R Programming Language is a robust open-source tool for data analysis, statistics, and graphics. With its user-friendly syntax, R has garnered immense popularity among data scientists, statisticians, and researchers worldwide.
Key Attributes of R Programming Language:
- Open-Source Nature: Being open-source, R is freely accessible and offers customization flexibility.
- Diverse Statistical Techniques: R boasts a comprehensive library with statistical and graphical methods, catering to diverse data analysis requirements.
- Platform Independence: R’s compatibility with Windows, Mac, and Linux ensures a broad user reach.
- Efficient Data Handling: Built-in functions in R facilitate seamless data manipulation, including tasks like merging, sorting, and reshaping datasets.
- Reproducibility: R’s design emphasizes reproducible analyses, making it a preferred choice for scientific research and studies.
We’ll now walk you through the steps to install R Programming Language utilizing the command line terminal and the official CRAN repository for the most up-to-date version.
Prerequisites for Installing R Programming Language
To successfully install the R programming language on Ubuntu, ensure you meet the following requirements:
System Requirements and Supported Ubuntu Versions
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Processor | 2 gigahertz (GHz) or faster dual-core processor |
| RAM | 4 GB or more |
| Disk Space | 25 GB of free space |
| Network | Broadband internet connection |
| Supported Versions | Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble), Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy), Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal) |
Additional Requirements
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Internet Connection | Required to download R and updates, as well as for installing packages from CRAN. |
| Terminal Conventions | All terminal commands should be run as a regular user with sudo privileges. |
| CLI Commands | Use the Command Line Interface (CLI) for installation and setup. |
Optional Accessories
| Accessory | Description |
|---|---|
| External Storage | Recommended for backing up R scripts and data. |
| IDE | RStudio or another Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for enhanced development experience. |
Import CRAN APT Repository
Update Ubuntu Before R Installation
Before installing R Programming Language on Ubuntu, it’s crucial to start by updating your system. This ensures all existing packages are current. To do this, open your terminal and execute:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstalling Necessary Packages
Following the system update, the next step involves installing required packages. These packages are essential for the successful installation of R. Input the following command:
sudo apt install curl dirmngr apt-transport-https ca-certificates software-properties-commonImporting the GPG Key for R Package Verification
To ensure the authenticity of the R package from the CRAN repository, you must import the GPG key with the following command:
curl -fSsL https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/marutter_pubkey.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/cran.gpg >> /dev/nullThis key verifies the integrity and origin of the package.
Adding the CRAN Repository
Once the GPG key is in place, the next action is to add the CRAN repository to your system’s sources. This repository provides the latest R packages. Implement this by entering:
