Timeshift creates system snapshots that allow you to roll back your Debian installation to a previous state after failed updates, configuration mistakes, or software conflicts. Whether you need to protect a workstation before experimenting with new packages or maintain a reliable recovery point for a home server, Timeshift provides scheduled backups using either rsync with hard links or native BTRFS snapshots. By the end of this guide, you will have Timeshift installed and configured to protect your Debian system with automated snapshots.
Update Debian Before Installing Timeshift
First, open a terminal by searching for ‘Terminal’ in Activities. Before installing any new software, update your package lists and upgrade existing packages to ensure compatibility:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command refreshes the package index and installs available updates for your current packages. Running updates before installing new software helps prevent dependency conflicts.
Install Timeshift on Debian
Timeshift is available in Debian’s default repositories, so installation requires a single command. Run the following to install the application along with its dependencies:
sudo apt install timeshiftAPT automatically installs all required dependencies, including rsync for file synchronization and the graphical toolkit for the interface.
Once the installation completes, verify that Timeshift is accessible by displaying its version and command-line options:
timeshift --helpThe first lines of output display the version number:
Timeshift v24.06.6 by Tony George (teejeetech@gmail.com)
Syntax:
timeshift --check
timeshift --create [OPTIONS]
timeshift --restore [OPTIONS]
timeshift --delete-[all] [OPTIONS]
timeshift --list-{snapshots|devices} [OPTIONS]
