phpBB is a widely used open-source forum software for creating and managing online communities. It handles discussion boards ranging from small hobby communities to high-traffic tech support forums. When combined with Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP, you get a performant stack that scales efficiently as your community grows. Nginx serves as the web server, MariaDB as the database management system, and PHP-FPM as the server-side scripting language.
This guide walks through installing phpBB forum software on Debian Linux with the complete LEMP stack (Nginx, MariaDB, PHP-FPM). First, you will download and configure phpBB 3.3.x, then create a dedicated MariaDB database with restricted user permissions. Next, you’ll set up Nginx server blocks with PHP-FPM integration, followed by securing the installation with Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates. Finally, you’ll configure automated cron jobs for forum maintenance. The result is a production-ready forum that can scale from small communities to high-traffic discussion boards.
Install LEMP (Nginx, MariaDB, PHP)
Update Debian Before phpBB Installation
First, ensure that your Debian system is up-to-date before installing the LEMP stack. This step helps avoid package conflicts and ensures smooth execution of subsequent processes. Additionally, it aligns your system with the latest security patches and software improvements.
To update your system, execute the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThe sudo apt update command updates the list of available packages and their versions, while the sudo apt upgrade installs the latest versions of your packages.
Install Nginx
Nginx, an open-source, high-performance HTTP server and reverse proxy, is the cornerstone of the LEMP stack. To install Nginx, execute the following command:
sudo apt install nginxAfter the installation of Nginx, the service usually starts automatically. However, it’s good practice to confirm this and ensure it’s operating as expected. Therefore, verify the status of the Nginx service by issuing the following command:
systemctl status nginxExpected output showing the service is active and running:
● nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since [timestamp]
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Main PID: [pid] (nginx)
Tasks: [number]
Memory: [memory]
CPU: [cpu]
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─[pid] "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;"
└─[pid] "nginx: worker process"
The active (running) status confirms Nginx started successfully. Conversely, if the service is inactive, start it with the following command:
sudo systemctl enable nginx --nowThis command ensures that the Nginx service can start on boot (enable) and start immediately (–now).
Optionally, open a web browser and navigate to http://your-server-ip to verify Nginx is installed; you should see a similar test page:
Install MariaDB
Next, installing the database module is the crucial step in setting up the LEMP stack. MariaDB, known for its performance and various supplementary attributes, is preferred over MySQL within the LEMP stack. Therefore, to install MariaDB, execute the following command:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-clientVerify MariaDB Service Status
Once MariaDB is installed, it’s crucial to confirm the status of the MariaDB service. It’s important to ensure the MariaDB service is enabled and operating correctly. The command to inspect the service’s status is as follows:
systemctl status mariadbExpected output showing MariaDB is active and running:
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 11.x.x database server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since [timestamp]
Docs: man:mariadbd(8)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
Main PID: [pid] (mariadbd)
Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..."
Tasks: [number]
Memory: [memory]
CPU: [cpu]
CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service
└─[pid] /usr/sbin/mariadbd
The active (running) status and the message “Taking your SQL requests now…” confirm MariaDB is operational and ready to accept database connections. If the service is not active, enable and start it:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb --nowSecure MariaDB Installation (Security Run-Script)
Securing your database is fundamental in setting up a robust and reliable system; MariaDB is no exception. After the installation, it’s highly recommended that the security script that comes with the installation be run. Furthermore, this script strengthens the MariaDB installation by modifying its default settings, often considered insecure, thereby protecting the system from potential unauthorized access or exploitation.
Run the Security Script
To run the MariaDB security script, known as mysql_secure_installation, issue the following command:
sudo mysql_secure_installationYou will see prompts similar to:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): [Press Enter] Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n]: n Change the root password? [Y/n]: Y New password: [Enter strong password] Re-enter new password: [Confirm password] Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y Remove test database? [Y/n]: Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
Understanding Security Settings
Once the security script is executed, the next step involves adjusting various settings to enhance the security of your MariaDB installation. Specifically, these changes include setting up the root password, restricting remote access, eliminating anonymous user accounts, and removing the test database. Moreover, each of these adjustments adds a layer of security to your MariaDB installation, helping to protect it from potential security threats.
Let’s delve into each of these adjustments:
- Setting up the root password: This is the password for the root user of your MariaDB installation. It’s crucial to choose a strong password to prevent unauthorized access.
- Restricting remote access: The root user can access the database from any location by default. Restricting remote access ensures that the root user can only access the database from the local machine, reducing the risk of remote attacks.
- Eliminating anonymous user accounts: Anonymous user accounts have no names. These accounts pose a security risk as they can be used to gain unauthorized access to the database. The security script allows you to remove these accounts.
- Removing the test database: MariaDB has a test database that any user can access. This database is unnecessary for production use and can be safely removed to reduce the attack surface.
