Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer that captures and inspects network traffic in real-time. Network administrators use Wireshark to diagnose connectivity problems, security analysts rely on it to detect malicious traffic patterns, and developers use it to debug application protocols. It decodes over 2,000 protocols, from common ones like HTTP, DNS, and TCP to specialized industrial and VoIP protocols. By the end of this guide, you will have Wireshark installed on Debian with the appropriate user permissions configured for non-root packet capture.
Wireshark is available in Debian’s default repositories, which means installation requires only a single APT command. System updates automatically include Wireshark security patches, keeping your installation current without manual intervention. While Wireshark is also available as a Flatpak on Flathub, that version cannot capture live network traffic and only supports analyzing saved capture files. For full functionality, install via APT as shown below.
Update Debian Before Installing Wireshark
Before installing new software, refresh your package index and upgrade existing packages to ensure compatibility. Open a terminal and run the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command updates the local package database and then upgrades any outdated packages on your system.
Install Wireshark with APT
With your system updated, install Wireshark using the following command:
sudo apt install wiresharkDuring installation, APT installs the Wireshark graphical interface along with the required libraries and dependencies.
Verify the Installation
After the installation completes, confirm that Wireshark installed correctly by checking the version. Since Wireshark is a GUI application, use the CLI tool tshark (included with Wireshark) for verification:
tshark --versionThe output displays the installed version and build information:
TShark (Wireshark) 4.4.7. Copyright 1998-2025 Gerald Combs <gerald@wireshark.org> and contributors. Licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (version 2 or later).
Your version number may differ depending on your Debian release. Debian 13 (Trixie) includes Wireshark 4.4.x, while Debian 12 (Bookworm) provides version 4.0.x, and Debian 11 (Bullseye) includes version 3.4.x.
Configure Non-Root Packet Capture Permissions
During installation, a prompt asks whether non-superusers should be allowed to capture packets. Selecting “Yes” creates a wireshark group and configures the necessary permissions automatically. If you selected “No” or want to change this setting later, you can reconfigure it using:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-common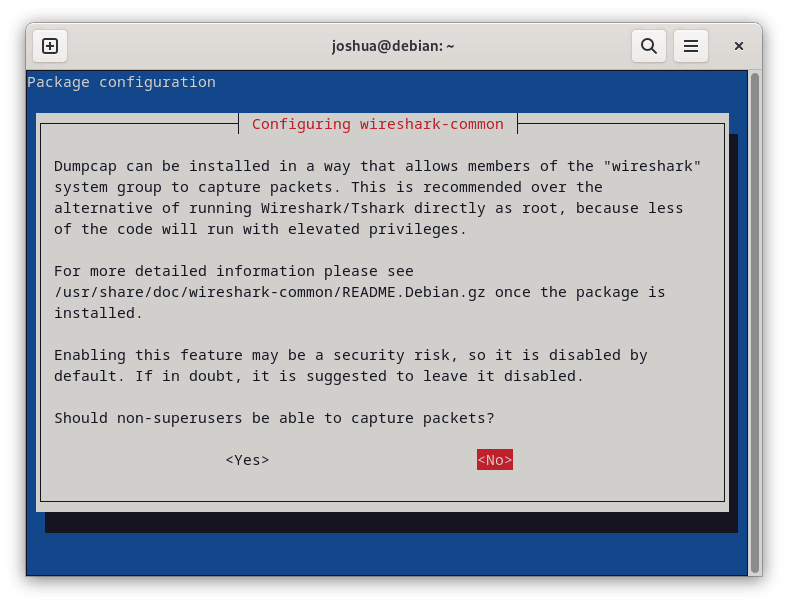
Add Your User to the Wireshark Group
After selecting “Yes” in the configuration prompt, you need to add your user account to the wireshark group. This grants permission to capture packets without running Wireshark as root. Run the following command, replacing your_username with your actual username:
sudo usermod -aG wireshark your_usernameFor example, to add a user named joshua:
sudo usermod -aG wireshark joshuaImportant: Group membership changes require logging out and back in to take effect. Alternatively, you can run
newgrp wiresharkto activate the new group in your current terminal session without a full logout.