The version number varies by Debian release. Debian 13 (Trixie) provides version 24.06.6, Debian 12 (Bookworm) provides 22.11.2, and Debian 11 (Bullseye) provides 20.11.1. All versions support the same core functionality for creating and restoring snapshots.
Launch Timeshift
Timeshift requires root privileges to access system files and create snapshots. To launch the graphical interface from the terminal, use:
sudo timeshift-gtkAlternatively, launch Timeshift from your desktop environment’s application menu. On GNOME, navigate to:
Activities > Show Applications > Timeshift
The system prompts for your administrator password since Timeshift requires elevated privileges to manage system snapshots. This behavior is handled by PolicyKit, which allows graphical applications to request root access securely.
Configure Timeshift for Your First Snapshot
When you first launch Timeshift, the setup wizard guides you through initial configuration. The following sections explain each step to help you make informed choices about snapshot modes, storage locations, and scheduling.
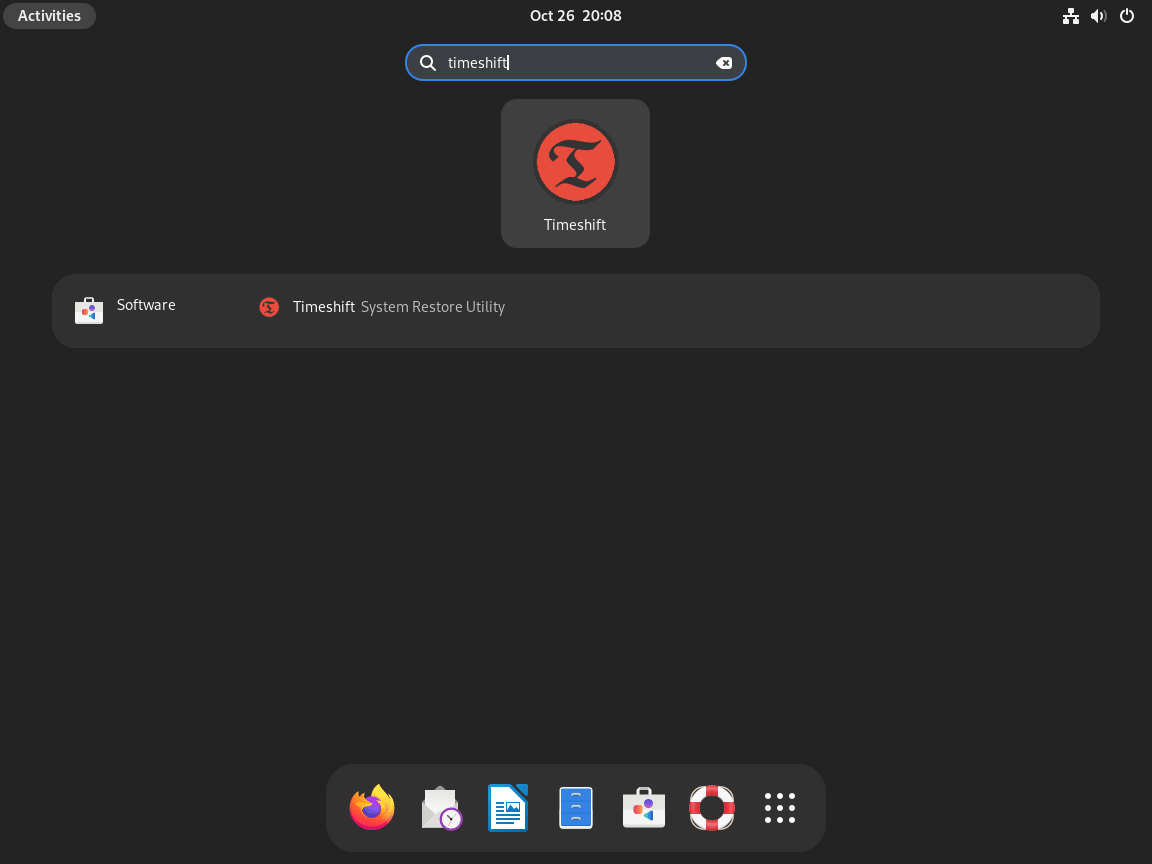
Choose a Snapshot Mode
Timeshift offers two snapshot modes, each suited to different filesystem configurations:
RSYNC Mode
- Works with any Linux filesystem (ext4, XFS, BTRFS, etc.)
- Uses rsync and hard links to efficiently store incremental backups
- Recommended for Debian installations since the default installer creates ext4 partitions
- Snapshots can be stored on any mounted partition with sufficient space
BTRFS Mode
- Uses native BTRFS filesystem snapshots for near-instant backup creation
- Requires a BTRFS filesystem with Ubuntu-style subvolume layout (@, @home)
- Debian’s default installer does not create this subvolume layout automatically
- Only suitable if you manually configured BTRFS subvolumes during installation
For most Debian users, select RSYNC mode. BTRFS mode requires specific subvolume configuration that Debian does not create by default. If you installed Debian with the standard installer and default partitioning, RSYNC provides full functionality. You can verify your filesystem type by running