Ultimately, by taking the time to secure your MariaDB installation, you’re taking a significant step toward ensuring the integrity and security of your data.
Install PHP-FPM
Finally, the last component of the LEMP stack is the PHP service, which acts as the bridge between Nginx and MariaDB. This bridging is accomplished by the PHP-FPM service and extra modules required by phpBB. Therefore, to install PHP-FPM and the required modules on your Debian system, run the following command:
sudo apt install php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-curl php-common php-mbstring php-xml -yVerify that essential PHP modules are installed:
php -m | grep -E 'mysql|curl|mbstring'Expected output:
curl mbstring mysqli
Verify PHP-FPM Service Status
After installation, subsequently confirm the PHP-FPM service status to ensure it is enabled and operating correctly. Notably, the service name includes the PHP version number, which varies by Debian release.
To find your installed PHP version, run
php --versionor checkls /etc/php/to see available versions. Debian 13 ships PHP 8.4, Debian 12 ships PHP 8.2, and Debian 11 ships PHP 7.4. Substitute the correct version number in the commands below.
Check the PHP-FPM service status (replace 8.x with your actual version):
systemctl status php8.x-fpmExpected output:
● php8.x-fpm.service - The PHP 8.x FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.x-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since [timestamp]
Docs: man:php-fpm8.x(8)
Main PID: [pid] (php-fpm8.x)
Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec"
Tasks: 3 (limit: [limit])
Memory: [memory]
CPU: [cpu]
CGroup: /system.slice/php8.x-fpm.service
Expected output:
● php8.x-fpm.service - The PHP 8.x FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.x-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since [timestamp]
Docs: man:php-fpm8.x(8)
Main PID: [pid] (php-fpm8.x)
Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec"
Tasks: 3 (limit: [limit])
Memory: [memory]
CPU: [cpu]
CGroup: /system.slice/php8.x-fpm.service
Enable PHP-FPM Service
If the PHP-FPM service is inactive, enable it to start immediately and automatically at boot:
sudo systemctl enable php8.x-fpm --nowReplace 8.x with your installed PHP version (8.4 for Debian 13, 8.2 for Debian 12, 7.4 for Debian 11).
Download and Configure phpBB
With the LEMP stack installed, the next phase involves downloading and configuring the phpBB forum software. Accordingly, the following commands download phpBB 3.3.10, extract it to the web root, and set appropriate file permissions for Nginx.
Version 3.3.10 was current at publication. Check the phpBB downloads page for the latest stable release and adjust the version number in the download URL below. Newer versions typically release every six months.
Download phpBB and Setting Up Directories
First, install the required tools for downloading and extracting phpBB:
sudo apt install wget unzip -yNext, download the phpBB package using an automated command that fetches the latest stable 3.3.x version:
cd /tmp
VERSION=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/phpbb/phpbb/tags | grep "name.*release-3.3" | head -1 | sed -n 's/.*release-3\.3\.\([0-9]*\).*/\1/p')
wget https://download.phpbb.com/pub/release/3.3/3.3.$VERSION/phpBB-3.3.$VERSION.zipThis automated approach ensures you always download the current stable release without manually checking version numbers. Specifically, here is how it works:
curl -s: Queries the phpBB GitHub repository tags APIgrep: Filters for 3.3.x release tagssed: Extracts the version number using pattern matchingwget: Downloads the corresponding zip file from phpBB’s official download server
If the automated syntax seems confusing, you can download manually instead: visit the phpBB downloads page, note the latest 3.3.x version number, and run
wget https://download.phpbb.com/pub/release/3.3/3.3.15/phpBB-3.3.15.zip(replacing 3.3.15 with the current version). The automated command above simply does this version lookup step for you.
Extract and move the phpBB files to the web root:
unzip phpBB-*.zip
sudo mv phpBB3 /var/www/html/phpbbNext, modify the directory permissions for Nginx:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/phpbb
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/phpbbConfiguring MariaDB for phpBB
Now, create a database for your phpBB installation. First, you’ll need to open the MariaDB terminal as root:
sudo mysql -u root -pCreate the database for your forums:
CREATE DATABASE phpbb;Create a new database user called phpbbuser with a strong password:
CREATE USER 'phpbbuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_secure_password';Grant the user full access to the phpBB database:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON phpbb.* TO 'phpbbuser'@'localhost';Flush the privileges to apply the changes:
Replace
your_secure_passwordwith a strong password containing uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Store these database credentials securely. You will need them during the web-based installation wizard.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;These commands create an isolated database (phpbb), a dedicated user (phpbbuser) with access restricted to localhost, grant full permissions on the phpBB database only, and reload the privilege tables to apply changes immediately.
Your phpBB database is now ready. You will enter these details during the web UI installation part of the tutorial.
Configuring PHP for phpBB
To ensure a successful phpBB installation and its optimal operation, consequently, you should adjust a few options in the php.ini configuration file.
