenvironRStudio stores configuration and cached data in these locations:
rm -rf ~/.config/rstudio
rm -rf ~/.local/share/rstudioDisable the cran2copr Repository
If you enabled the cran2copr COPR repository and no longer need it:
sudo dnf copr remove iucar/cranThis removes the repository configuration but does not uninstall packages already installed from it.
Conclusion
You now have R installed from the Fedora repositories and, optionally, RStudio Desktop from Posit. The R console provides access to CRAN’s extensive package ecosystem for statistical computing, data analysis, and visualization. With the cran2copr repository, you can also install popular R packages as system packages that update alongside Fedora. Whether you work in a terminal or prefer RStudio’s integrated environment, your Fedora system is ready for data science projects of any scale.
For version control with your R projects, consider installing Git on Fedora. If you work with other programming languages alongside R, you may also find our guides for Golang on Fedora and Rust on Fedora useful.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><blockquote>quote</blockquote>