df -T /in a terminal.
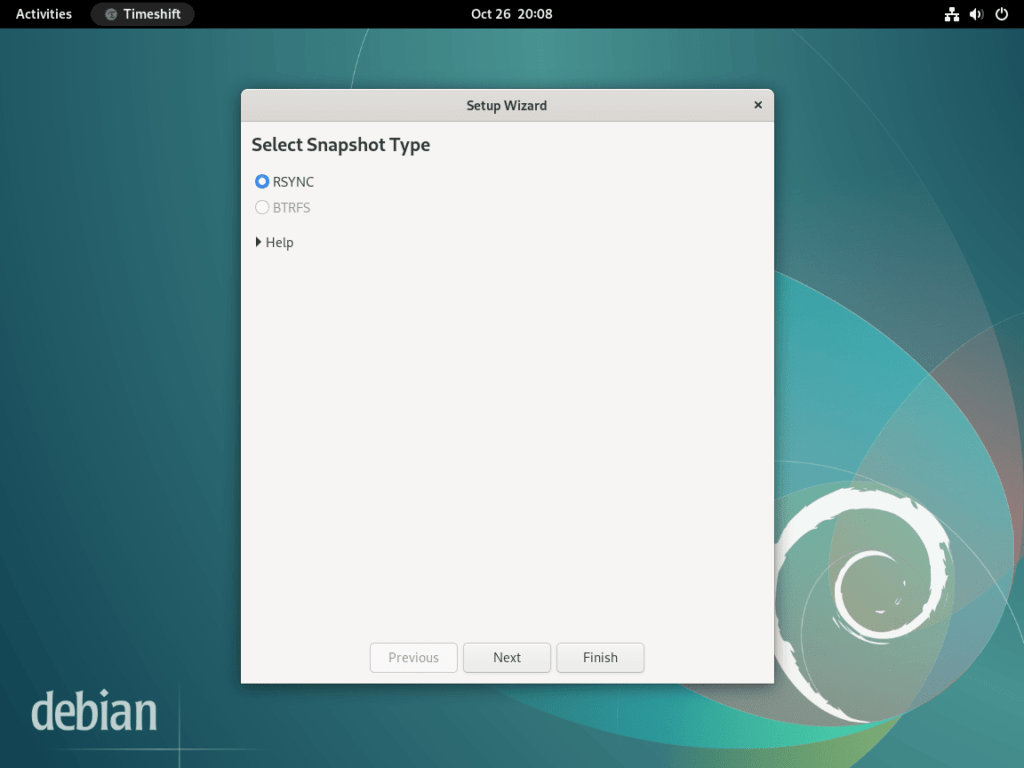
Select a Snapshot Storage Location
Next, choose where Timeshift stores your snapshots. The wizard displays all available partitions with their size and available space. For best results, select a location that meets these criteria:
- Sufficient free space (at least 10GB, though more is recommended for multiple snapshots)
- Preferably on a separate drive or partition from your system drive
- Accessible during system recovery (internal drives recommended over USB for boot recovery)
Storing snapshots on a separate drive protects against drive failure. However, if you only have one drive, Timeshift can still protect against software issues, configuration mistakes, and failed updates. The first snapshot typically uses 3-5GB for a minimal installation, with subsequent snapshots requiring less space due to hard link deduplication.
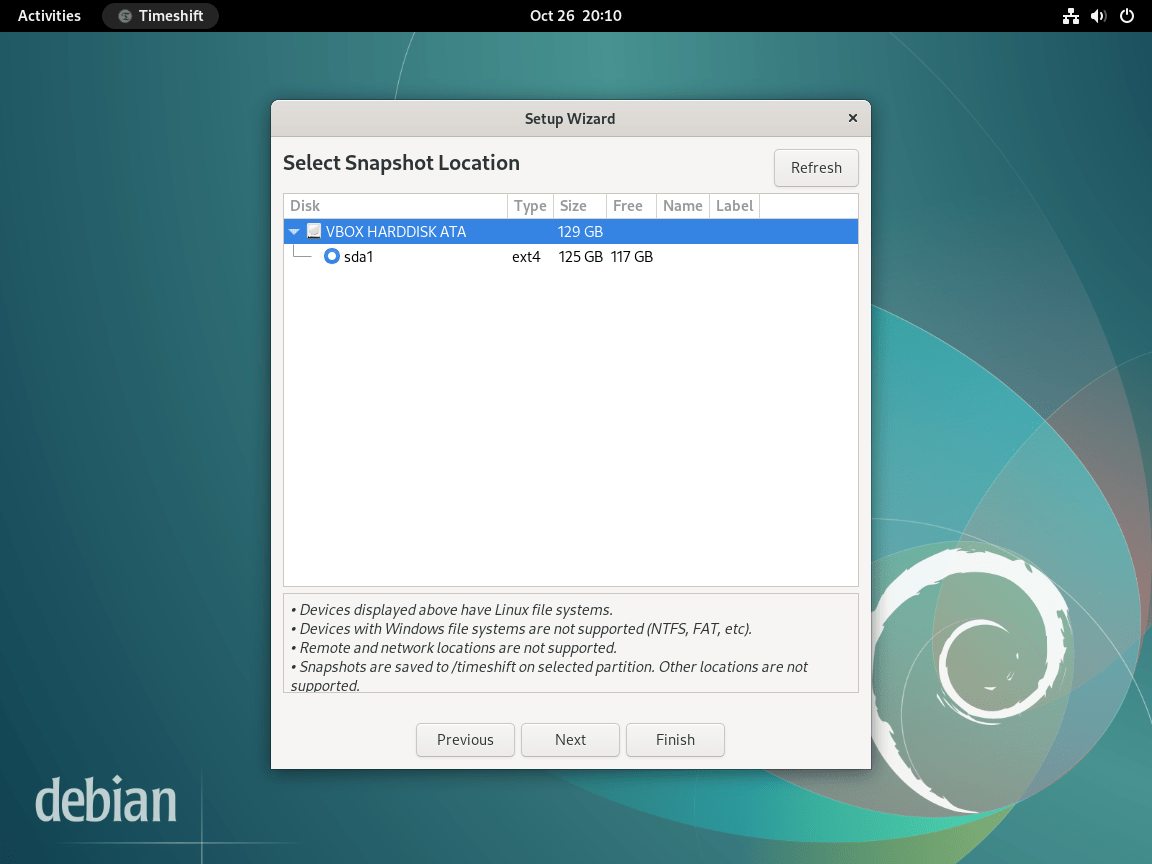
Configure Scheduled Snapshots
Timeshift can automatically create snapshots on a schedule, ensuring you always have recent recovery points. The wizard offers multiple schedule levels that you can combine:
- Monthly: Long-term recovery points for major system changes
- Weekly: Balanced protection for regular updates
- Daily: Frequent protection for active development systems
- Hourly: Maximum protection for critical systems (uses more storage)
- Boot: Creates a snapshot each time the system starts
For desktop systems, weekly snapshots with 2-3 retained copies provides a good balance between protection and storage usage. Enable daily snapshots if you frequently install or update packages. Timeshift uses cron for scheduling, so scheduled snapshots run automatically in the background without requiring the GUI to be open.
