While Python 3.11 is no longer the latest release, it remains an option for many developers. Despite the advent of Python 3.12 and the upcoming Python 3.13, 3.11 still offers a solid foundation with notable improvements that make it a viable choice for Ubuntu users.
Key features of Python 3.11:
- Structural Pattern Matching: Simplifies the process of matching complex data structures.
- Parenthesized Context Managers: Introduces a more readable syntax for using context managers.
- Improved Error Messages: Eases debugging with more informative and user-friendly error messages.
- Runtime Audit Hooks: Provides a new API for monitoring and modifying Python program behavior.
- Additional Standard Library Modules: Adds new modules like ‘zoneinfo’ for better time zone support and ‘http.client’ for high-level HTTP client functionality.
These features make Python 3.11 a strong candidate for those looking to balance stability with enhanced functionality. Now, let’s install Python 3.11 on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04 via terminal commands.
Update Ubuntu Before Python 3.11 Installation
We highly recommend running an update in your terminal before installing Python 3.11 to avoid potential conflicts during installation. Updating your terminal ensures that all packages are current using the following command:
sudo apt updateYou can upgrade any outdated packages by using the following command.
sudo apt upgradeImport Python PPA
Ubuntu distributions typically include Python by default but often lack options for updates with new releases. To install the latest version of Python 3.11, this guide will use a reputable and widely recognized third-party PPA.
First, import the Python repository with the most up-to-date stable releases.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa -yRun an APT update before proceeding to ensure reflection of the newly imported PPA.
sudo apt updateInstall Python 3.11 via APT Terminal Command
Once you’ve successfully imported the Python 3.11 PPA, install Python 3.11 by executing the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install python3.11Use the following command to verify the installation and build version of Python 3.11.
python3.11 --versionIf desired, you can also install the following additional extras for Python 3.11:
- Debug module:
sudo apt install python3.11-dbg- Developer (dev) module:
sudo apt install python3.11-dev- VENV (virtual environment) module:
sudo apt install python3.11-venv- Distutils module:
sudo apt install python3.11-distutils- lib2to3 utility module:
sudo apt install python3.11-lib2to3- DBM.GNU module:
sudo apt install python3.11-gdbm- Tkinter module:
sudo apt install python3.11-tkTo install all the extras in one go, run the following command.
sudo apt install python3.11-fullInstall PIP with Python 3.11
Most users can easily install Python 3.11 from the Python PPA repository by running the following APT command:
sudo apt install python3-pipEnsure Python Pip is installed. If issues arise, reinstall it manually by following these steps to download get-pip.py with the wget command:
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.pyAfter downloading the file, the next step is to install it.
python3 get-pip.pyWe recommend you check for upgrades after installing Pip to ensure you have the latest version. This will help you stay up-to-date with the latest features and improvements.
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pipTo verify the installed version of Pip 3.11, run the following command:
pip --versionWith these commands, you can install and upgrade Pip for Python 3.11, enabling you to install additional Python packages and libraries.
Additional Command: Switch Default Python Versions
If you have multiple versions of Python installed on your system and want to set a particular version as the default, you can follow these steps to switch between them.
Firstly, you need to add symbolic links for each Python version separately. To do this, run the following commands:
Here’s an example (you can customize this or copy it):
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python2.7 1
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.7 2
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.8 3
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.9 4
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.10 5
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.11 6
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.12 7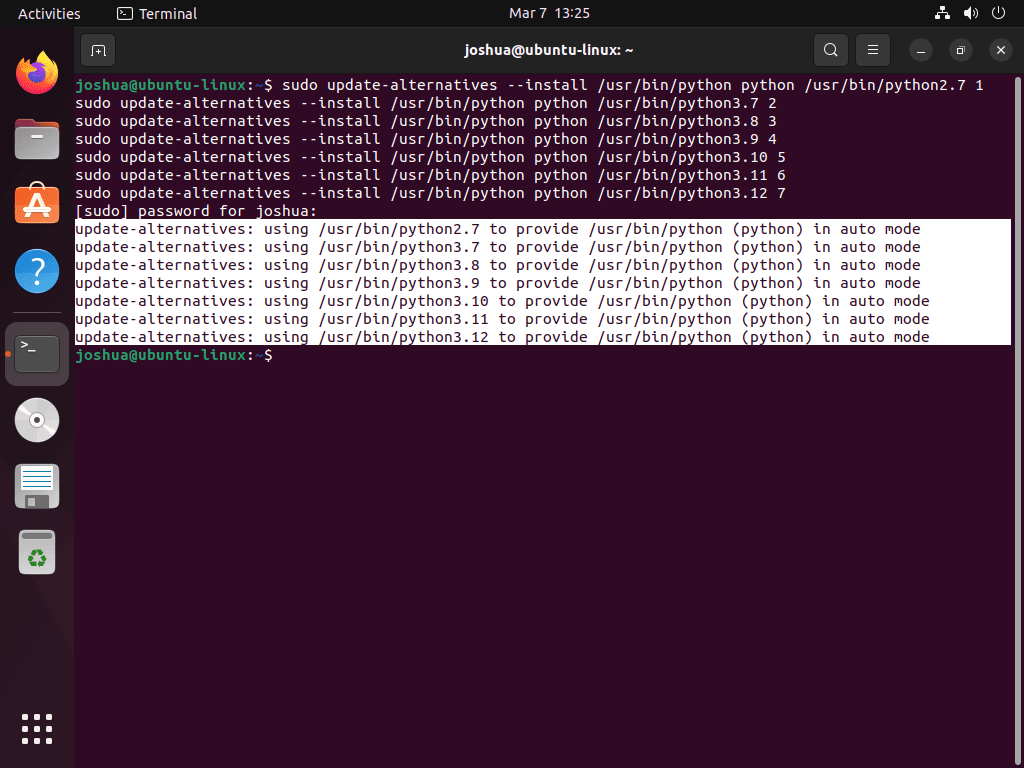
Note that the number at the end of each command (e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc.) represents the version’s priority. A higher number means a higher priority. In this example, Python 3.12 has the highest priority (7), and Python 2.7 has the lowest priority (1).