Open the php.ini configuration file for PHP-FPM:
sudo nano /etc/php/8.x/fpm/php.iniReplace 8.x with your installed PHP version (8.4 for Debian 13, 8.2 for Debian 12, 7.4 for Debian 11). To confirm the path, run ls /etc/php/ to see available versions.
Locate the following settings and adjust them as follows:
max_execution_time = 180 max_input_time = 90 memory_limit = 256M upload_max_filesize = 64M
These settings control resource limits: specifically, max_execution_time prevents scripts from running indefinitely (useful during database maintenance), max_input_time limits how long PHP parses input data (protects against slowloris attacks), memory_limit sets the maximum memory a PHP script can consume (increase for large forums with many extensions), and upload_max_filesize controls attachment sizes.
These settings are generally standard, but if you’re using a VPS with limited resources or shared hosting, you may need to adjust them lower. Furthermore, remember that each phpBB installation, like any other CMS system, can vary.
Save the file and exit the editor. Restart PHP-FPM to apply the configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart php8.x-fpmReplace 8.x with your PHP version.
Configuring Nginx for phpBB
In your Nginx server block, declare the PHP upstream and then the PHP locations. Typically, the best way to do this is to create a new server block using a subdomain such as forums or community.
First, create the server block:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/phpbb.confCopy and paste the following into the server block, modifying the domain name, SSL, root path, and anything else to suit your needs. However, do not touch the locations or PHP unless you know what you’re doing.
Attention: The following Nginx configuration syntax markdown includes annotated comments to guide you in personalizing the configuration according to your specific requirements. Therefore, we highly recommend carefully scrutinizing each segment and making appropriate adjustments to suit your system configuration. Your attention to these details is greatly appreciated.
# Upstream to abstract backend connection(s) for PHP
upstream phpbb {
# Path to PHP-FPM socket - adjust version number to match your installation
# Debian 13: /run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock
# Debian 12: /run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock
# Debian 11: /run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock
server unix:/run/php/php8.x-fpm.sock;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
# Change this to your domain name
server_name forums.example.com;
# phpBB installation directory
root /var/www/html/phpbb/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
# Log files, replace these paths if you have different log file paths
access_log /var/log/nginx/forums-access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/forums-error.log;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @rewriteapp;
# PHP processing, make sure to use your own upstream name if different
location ~ \.php(/|$) {
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
try_files $uri $uri/ /app.php$is_args$args;
fastcgi_pass phpbb;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
# Deny access to certain PHPBB files
location ~ /(config\.php|common\.php|cache|files|images/avatars/upload|includes|(?<!ext/)phpbb(?!\w+)|store|vendor) {
deny all;
internal;
}
}
location @rewriteapp {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /app.php/$1 last;
}
location /install/ {
try_files $uri $uri/ @rewrite_installapp =404;
# PHP processing for installer
location ~ \.php(/|$) {
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
try_files $uri $uri/ /install/app.php$is_args$args =404;
fastcgi_pass phpbb;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
}
location @rewrite_installapp {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /install/app.php/$1 last;
}
# Deny access to version control system directories
location ~ /\.svn|/\.git {
deny all;
internal;
}
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_min_length 1000;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_disable "msie6";
# Gzip compression types
gzip_types
application/atom+xml
application/geo+json
application/javascript
application/x-javascript
application/json
application/ld+json
application/manifest+json
application/rdf+xml
application/rss+xml
application/xhtml+xml
application/xml
font/eot
font/otf
font/ttf
image/svg+xml
text/css
text/javascript
text/plain
text/xml;
# Static assets, media
location ~* \.(?:css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv)$ {
expires 90d;
access_log off;
}
# SVG, fonts
location ~* \.(?:svgz?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff2?)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*";
expires 90d;
access_log off;
}
}Test and Enable Nginx Configuration
After setting up, enable the new server block:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/phpbb.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/You can now check the configuration:
sudo nginx -t Expected output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Restart the Nginx service to make phpBB accessible via the web UI:
sudo systemctl restart nginxConsequently, this completes the backend installation of phpBB.
Implementing SSL Encryption with Let’s Encrypt (Optional)
If you intend to secure your Nginx server with HTTPS, a smart choice would be to utilize Let’s Encrypt. Notably, Let’s Encrypt is a reputable, free, fully automated certificate authority governed by the nonprofit Internet Security Research Group (ISRG).
Installing Certbot
Our first step involves installing the Certbot package. Specifically, Certbot is an efficient client for Let’s Encrypt that can automate certificate issuance and installation with no downtime. Additionally, it also has a fairly rich command-line interface.