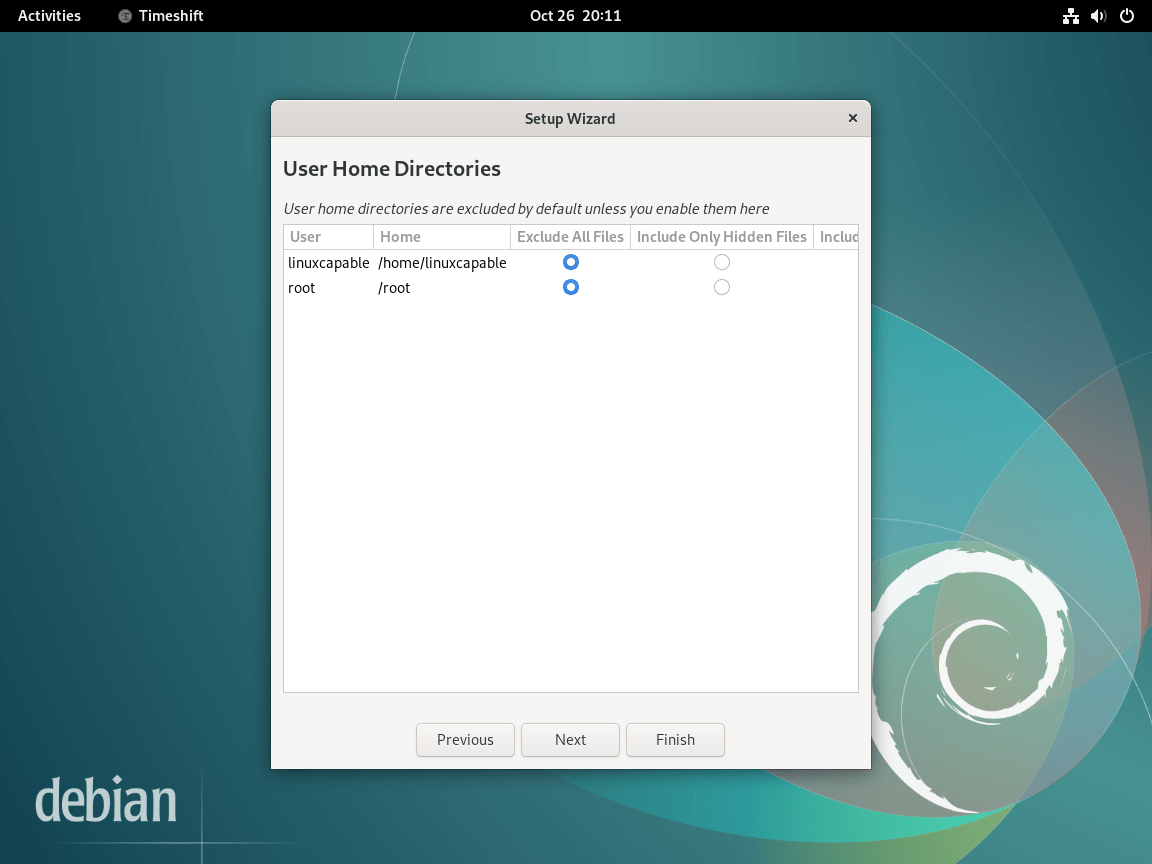
Configure User Home Directory Inclusion
By default, Timeshift excludes user home directories from snapshots. This design focuses on system recovery rather than personal file backup, which keeps snapshots smaller and allows faster restoration. You can adjust this behavior for each user:
- Exclude (default): Home directory is not included in snapshots
- Include hidden files: Backs up configuration files (dotfiles like
.bashrc,.config/) but not documents or media - Include all: Full home directory backup (significantly increases snapshot size)
For personal file backup, consider a dedicated tool like Deja Dup or rsync scripts. Timeshift excels at system recovery, allowing you to restore your Debian installation without affecting personal files stored in your home directory. This separation means you can roll back system changes while keeping your documents, downloads, and application data intact.
