Nala is a front-end for the APT package manager that transforms the terminal package management experience on Debian. Instead of scrolling through walls of text during installations, Nala displays clear, color-coded output showing exactly which packages will be installed, removed, or upgraded. Additionally, the parallel download feature pulls multiple packages simultaneously from the fastest available mirrors, which significantly reduces installation time for large package sets. Furthermore, the built-in history system lets you undo or redo any transaction, making it straightforward to recover from problematic updates.
This guide walks you through installing Nala from Debian’s default repositories (Debian 12 and 13) and from the Volian third-party repository (required for Debian 11). By the end, you will know how to configure optimized mirrors, manage package transactions with full undo capability, and use Nala as a drop-in replacement for your daily APT commands.
Choose Your Installation Method
Nala’s availability depends on your Debian version, so choose the appropriate method:
| Method | Channel | Debian Version | Updates | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default Repositories | Debian Repos | Debian 12, 13 | Automatic via apt upgrade | Most users on current Debian releases |
| Volian Repository | Volian Nala | Debian 11, 12, 13 | Automatic via apt upgrade | Debian 11 users or those wanting newest versions |
For Debian 12 and 13 users, the default repository method is recommended because Nala is included in the official Debian repositories and receives updates through standard system maintenance. In contrast, Debian 11 users must use the Volian repository since Nala is not available in Bullseye’s default repositories.
If you are still running Debian 11, consider upgrading to Debian 12 to access Nala directly from official repositories along with newer packages and extended security support.
Update Debian Before Installation
First, before installing any new software, update your package lists and upgrade existing packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall Nala from Default Repositories (Debian 12/13)
Debian 12 (Bookworm) and Debian 13 (Trixie) include Nala in their official repositories, which makes installation straightforward.
Install Nala
Next, install Nala using APT:
sudo apt install nalaVerify Installation
Then, confirm Nala installed correctly by checking its version:
nala --versionExpected output:
nala 0.x.x
Debian 12 (Bookworm) provides Nala 0.12.2 while Debian 13 (Trixie) includes Nala 0.16.0. Both versions support all the core features covered in this guide, so your output will vary depending on your Debian release.
Install Nala via Volian Repository (All Versions)
The Volian project maintains a third-party repository that provides the latest Nala version along with all required dependencies. Debian 11 (Bullseye) users must use this method since Nala is not available in Bullseye’s default repositories. Debian 12 and 13 users can also use this method to get newer Nala versions before they reach the official Debian repositories.
Install Repository Prerequisites
First, install the packages needed to download files over HTTPS:
sudo apt install wget ca-certificates -yAdd Volian Repository
The Volian project provides helper packages that automatically configure the repository and GPG signing key using the modern DEB822 format. As a result, this approach keeps the signing key scoped to only the Volian repository rather than trusting it system-wide.
Next, download and install the repository configuration packages:
wget -P /tmp https://deb.volian.org/volian/pool/main/v/volian-archive/volian-archive-nala_0.3.1_all.deb
wget -P /tmp https://deb.volian.org/volian/pool/main/v/volian-archive/volian-archive-keyring_0.3.1_all.deb
sudo apt install /tmp/volian-archive-nala_0.3.1_all.deb /tmp/volian-archive-keyring_0.3.1_all.debSpecifically, these packages create two files on your system:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/volian-archive-nala-unstable.sources: Repository configuration in DEB822 format/usr/share/keyrings/volian-archive-scar-unstable.gpg: GPG signing key for package verification
Afterward, you can verify the repository was configured correctly:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/volian-archive-nala-unstable.sourcesExpected output:
Types: deb deb-src URIs: https://deb.volian.org/volian/ Suites: nala Components: main Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/volian-archive-scar-unstable.gpg
The
Signed-Byfield points to a scoped keyring file, which is the recommended security practice for third-party repositories. This ensures the Volian GPG key can only sign packages from the Volian repository, not packages from other sources.
Finally, update the package lists to include the new repository:
sudo apt updateVerify the Volian repository is active and provides Nala:
apt-cache policy nalaExpected output showing Nala available from the Volian repository:
nala:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 0.x.x
Version table:
0.x.x 990
100 https://deb.volian.org/volian nala/main amd64 Packages
The version numbers shown are placeholders. At the time of writing, the Volian repository provides Nala 0.16.0. The priority value (990/100) indicates APT will prefer this source for the Nala package.