To install the Certbot package, use the following command:
sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx -yCreating Your Certificate
With Certbot installed, we can now generate your SSL certificate. Subsequently, this procedure involves running the following command:
sudo certbot --nginx --agree-tos --redirect --hsts --staple-ocsp --email you@example.com -d forums.example.com
The flags configure SSL best practices: specifically, --agree-tos accepts terms of service, --redirect automatically redirects HTTP to HTTPS, --hsts enables HTTP Strict Transport Security to prevent downgrade attacks, and --staple-ocsp enables OCSP stapling for faster certificate validation.
Replacing ‘you@example.com’ and ‘forums.example.com’ with your email and domain name is crucial.
Transition to HTTPS
Upon successfully executing these commands, your forum should now be accessible via HTTPS at https://forums.example.com instead of the previous http://forum.example.com. Additionally, any attempts to access the old HTTP URL will be seamlessly redirected to the secure HTTPS version.
For detailed information on securing Nginx with Let’s Encrypt, including automatic renewal configuration and advanced SSL hardening, refer to our comprehensive guide: How to Secure Nginx with Let’s Encrypt on Debian Linux.
Configure Firewall (Optional)
If you use UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your Debian system, configure it before enabling to avoid SSH lockout. Specifically, ensure HTTP and HTTPS traffic can reach your phpBB forum by opening ports 80 and 443. Notably, this step is necessary only if you have enabled a firewall.
Critical for SSH users: If you are connected via SSH, allow SSH access before enabling UFW to prevent lockout. Run
sudo ufw allow OpenSSHbeforesudo ufw enable.
Allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'This rule opens both ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) simultaneously. Alternatively, you can configure individual ports:
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow 443/tcpVerify the firewall status and active rules:
sudo ufw statusExpected output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Nginx Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Complete the phpBB Web UI Installation
Having successfully set up the backend, we’ll now transition to the frontend to complete the phpBB installation. Accordingly, you can access the installation page by visiting your designated phpBB forum URL. For illustrative purposes, we’re using https://forums.linuxcapable.com.
Initiating the Installation
Upon visiting the specified URL, you’ll land on the phpBB installation page. Initiate the process by clicking the install button in the page’s upper left corner.
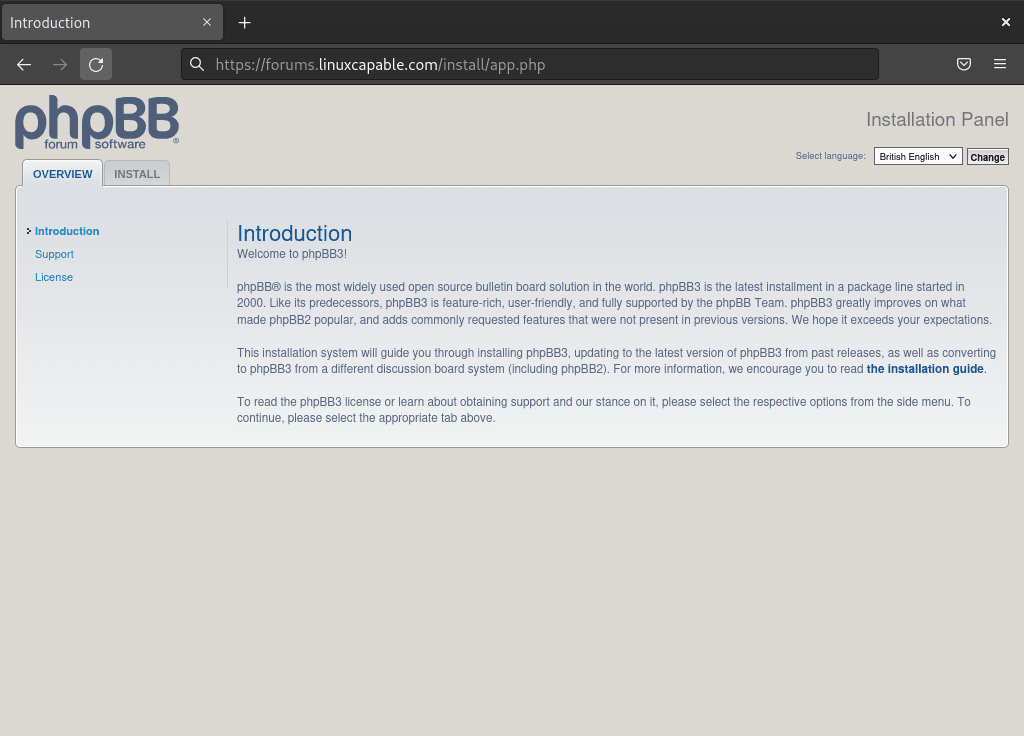
You will then be directed to a page detailing the minimum system requirements and other essential technical specifications for phpBB.
Subsequently, once your system meets these prerequisites, click Install at the bottom of the page.