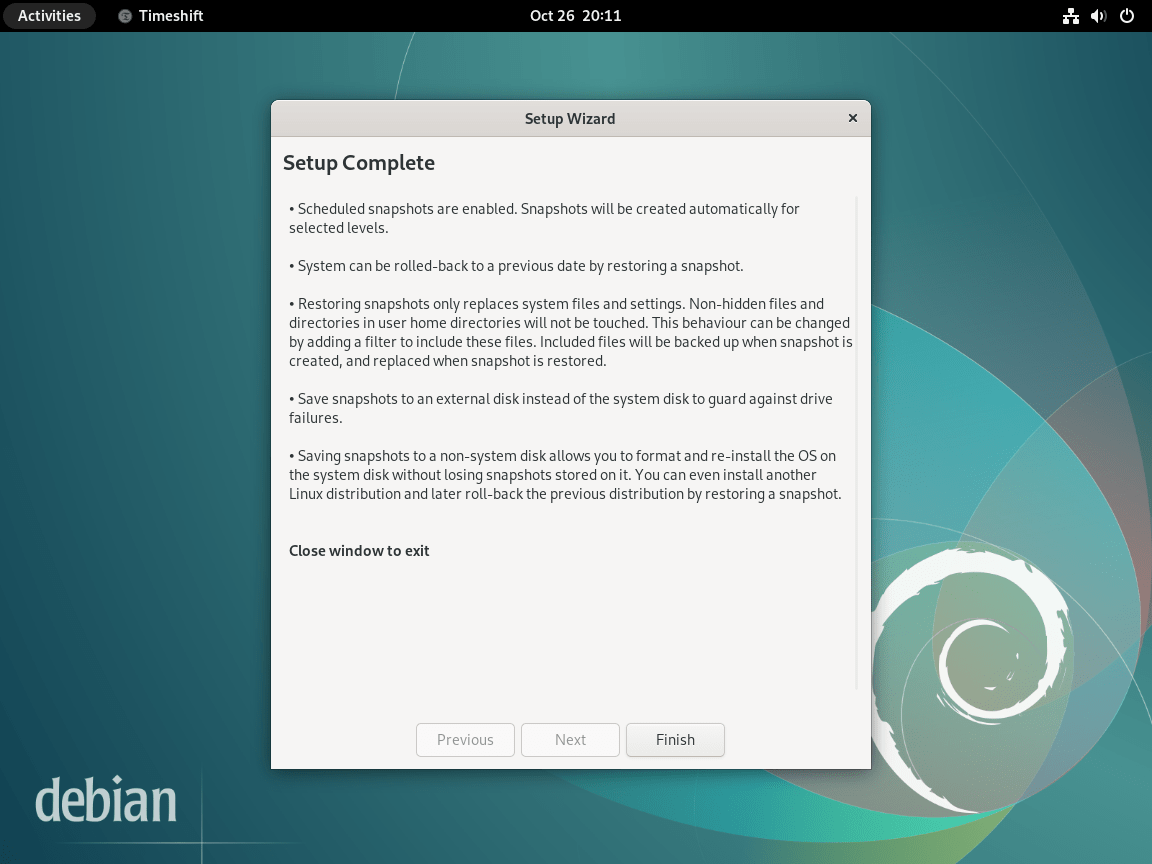
Complete Setup and Create Your First Snapshot
After completing the wizard, Timeshift displays the main interface. Review your settings and click Create to generate your first snapshot. The initial snapshot takes longer since it copies all system files. Subsequent snapshots complete faster because RSYNC mode uses hard links to share unchanged files between snapshots, meaning only modified files require additional storage.