Install Nala from Volian Repository
Notably, the installation command differs slightly depending on your Debian version due to Python dependency requirements.
Debian 12 and 13: Install Nala using the standard command:
sudo apt install nalaDebian 11: Use the -t nala flag to pull newer Python dependencies from the Volian repository:
sudo apt install -t nala nalaThe
-t nalaflag tells APT to prefer packages from the Volian “nala” suite when resolving dependencies. Debian 11’s default repositories contain older versions of Python packages likepython3-httpxthat are incompatible with Nala. The flag ensures APT pulls the newer versions from Volian instead, avoiding dependency conflicts.
Verify Volian Installation
Then, confirm Nala installed correctly:
nala --versionExpected output:
nala 0.x.x
The Volian repository typically provides the latest stable Nala release (currently 0.16.0 at time of writing). Your version may differ if newer releases have been published.
Essential Nala Commands
Nala uses the same command structure as APT, so existing muscle memory transfers directly. However, the key difference is the output: Nala displays progress bars, color-coded package actions, and cleaner formatting that makes it easier to understand what changes are happening to your system.
Update Package Lists
Synchronize package information from your configured repositories:
sudo nala update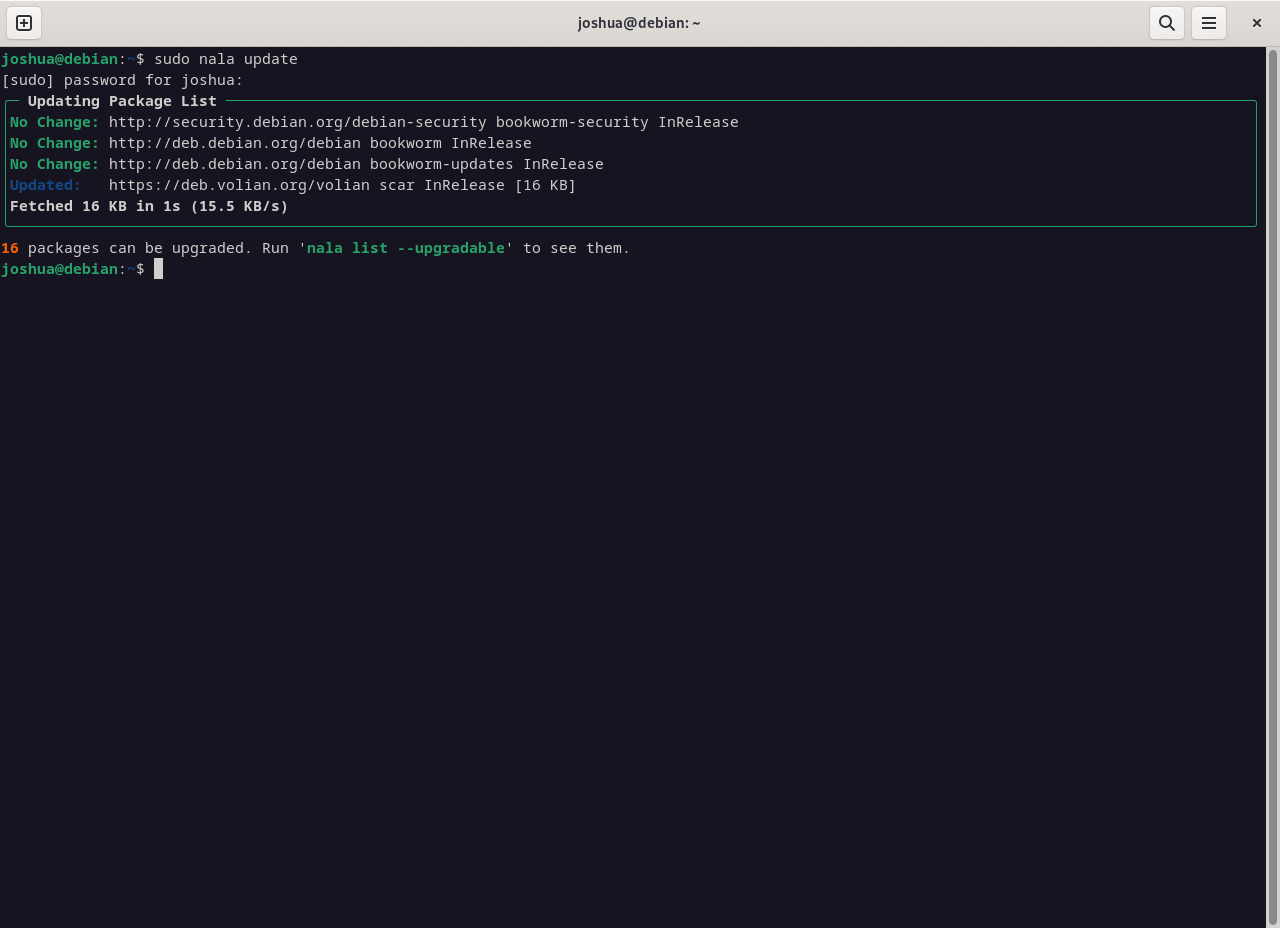
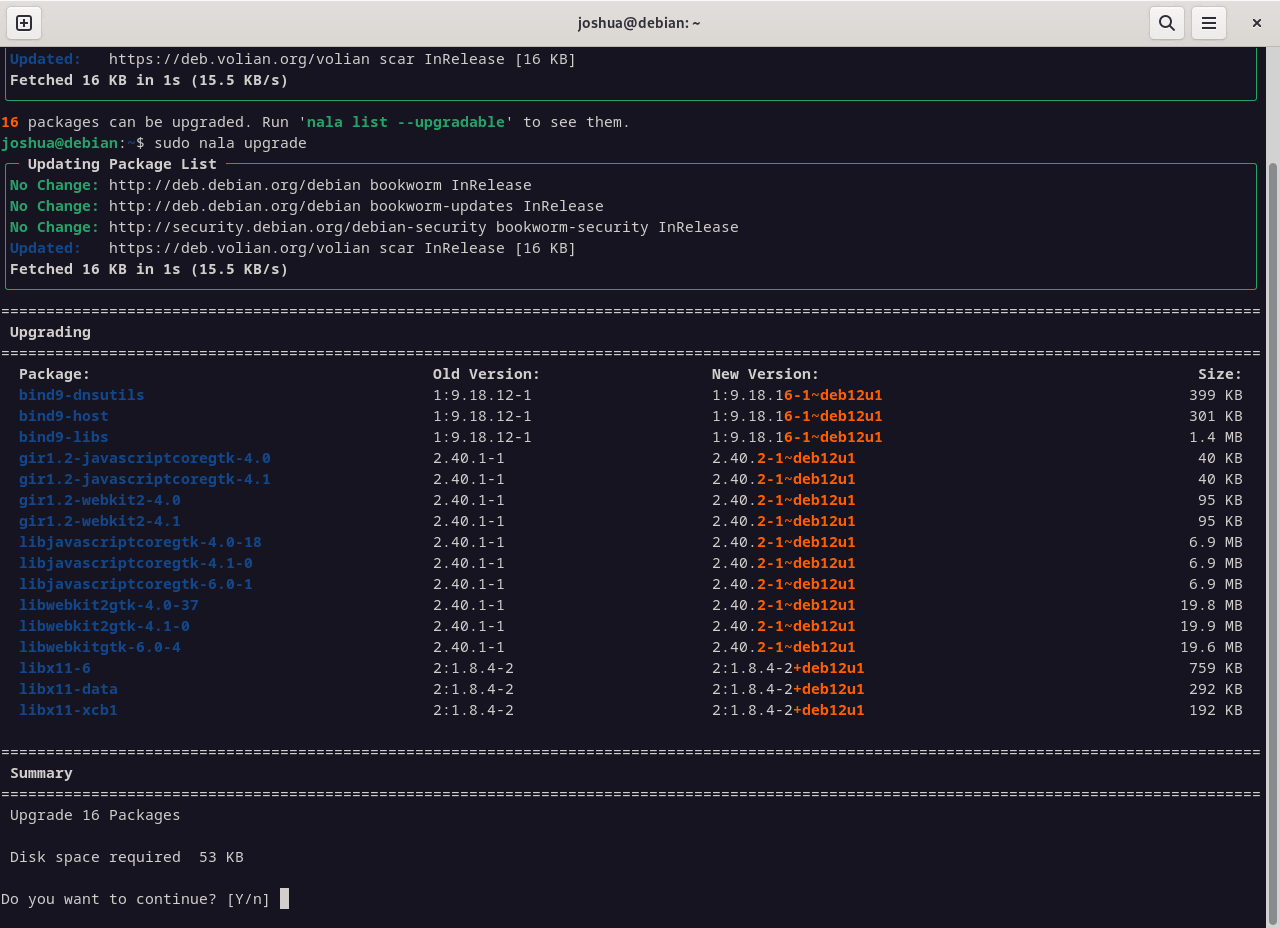
Upgrade Installed Packages
Upgrade all packages with available updates:
sudo nala upgradeAs a result, Nala shows a clear summary of packages to be upgraded, installed, or removed before prompting for confirmation.