To switch to a different version of Python, you can enter the corresponding selection number in the following command:
sudo update-alternatives --config python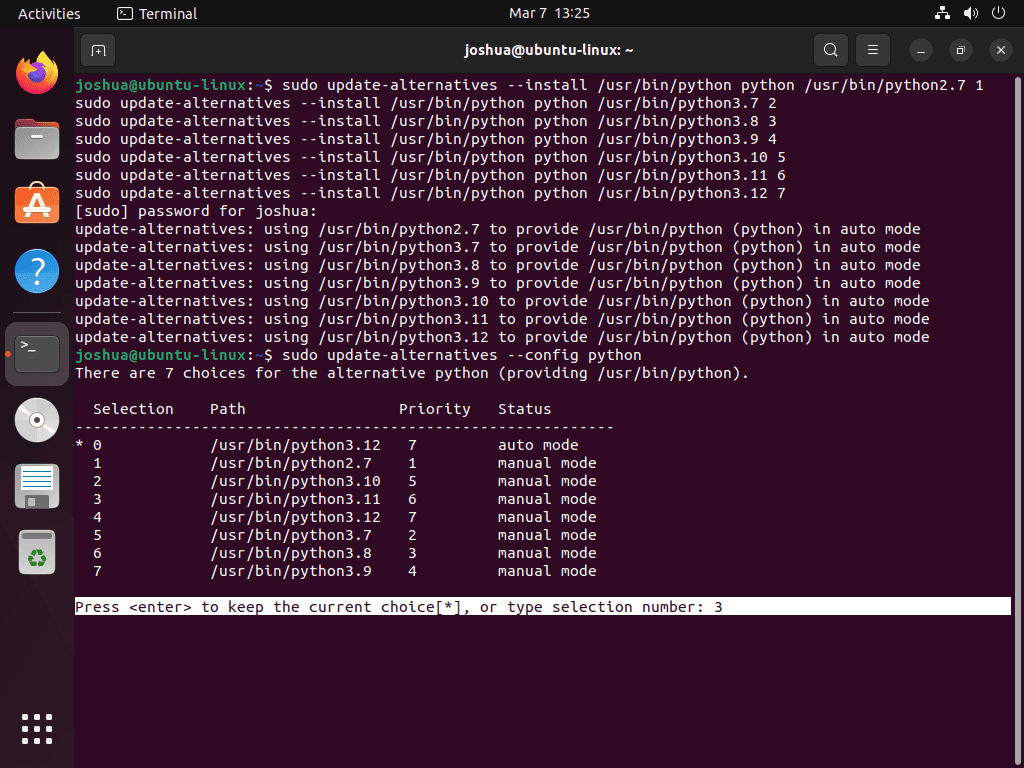
For instance, if you want to set Python 3.11 as the default, you would enter the number 3. The output of the command should look like this:
If the command is successful, you will see the following output:
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/python3.11 to provide /usr/bin/python (python) in manual modeThese steps will help you set Python 3.11 as the default version on your Ubuntu Linux system. By doing so, you will be able to switch between various versions of Python effortlessly.
Conclusion
To conclude, one can easily install Python 3.11 on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04 or 20.04 by utilizing a PPA repository and APT commands. Python 3.11 offers a range of new features, bug fixes, and improvements compared to its predecessors, making it an ideal choice for various use cases such as web development, data analysis, scientific computation, and artificial intelligence. By following the commands outlined in this guide, users can effortlessly set up and switch between different Python versions on their Ubuntu Linux systems, thus leveraging the latest features and enhancements of the Python programming language.