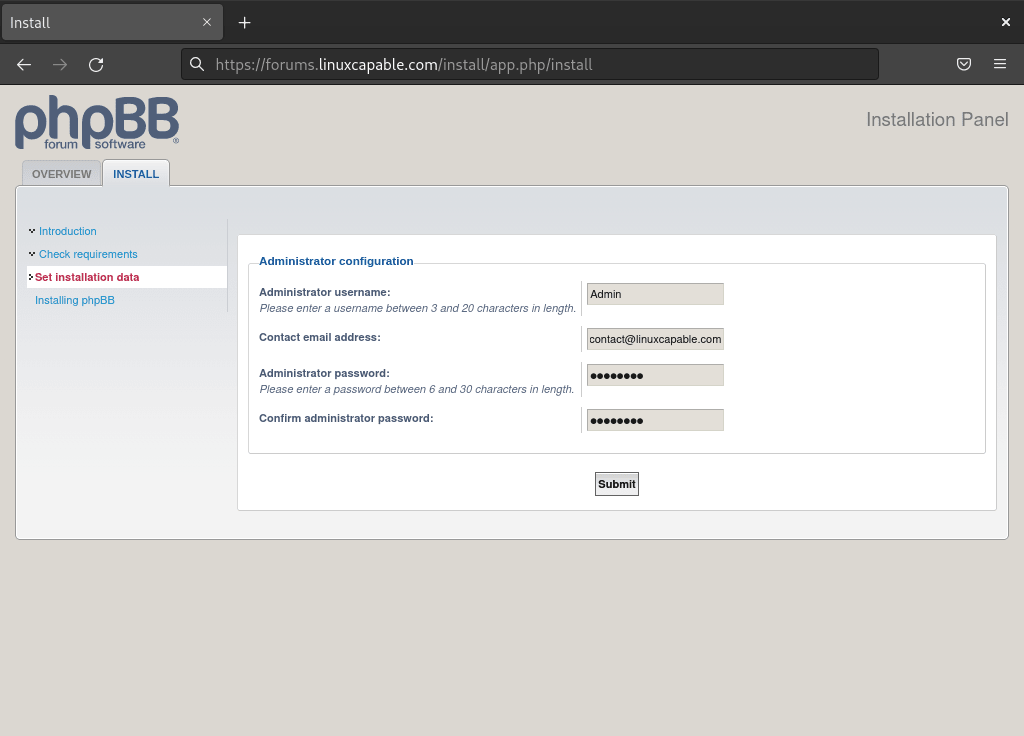
Setting Up the Admin Account
The next stage involves creating your phpBB admin account. Importantly, a strong password for this account is vital for recovery and overall security.
Configuring Database Details
After establishing your admin account, you’ll be prompted to provide database details. Typically, maintain the default ‘MySQL with MySQLi Extension’ and enter ‘localhost’ unless your database resides on a different server. In that case, input the server IP and port (if it’s not the default).
Our tutorial utilizes a database named ‘phpbb’, with ‘phpbbuser’ as the user granted access (alongside root) to the phpBB database. Retain the default prefix’ phpbb_’, unless you plan on hosting multiple forums, in which case, altering the prefix can help differentiate them.
Finalizing Server Configuration
Next, you’ll have the opportunity to configure your server settings. Typically, the default configurations should suffice if you’re not running SSL. However, if you’ve implemented SSL, adjust the settings to align with your specific requirements.
SMTP Setup
Following server configuration, you can establish SMTP settings, if applicable. Alternatively, if not, you can skip this step and proceed with the default settings.
Establishing Forum Details
Finally, designate your forum title and choose the desired language. Moreover, if you’re uncertain about the forum title, use the default option for now; you can always revise it later.
Upon completing these steps, you should reach a concluding screen, confirming the successful installation of your phpBB forum, along with a link directing you to the ACP (Admin Control Panel). However, if you encounter any errors, you might need to revisit previous steps to ensure no steps or permissions have been overlooked.