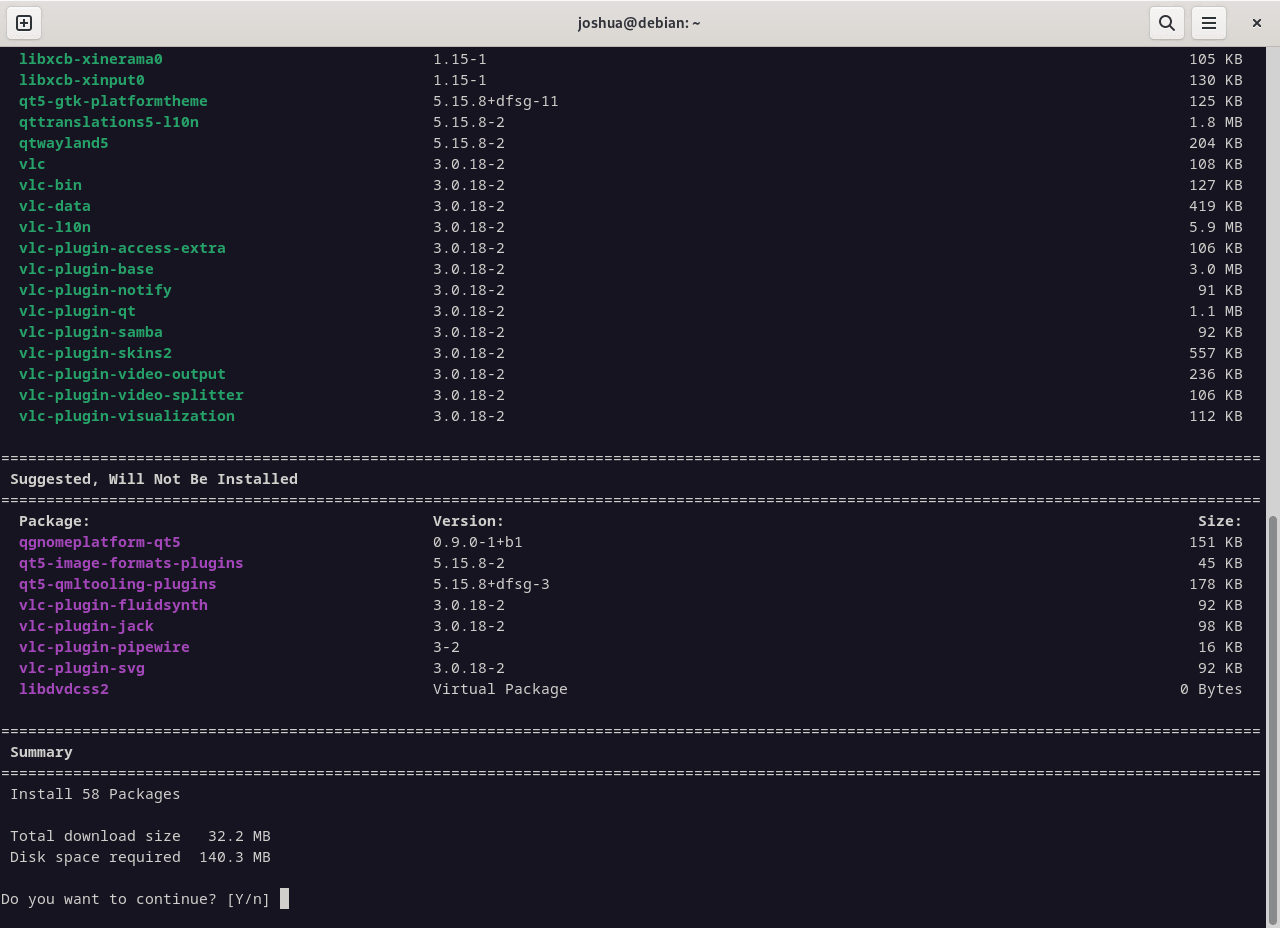
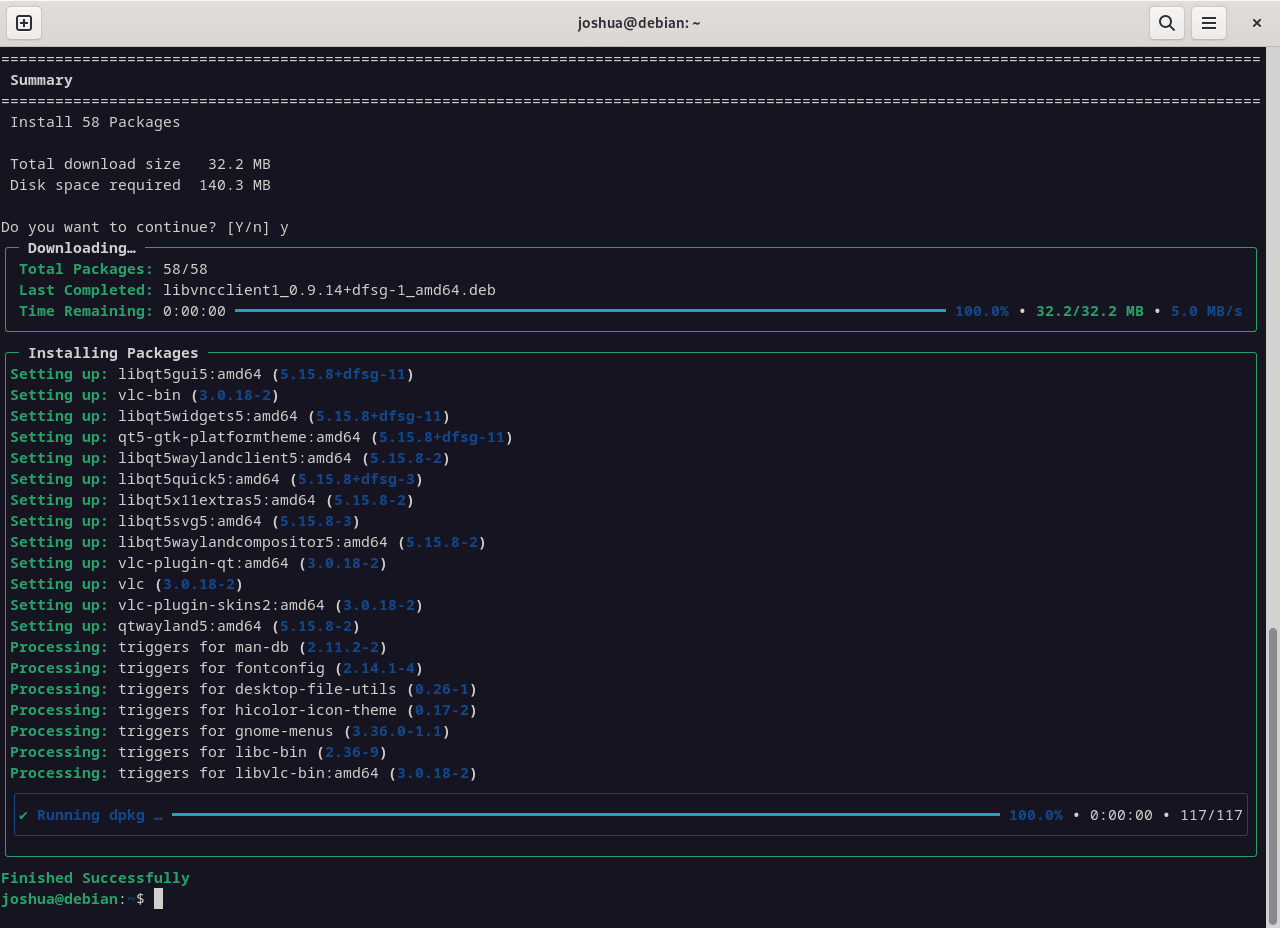
Install Packages
Install new packages with parallel downloads:
sudo nala install <package-name>Replace <package-name> with the package you want to install.