To confirm your group membership after logging back in, run:
groupsThe output lists all groups your user belongs to:
joshua sudo wireshark
If wireshark appears in the list, you have the necessary permissions to capture packets.
Launch Wireshark
Once installed and configured, you can launch Wireshark using either the terminal or your desktop environment’s application menu.
Launch from Terminal
To start Wireshark from the command line, run:
wiresharkLaunch from Applications Menu
For desktop users, search for “Wireshark” in your application launcher. On GNOME, navigate to Activities, then Show Applications, and search for Wireshark. Other desktop environments like KDE Plasma, Xfce, or Cinnamon include Wireshark in their application menus after installation.
Use tshark for Command-Line Packet Analysis
For headless servers or scripted analysis, use tshark, the command-line version of Wireshark. It provides the same protocol dissection capabilities without requiring a graphical environment. To list available capture interfaces, run:
tshark -DExample output listing network interfaces:
1. eth0 2. lo (Loopback) 3. any 4. docker0
For a quick capture, specify the interface and packet count. The following command captures 10 packets from eth0:
tshark -i eth0 -c 10To save a capture for later analysis in the GUI, use the -w flag:
tshark -i eth0 -w capture.pcapngYou can then open capture.pcapng in Wireshark’s graphical interface for detailed examination.
Troubleshoot Common Wireshark Issues
No Network Interfaces Visible
If Wireshark launches but shows no network interfaces to capture from, a permission issue is preventing access to the capture subsystem. When this occurs, attempting to start a capture displays an empty interface list or a warning.
First, check whether your user belongs to the wireshark group:
groups | grep wiresharkIf there is no output, your user is not in the group. Add your user with:
sudo usermod -aG wireshark $USERAfter adding your user to the group, log out and back in for the change to take effect. Then verify by running groups again.
If your user is already in the group but interfaces still do not appear, the wireshark-common package may not be configured for non-root capture. Reconfigure it:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-commonSelect “Yes” when prompted, then log out and back in.
Permission Denied When Starting Capture
If clicking an interface in Wireshark displays “You do not have permission to capture on that device” or tshark returns “Operation not permitted”, the dumpcap binary may lack the required Linux capabilities.
Check the binary capabilities:
getcap /usr/bin/dumpcapExpected output when properly configured:
/usr/bin/dumpcap cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw=eip
If the output is empty or missing the capabilities, reconfigure wireshark-common and select “Yes”:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-commonAfter reconfiguring, verify the capabilities were applied:
getcap /usr/bin/dumpcapInterfaces Visible But “Couldn’t Run Dumpcap” Error
This error typically occurs when you have recently added yourself to the wireshark group but have not logged out to apply the change. Even though groups might show you in the wireshark group after running newgrp, some system processes require a full logout.
Log out completely from your desktop session and log back in. For remote SSH sessions, disconnect and reconnect. Then launch Wireshark again.
Manage Wireshark
Update Wireshark
Wireshark updates arrive through Debian’s standard package management. To update only Wireshark without upgrading all system packages, use:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install --only-upgrade wiresharkAlternatively, a full system upgrade includes Wireshark updates along with all other packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeRemove Wireshark
If you no longer need Wireshark, remove it along with its dependencies:
sudo apt remove wireshark
sudo apt autoremoveThe first command removes the Wireshark package, while apt autoremove cleans up orphaned dependencies that were installed alongside Wireshark but are no longer needed.
Wireshark stores user configuration in
~/.config/wireshark/. To completely remove all settings and capture profiles, delete this directory after uninstalling the package.
Additional Resources
To deepen your network analysis skills, consider exploring these related Debian guides:
- Install Nmap on Debian for network scanning and host discovery
- Enable SSH on Debian to securely connect to remote systems
- Install chkrootkit on Debian for security auditing
For comprehensive protocol documentation and capture filters, refer to the official Wireshark documentation.
Conclusion
You now have Wireshark installed on Debian with non-root capture permissions configured. From here, you can capture live traffic, analyze saved packet captures, and troubleshoot network issues using Wireshark’s filtering and protocol decoding capabilities.


Thank you for sharing. Cheers.