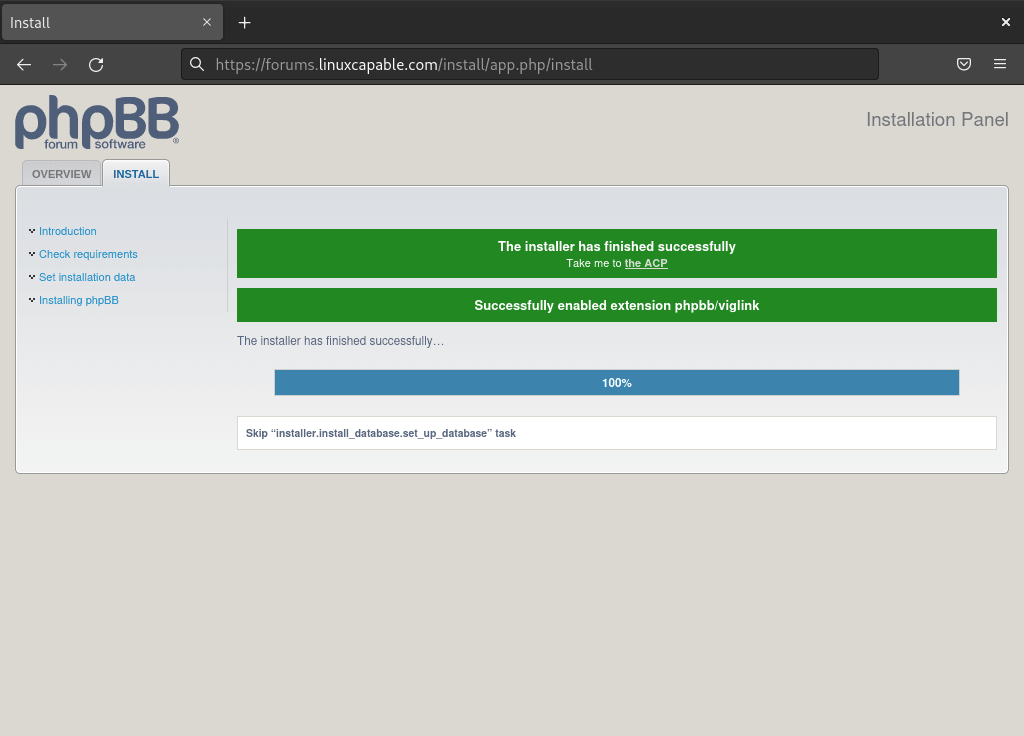
Post-Installation Security Configuration
Remove Installation Directory
After completing the web-based installation, the phpBB Admin Control Panel displays a security warning requiring you to delete the installation directory. Specifically, this prevents unauthorized users from re-running the installer and potentially overwriting your forum configuration.
Critical security step: Your forum will remain inaccessible until the installation directory is removed. phpBB enforces this as a mandatory security measure to protect against installation hijacking attacks.
Delete the installation directory:
sudo rm -R /var/www/html/phpbb/installIf you do not do this, you will most likely find your forum will not be able to be used until you have removed the install directory:
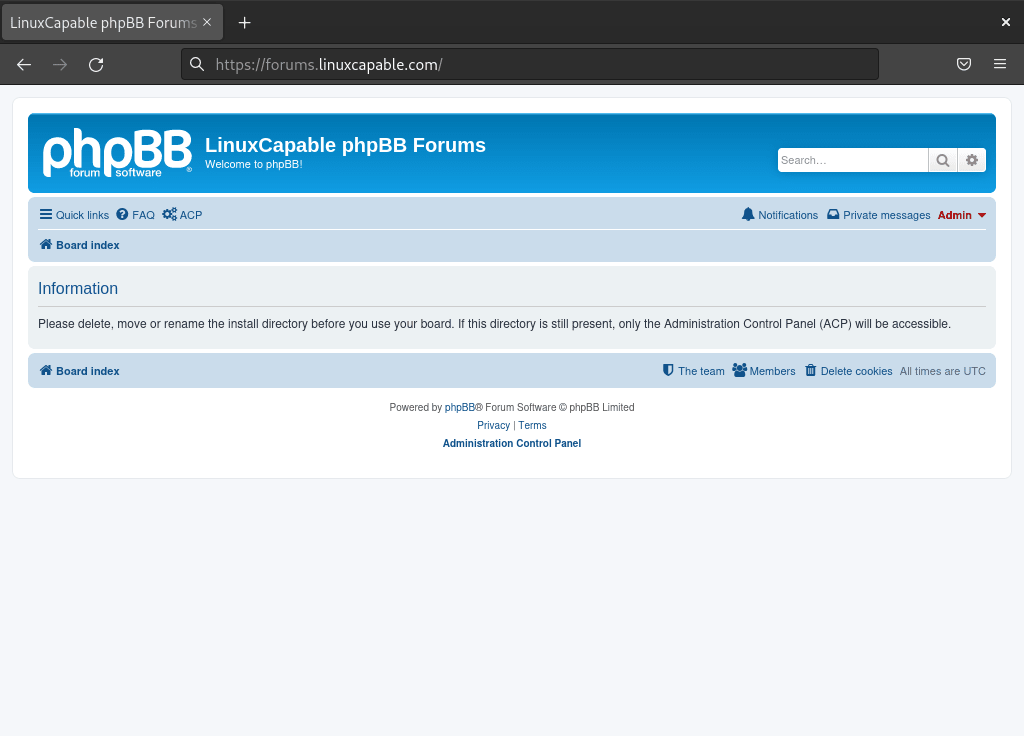
Configure File Permissions
Proper file permissions are critical for phpBB security and functionality. Specifically, the following commands set restrictive default permissions for all files and directories, then grant write access only to specific directories that phpBB requires for uploads, caching, and temporary storage.