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/cran.gpg] https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs)-cran40/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cran.listFinalizing with an APT Repository Update
After adding the CRAN repository, conclude the setup process by updating your APT repository list. This update ensures your system recognizes the newly added CRAN repository. Execute the following command:
sudo apt updateFinalize R Installation with Terminal Commands
Core R Installation
After adding the CRAN repository to your Ubuntu system, you can install the R Programming Language. This foundational installation equips your system with the base R environment. To initiate the installation, open your terminal and execute:
sudo apt install r-baseInstalling R Development Tools (Optional)
For an enhanced development experience, you might consider installing r-base-dev. This package includes additional development tools and libraries essential for more advanced R programming tasks. Install it using the following command:
sudo apt install r-base r-base-devVerifying the R Installation
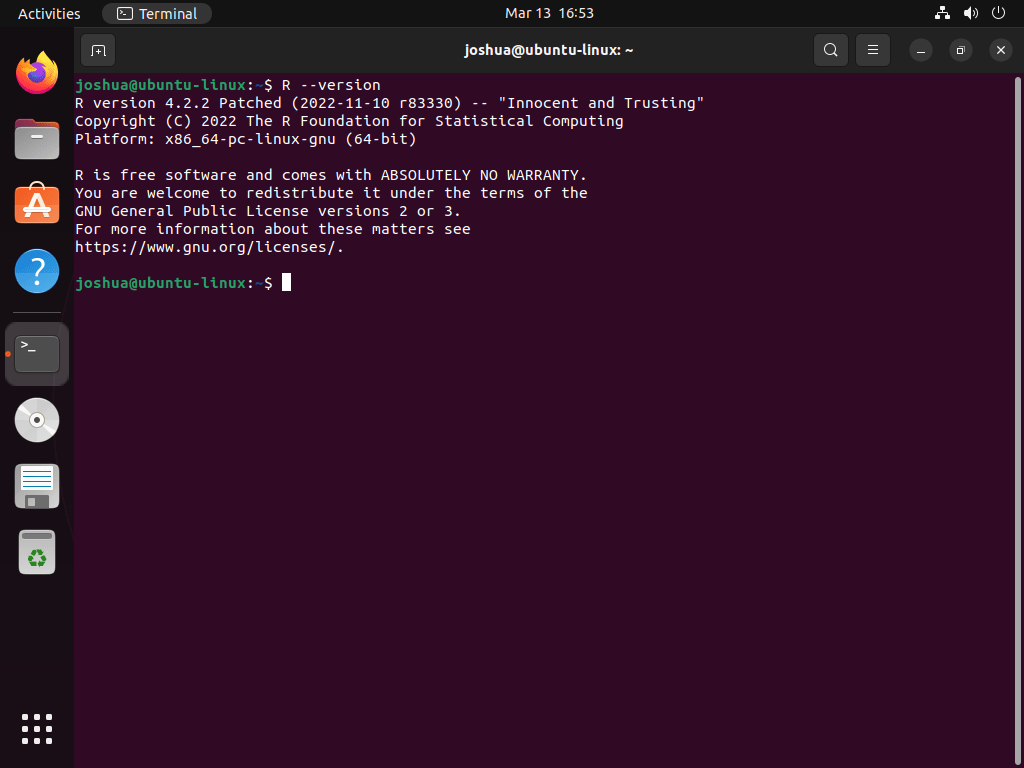
To confirm a successful installation, it’s important to check the installed version of R. This step ensures that R is correctly installed on your system. In the terminal, run:
R --versionThis command displays the version and build information of R, confirming the success of your installation.
Additional R Installation Options
Installing Recommended R Packages
r-recommended is a valuable package that includes a curated selection of R packages, widely used in data analysis and statistical modeling. To install this package, use the command:
sudo apt install r-recommendedInstalling SSL Support for CRAN Packages
For installing CRAN packages that require SSL encryption, such as the “httr” package, libssl-dev is necessary. Install this package with:
sudo apt install libssl-devAdding XML Parsing Capability
To install CRAN packages needing XML parsing, libxml2-dev is required. This is particularly crucial for packages like “XML”. Install it using:
sudo apt install libxml2-devEnabling CURL Support in R
For CRAN packages that require CURL (Client URL) support, like the “curl” package, libcurl4-openssl-dev is essential. Use this command for installation:
sudo apt install libcurl4-openssl-devThese additional packages enhance R’s functionality on Ubuntu, enabling it to interact with various software and tools efficiently.
Install R Packages via CRAN
Launching the R Interpreter
With the R Programming Language installed on your Ubuntu system, you can install R packages from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). To start the R interpreter, open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo -i RThis command initiates the R interpreter with root user privileges, granting you the necessary permissions to install packages system-wide.
Installing R Packages
In the R environment, you can install packages using the install.packages() function. This function is the standard method for adding new packages to your R setup. For instance, to install the ggplot2 and tidyr packages, input:
install.packages(c("ggplot2", "tidyr"))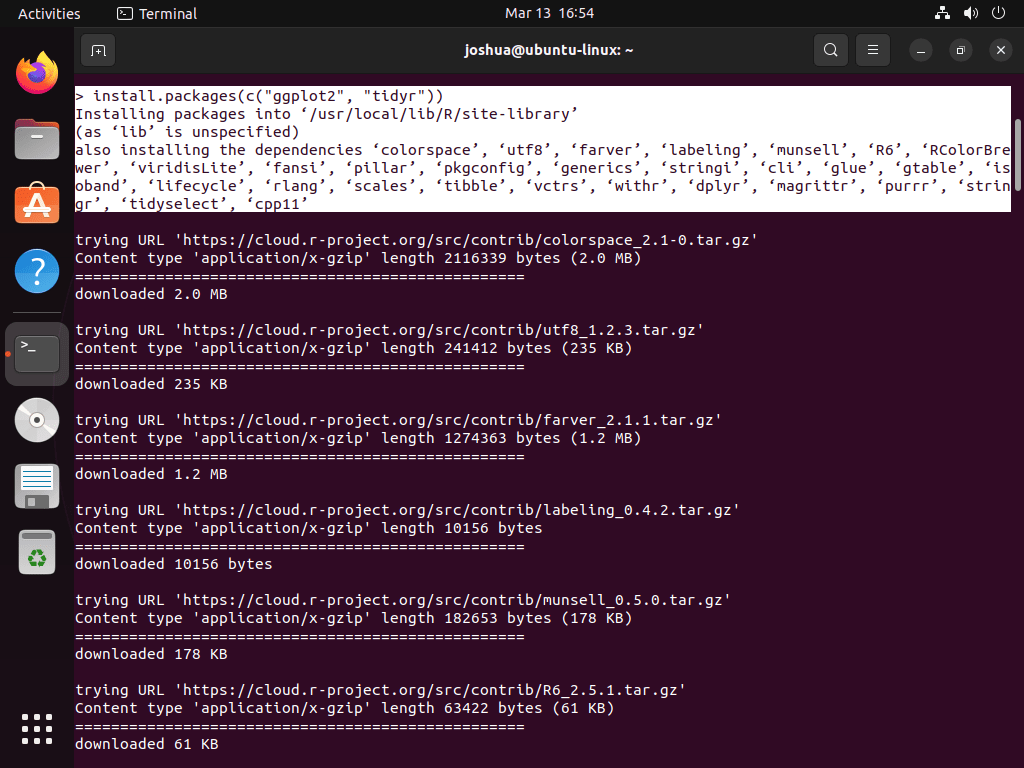
Searching for CRAN Packages
To explore available packages in CRAN, utilize the available.packages() function. This is particularly useful for finding packages related to specific fields like machine learning. To search for machine learning-related packages, use:
available.packages("machine learning")This function returns a comprehensive list of relevant packages and their descriptions, aiding in informed decision-making about which packages to install.