Remove Packages
Uninstall a package while keeping its configuration files (useful if you plan to reinstall later):
sudo nala remove <package-name>Alternatively, to remove both the package and its configuration files for a clean uninstall, use purge:
sudo nala purge <package-name>Afterward, clean up orphaned dependencies that are no longer needed:
sudo nala autoremoveSearch for Packages
Find packages matching a keyword:
nala search <keyword>View Package Information
Display detailed information about a package:
nala show <package-name>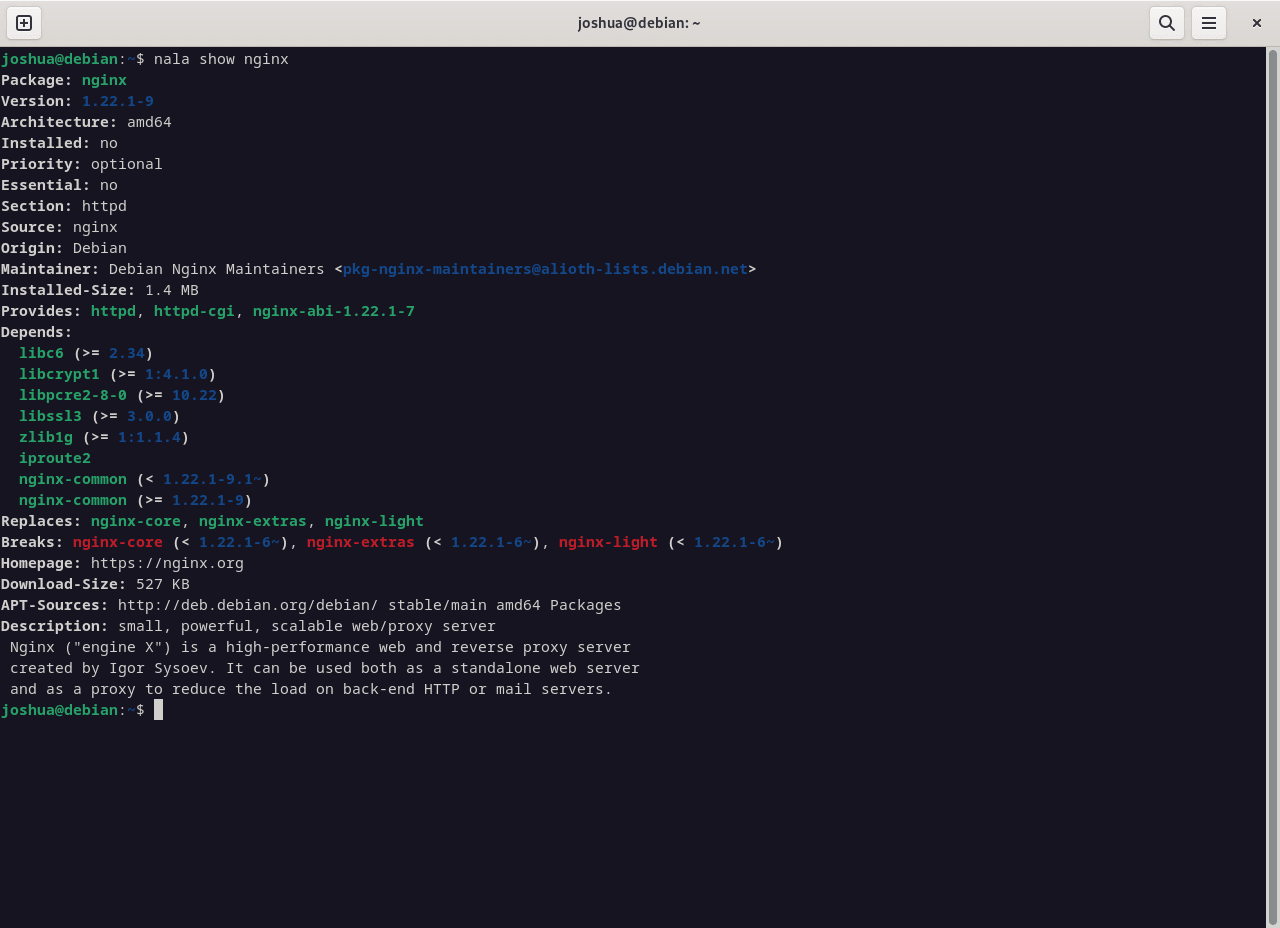
Optimize Mirror Selection with Fetch
One of Nala’s most useful features is automatic mirror optimization. Rather than manually editing /etc/apt/sources.list, Nala tests available Debian mirrors and ranks them by speed:
sudo nala fetchNala presents an interactive list showing latency to each mirror. Simply use the number keys to select mirrors (typically 3-4 fast mirrors provide good redundancy), then press Enter to confirm. Subsequently, Nala writes your selection to /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nala-sources.list, which takes priority over the default sources.