Set base permissions for all phpBB files and directories:
sudo find /var/www/html/phpbb -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/phpbb -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;Grant write permissions to phpBB’s data directories:
sudo chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/phpbb/files
sudo chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/phpbb/cache
sudo chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/phpbb/store
sudo chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/phpbb/images/avatars/uploadSecurity consideration: The 777 permissions (world-writable) are required by phpBB for these specific directories to handle file uploads, cache generation, and session storage. This is a documented phpBB requirement, though it increases security risk. On shared hosting or high-security environments, consider using more restrictive permissions (775 or 770) with proper group ownership, though this may require additional web server configuration.
Verify the permissions were applied correctly:
ls -ld /var/www/html/phpbb/files /var/www/html/phpbb/cacheExpected output:
drwxrwxrwx 2 www-data www-data 4096 [date] /var/www/html/phpbb/files drwxrwxrwx 2 www-data www-data 4096 [date] /var/www/html/phpbb/cache
Configure Automated Cron Jobs
phpBB requires periodic maintenance tasks to run in the background, such as database optimization, session cleanup, and notification processing. Therefore, configure a system cron job to execute these tasks automatically every 5 minutes, which is phpBB’s recommended interval for active forums.
Open the root user’s crontab:
sudo crontab -eAdd the following line at the end of the file:
*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/php /var/www/html/phpbb/bin/phpbbcli.php cron:run > /dev/null 2>&1The schedule
*/5 * * * *means “every 5 minutes” in cron syntax. The five fields represent: minute (*/5), hour (*), day of month (*), month (*), and day of week (*). Asterisks mean “every” and */5 means “every 5 units.” You can adjust the interval based on your forum’s traffic. Low-activity forums may use */15 (every 15 minutes) instead.
To save, press CTRL+O, and to exit, press CTRL+X. If done correctly, you’ll see the following response in your terminal:
crontab: installing new crontabThis response indicates that the cronjob is active and functioning. Although phpBB recommends running cronjobs every 5 minutes, alternatively, you can adjust the frequency to suit your needs.
Finally, return to your phpBB Admin Panel and enable the server cron job in your server settings.
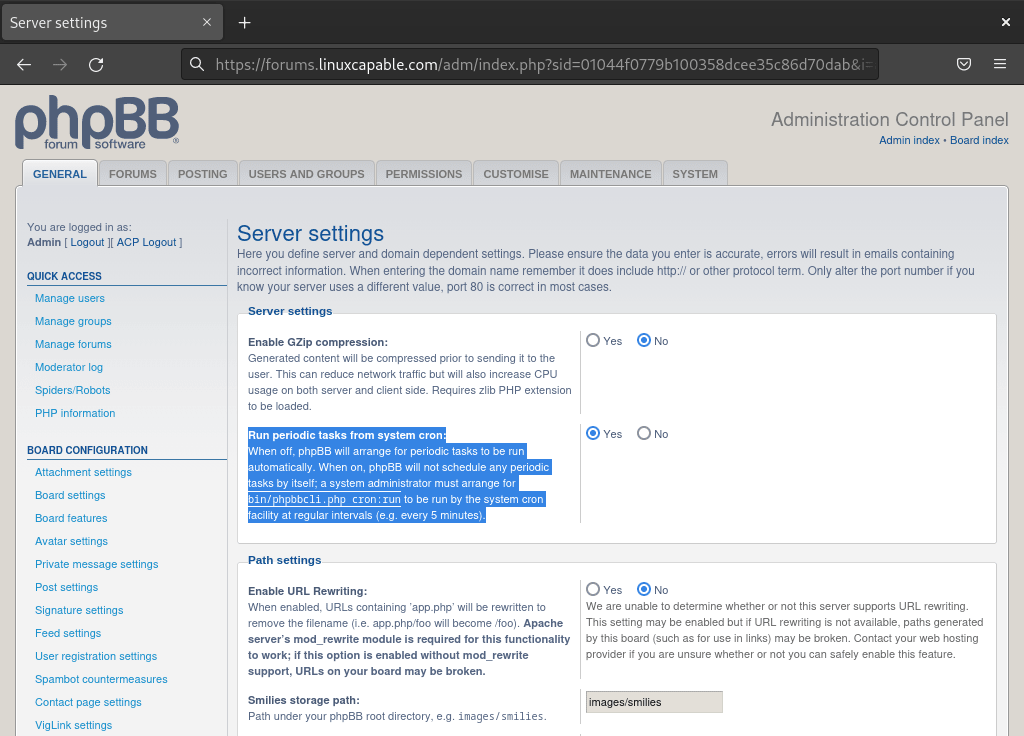
With these steps, you’ve completed the post-installation configuration for your phpBB installation on Debian. Consequently, your forum is now secure, properly configured, and ready to serve your community.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems during or after installation, the following troubleshooting steps address the most common phpBB configuration issues on Debian systems.