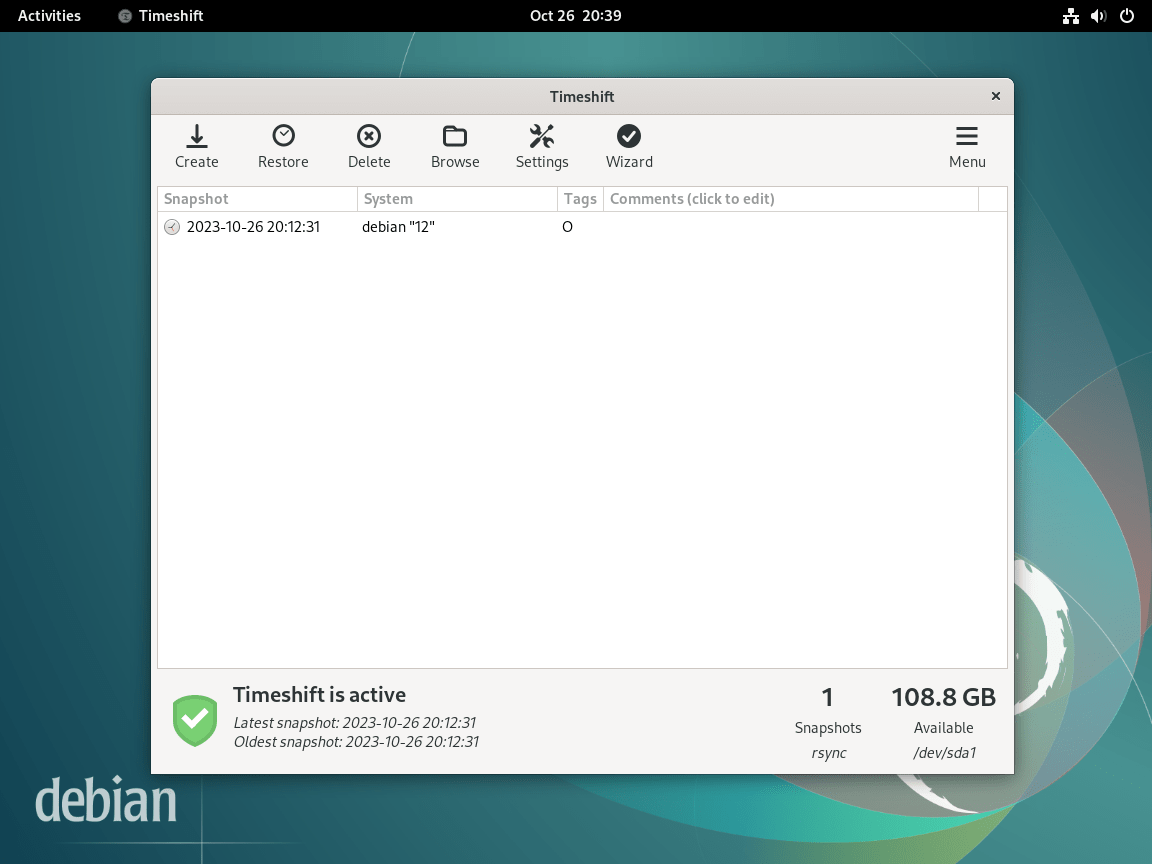
Use Timeshift from the Command Line
While the graphical interface covers most use cases, Timeshift also provides a command-line interface for scripting, remote servers, or headless systems. The following commands demonstrate common operations:
List Available Snapshots
View all existing snapshots with their creation dates and tags:
sudo timeshift --listExample output showing two snapshots:
Num Name Tags Description ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0 > 2024-12-15_10-30-45 O Initial snapshot 1 > 2024-12-19_08-00-01 W Weekly scheduled
Create a Manual Snapshot
Create a snapshot with a custom description, useful before making significant system changes:
sudo timeshift --create --comments "Before kernel upgrade" --tags OThe --tags option accepts these values: O (on-demand), B (boot), H (hourly), D (daily), W (weekly), M (monthly). Tags help organize snapshots and determine which ones Timeshift retains based on your schedule settings.