Running
nala fetchis optional but recommended after installation. Faster mirrors reduce download times significantly when installing large packages or performing system upgrades.
View and Manage Transaction History
List all recorded package transactions:
nala historyFor example, to undo a specific transaction, use its ID number:
sudo nala history undo <ID>Similarly, to redo a previously undone transaction:
sudo nala history redo <ID>The history feature is particularly valuable after system upgrades. If an update breaks something, you can quickly identify which transaction caused the issue and roll it back while you investigate.
Troubleshooting
Dependency Conflicts on Debian 11
If you see an error like this when installing on Debian 11:
The following packages have unmet dependencies: nala : Depends: python3-httpx (>= 0.17.0) but 0.16.1-1 is to be installed
This indicates APT is trying to use Debian 11’s older Python packages instead of the Volian repository versions. Therefore, ensure you use the -t nala flag:
sudo apt install -t nala nalaNext, verify the Volian repository is configured correctly:
apt-cache policy nalaExpected output showing the Volian repository as a source:
nala:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 0.x.x
Version table:
0.x.x 990
100 https://deb.volian.org/volian nala/main amd64 Packages
The version numbers are placeholders. Verify that the Volian URL appears in the output, confirming the repository is active and providing Nala packages.
Mirror Fetch Fails or Times Out
If nala fetch hangs or fails to test mirrors:
ERROR: Unable to connect to any mirrors
To troubleshoot, first verify basic network connectivity:
ping -c 3 deb.debian.orgIf the network is functional, then the issue may be firewall rules blocking Nala’s mirror tests. In that case, you can skip the fetch step entirely and use Nala with your existing /etc/apt/sources.list mirrors. Note that the fetch feature is entirely optional.
Package Not Found in Debian 11
If apt install nala returns “package not found” on Debian 11:
E: Unable to locate package nala
As mentioned earlier, Nala is not available in Debian 11’s default repositories. Instead, follow the Volian Repository installation method above to add the third-party repository containing Nala.
Remove Nala
If you no longer need Nala, follow these steps to remove it cleanly.
Remove Nala Package
First, uninstall Nala and remove orphaned dependencies:
sudo apt remove nala
sudo apt autoremoveRemove Volian Repository (If Installed)
If you installed Nala via the Volian repository, purge the repository configuration packages to remove them completely along with the sources file and GPG key:
sudo apt purge volian-archive-nala volian-archive-keyring
sudo apt autoremoveUsing
purgeinstead ofremoveensures the repository configuration file at/etc/apt/sources.list.d/is also deleted. The standardremovecommand would leave this file behind.
Then, verify the repository files were removed:
ls /etc/apt/sources.list.d/volian* 2>/dev/null || echo "Volian repository removed"
ls /usr/share/keyrings/volian* 2>/dev/null || echo "Volian keyring removed"Finally, refresh the package lists and verify the Volian source is no longer present:
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy nalaExpected output confirming removal (Debian 11):
N: Unable to locate package nala
On Debian 12/13, the output will show the default repository version as available but not installed:
nala:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 0.x.x
Version table:
0.x.x 500
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian [your-release]/main amd64 Packages
The version and release codename are placeholders. Debian 12 shows
bookwormwith version 0.12.2, while Debian 13 showstrixiewith version 0.16.0.
Remove Nala Configuration
Additionally, Nala stores its history and mirror configuration in /var/lib/nala/. To remove this data:
Warning: The following command permanently deletes Nala’s transaction history and custom mirror configuration. This cannot be undone.
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/nala/Conclusion
You now have Nala installed and configured as a drop-in replacement for APT commands on Debian. The parallel download feature and optimized mirror selection through nala fetch noticeably speed up large package operations, while the transaction history with nala history undo provides a safety net for rolling back problematic updates.
To continue improving your Debian system, consider combining Nala with unattended upgrades for automatic security patches. Additionally, you can explore Flatpak on Debian for sandboxed application installation alongside your system packages. For more advanced Nala usage, run nala --help or visit the official Nala documentation.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>