PHP-FPM Socket Connection Errors
If Nginx displays “502 Bad Gateway” errors, typically, the PHP-FPM socket path in your Nginx configuration may not match your installed PHP version.
Error in Nginx logs:
connect() to unix:/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock failed (2: No such file or directory)
Verify the correct PHP-FPM socket path:
ls /run/php/php*-fpm.sockExpected output showing available socket:
/run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock
Subsequently, update the socket path in /etc/nginx/sites-available/phpbb.conf to match the actual version, then reload Nginx:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/phpbb.conf
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginxDatabase Connection Failures
If phpBB cannot connect to MariaDB during web installation, first verify the database user has correct permissions and the database exists.
Test database connectivity:
mysql -u phpbbuser -p phpbbIf this command fails, then recreate the database user with correct permissions:
sudo mysql -u root -pSHOW DATABASES LIKE 'phpbb';
SELECT user, host FROM mysql.user WHERE user = 'phpbbuser';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON phpbb.* TO 'phpbbuser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;File Upload and Cache Errors
If phpBB reports permission errors for file uploads or cache writes, first verify the writable directories have correct ownership and permissions.
Check current permissions:
ls -ld /var/www/html/phpbb/files /var/www/html/phpbb/cache /var/www/html/phpbb/storeThen, ensure directories are owned by www-data and have 777 permissions:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/phpbb
sudo chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/phpbb/files /var/www/html/phpbb/cache /var/www/html/phpbb/store /var/www/html/phpbb/images/avatars/uploadSSL Certificate Renewal Failures
If Let’s Encrypt automatic renewal fails, first check Certbot’s renewal timer status and logs.
Verify the renewal timer is active:
systemctl status certbot.timerTest renewal manually:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runIf renewal fails due to Nginx configuration, subsequently ensure your server block is accessible on port 80 for the ACME challenge:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginxRemove phpBB (Optional)
If you need to uninstall phpBB and the LEMP stack components, first back up your database and any custom files before proceeding. Subsequently, follow these steps to completely remove the installation. The removal process includes deleting phpBB files, removing the MariaDB database and user, cleaning up Nginx configuration, and optionally uninstalling the LEMP packages.
Remove phpBB Files and Database
First, remove the phpBB installation directory:
Warning: The following command permanently deletes all phpBB files, uploaded attachments, custom themes, and configuration. This action cannot be undone. Back up any data you wish to preserve before proceeding.
sudo rm -rf /var/www/html/phpbbRemove the phpBB database and user from MariaDB:
sudo mysql -u root -pExecute the following SQL commands:
DROP DATABASE phpbb;
DROP USER 'phpbbuser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;Remove Nginx Configuration
Next, remove the phpBB Nginx server block and reload Nginx:
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/phpbb.conf
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-available/phpbb.conf
sudo systemctl reload nginxIf you configured Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates for phpBB, additionally remove those as well:
sudo certbot delete --cert-name forums.example.comReplace forums.example.com with your actual domain name.
Remove Cron Job
Remove the phpBB cron job from the root crontab:
sudo crontab -eDelete the line containing /var/www/html/phpbb/bin/phpbbcli.php cron:run, then save and exit.
Uninstall LEMP Stack (Optional)
If you no longer need the LEMP stack components for other applications, remove them. Conversely, skip this section if other services depend on Nginx, MariaDB, or PHP.
Caution: Removing these packages will affect any other websites or applications using the LEMP stack. Verify no other services depend on these components before proceeding.
Stop and remove Nginx:
sudo systemctl stop nginx
sudo systemctl disable nginx
sudo apt remove --purge nginx nginx-common -y
sudo apt autoremove -yStop and remove MariaDB:
Warning: Removing MariaDB deletes all databases on the system. Back up any databases you need before proceeding.
sudo systemctl stop mariadb
sudo systemctl disable mariadb
sudo apt remove --purge mariadb-server mariadb-client -y
sudo apt autoremove -y
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysqlRemove PHP and related packages:
sudo apt remove --purge php* -y
sudo apt autoremove -yClean up remaining configuration files:
sudo rm -rf /etc/nginx /etc/php /var/log/nginxConclusion
You have successfully installed phpBB on Debian with the complete LEMP stack, implemented SSL encryption with Let’s Encrypt automatic renewal, configured restrictive file permissions, and automated forum maintenance tasks through system cron jobs. Consequently, your forum is now production-ready with secure database isolation, fast PHP-FPM processing, and efficient Nginx request handling.
For next steps, consider implementing Nginx FastCGI caching to reduce database load for high-traffic boards, review MariaDB performance tuning for query optimization, configure automated database backups with mysqldump cron jobs, and explore phpBB’s extension library for added functionality. Alternatively, if you prefer different web servers, consider Apache as an alternative with its .htaccess configuration flexibility. Finally, regular system updates (sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y) remain critical for maintaining security across all LEMP stack components.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><blockquote>quote</blockquote>