Updating Installed R Packages
Keeping your R packages up-to-date is crucial for security and functionality. To update all installed packages, use the update.packages() function. For example, to update without individual confirmations, execute:
update.packages(ask = FALSE)This command efficiently updates all your installed packages to their latest versions, bypassing the need for manual confirmation.
Removing R Packages
If you need to remove an installed R package, the remove.packages() function comes in handy. To delete a specific package, such as dplyr, from your system, input:
remove.packages("dplyr")This straightforward approach ensures that you can effectively manage your system’s packages, keeping only those necessary for your work.
Understanding CRAN in R and CRAN LaunchPAD PPA
When working with the R Programming Language on Ubuntu systems, it’s vital to distinguish between two methods of installing R packages: through the R interpreter and via the CRAN LaunchPAD Personal Package Archive (PPA). The CRAN repository within the R interpreter is used to install R packages directly in the R environment. In contrast, the CRAN LaunchPAD PPA enables Ubuntu users to install R packages system-wide using the APT package manager.
This distinction plays a significant role in package installation and management for R developers, particularly those new to the ecosystem.
Adding CRAN LaunchPAD PPA
To expand your Ubuntu system’s R package capabilities, add the current R 4.0 or later c2d4u repository. This repository enhances your system with a broader range of R packages optimized for Ubuntu-based distributions. Run the following command with root privileges or using sudo:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:c2d4u.team/c2d4u4.0+Adding this repository is crucial in accessing an extensive array of R packages through your system’s package manager.
Installing R Packages from the PPA
With the repository added, you can install R packages across the entire system. For instance, to install specific packages like r-cran-rstan or r-cran-tidyverse without the recommended dependencies, execute one of these commands:
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-cran-rstanor
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-cran-tidyverseUsing these commands, you install the desired R packages system-wide. This approach is particularly beneficial in shared or multi-user environments requiring system-wide access.
Note on LTS Releases and Unsupported Usage
It’s crucial to note that the c2d4u repository is officially supported only on Long-Term Support (LTS) releases of Ubuntu. Usage on non-LTS releases may lead to compatibility challenges. Although it’s feasible to modify the c2d4u_team-ubuntu-c2d4u4_0_-*.list file to use a focal repository for non-LTS versions, this method is not officially sanctioned and could result in unforeseen issues.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve walked through the essential steps to install R Programming Language on Ubuntu, showcasing how to add the CRAN LaunchPAD PPA for a more comprehensive array of R packages and manage these packages effectively. Choosing the suitable method for installing R packages—whether through the R interpreter or the CRAN LaunchPAD PPA—can significantly impact your development workflow.
Our final recommendation is to stay updated with the latest R versions and packages for optimal performance and security. Don’t forget, if you’re working with Ubuntu’s LTS releases; the c2d4u repository is handy for maintaining a robust and diverse R environment. Happy coding!
Useful Links
Here are some valuable links related to using R on an Ubuntu system:
- R Project Official Website: Visit the official R Project website for comprehensive information about R, its features, and the latest updates.
- R for Ubuntu: Access the dedicated page for installing R on Ubuntu, including binaries and installation instructions.
- R Project Help: Find various help resources for R, including mailing lists, documentation, and user guides.
- R FAQs: Browse the frequently asked questions to find answers to common queries about R.
- R Manuals: Access a collection of manuals covering different aspects of R, from primary usage to advanced programming.
- R Certification: Learn about certification programs for R to validate your skills and knowledge.
- R on Stack Overflow: Join the R community on Stack Overflow to ask questions, share solutions, and get help from other R users.