Restore a Snapshot
Restore the system to a previous state. Without additional arguments, Timeshift launches an interactive selection:
sudo timeshift --restoreTo restore a specific snapshot non-interactively:
sudo timeshift --restore --snapshot '2024-12-15_10-30-45' --yesImportant: After restoring a snapshot, reboot your system immediately to ensure all services load the restored configuration files. Some changes may not take effect until the next boot.
Manage Timeshift
Update Timeshift
Since Timeshift is installed from Debian’s repositories, it updates automatically with your regular system updates. To update only Timeshift without upgrading other packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install --only-upgrade timeshiftThis approach is useful when you want to apply a security fix to Timeshift without triggering a full system upgrade. For routine maintenance, consider enabling unattended upgrades on Debian to automatically install security updates.
Remove Timeshift
If you no longer need Timeshift, remove it along with any unused dependencies:
sudo apt remove timeshift
sudo apt autoremoveThe first command removes the Timeshift package and its configuration files. The second command removes any dependencies that were installed with Timeshift but are no longer required by other packages on your system.
Warning: Removing Timeshift does not delete existing snapshots. Snapshots are stored at the location you selected during setup (typically
/timeshifton your chosen partition). If you want to reclaim this disk space, manually delete the snapshot directory after verifying you no longer need the backups.
To remove snapshot data and reclaim disk space after uninstalling:
sudo rm -rf /timeshiftReplace /timeshift with your actual snapshot location if you configured a different storage path during setup.
Troubleshoot Timeshift
No Devices Found for Snapshot Storage
If Timeshift shows “No devices found” when selecting a storage location, the available partitions may lack sufficient space or use an unsupported filesystem. Check available space on your partitions:
df -hExample output showing available partitions:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 100G 45G 50G 48% / /dev/sdb1 500G 10G 465G 3% /mnt/backup
Ensure at least one partition has 10GB or more free space. If using an external drive, verify it is mounted and accessible. Timeshift supports ext4, XFS, and BTRFS filesystems for snapshot storage.
BTRFS Mode Shows Grayed Out
If BTRFS mode appears grayed out in the setup wizard, your system either does not use a BTRFS filesystem or lacks the required subvolume layout. Check your root filesystem type:
df -T /Example output for an ext4 filesystem (BTRFS mode unavailable):
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 ext4 102400000 47185920 50050080 49% /
If the Type column shows ext4, XFS, or another non-BTRFS type, use RSYNC mode instead. BTRFS mode requires both a BTRFS filesystem and Ubuntu-style subvolume configuration (@, @home), which Debian’s default installer does not create.
Snapshot Creation Fails with Permission Error
Permission errors typically occur when running Timeshift without root privileges. Always launch the application with administrator rights:
sudo timeshift-gtkWhen launching from the application menu, the system should prompt for your password automatically through PolicyKit. If no password prompt appears, verify that PolicyKit is running:
systemctl status polkitIf the service is inactive, start it with:
sudo systemctl start polkitScheduled Snapshots Not Running
If scheduled snapshots are not being created automatically, verify that the cron service is running:
systemctl status cronTimeshift uses cron to run scheduled snapshot jobs. If cron is not installed (common on minimal installations), install it:
sudo apt install cron
sudo systemctl enable cron
sudo systemctl start cronAfter installing cron, reopen Timeshift and configure your schedule again to register the cron jobs.
Conclusion
You now have Timeshift installed and configured on Debian, complete with automated snapshot scheduling, storage location selection, and command-line options for scripted operations. The RSYNC mode provides reliable incremental backups that protect against failed updates, configuration mistakes, and software conflicts while conserving disk space through hard link deduplication. For additional documentation including BTRFS setup guides and post-restore hooks, visit the Timeshift GitHub repository.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>