Steam Client has revolutionized gaming on Linux, bringing a vast library of games and an active community platform to Steam is the leading digital distribution platform for PC gaming, offering a vast library of games, community features, and an easy-to-use interface. It provides gamers with access to thousands of games, regular sales, and various community-driven features like achievements, cloud saves, and multiplayer matchmaking. Installing Steam on Ubuntu ensures that you can enjoy the latest games and updates directly from your Linux system.
To install Steam on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04, you can use Steam’s official APT repository mirror. This method provides access to the latest version of Steam and ensures that your installation receives future updates automatically. This guide will walk you through the installation process using the command-line terminal to set up Steam on your Ubuntu system.
Steam Pre-installation Steps
Update Ubuntu Before Steam Installation
Before proceeding with the installation process for Steam on your Ubuntu system, it is crucial to ensure your system is up-to-date. Keeping your system updated helps prevent any package conflicts that might arise during the installation.
To update all your system packages, run the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command will update your Ubuntu system packages and ensure you have installed the latest versions.
Install Initial Packages for Steam
In this step, install additional packages to facilitate Steam installation on your Ubuntu system. These widely used packages are available in most Linux distributions.
To install these packages, run the following command:
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https curl -yThese packages provide essential functionality like secure APT, certificate management, and HTTPS support, which helps ensure a smooth installation process.
Enable 32-bit Support For Steam (Optional)
To ensure compatibility with 32-bit and 64-bit games in Steam’s extensive library, enable 32-bit support. Lower-end systems, which often run 32-bit games, particularly benefit from this support. Meanwhile, high-powered systems experience no negative impact from installing additional packages.
To enable 32-bit support on your Ubuntu system, run the following command:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386Enabling 32-bit support, you can enjoy various games on your Ubuntu system, regardless of their requirements.
Select Steam APT Installation Method
Option 1: Install Steam with the Ubuntu Default Repository
To install Steam on your Ubuntu system, use the standard default repository for the initial approach. Although many recommend this method, it may not offer the most recent stable release of the Steam client. If you want the latest version, opt for the second method.
To install Steam using the Ubuntu default repository, run the following command:
sudo apt install steam-installer steam-devicesThis command installs the Steam installer and required device packages from the Ubuntu default repository.
Option 2: Install Steam on Ubuntu via Steam APT Repository
The second method of installing Steam on your Ubuntu system involves importing the official Steam repository using the APT package manager. While this approach requires a few more steps, it ensures that you always have the latest and most up-to-date version of Steam directly from the source.
Import Steam GPG Key
First, you need to import the GPG key that verifies the authenticity of the Steam package installer. Run the following command in your terminal:
curl -s http://repo.steampowered.com/steam/archive/stable/steam.gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/steam.gpg > /dev/nullThis command securely downloads the GPG key and stores it in your system’s keyring.
Add Steam APT Repository
Next, add the official Steam repository to your system by executing the following command:
echo deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/steam.gpg] http://repo.steampowered.com/steam/ stable steam | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam.listThis command adds the official Steam repository to your APT sources list, ensuring you can install packages.
Update APT Cache After Steam PPA Import
Now, update the APT package information to recognize the newly imported repository:
sudo apt updateThis command updates your system’s package information to include packages from the newly added Steam repository.
Install the Steam on Ubuntu via APT Command
Finally, install the Steam Launcher and its required dependencies with the following command:
sudo apt-get install \
libgl1-mesa-dri:amd64 \
libgl1-mesa-dri:i386 \
libgl1-mesa-glx:amd64 \
libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \
steam-launcherThis command installs the Steam Launcher and the necessary OpenGL libraries for 64-bit and 32-bit architectures.
Fix Steam Extra Sources List (Steam PPA)
Steam might have added two extra files for the stable and beta clients while installing the Steam PPA method. These need to be removed, or you cannot update your packages.
Note: This can be skipped if you did not install Steam from the Steam APT PPA and utilized the default Ubuntu repository.
List Steam Extra Sources Files
Run the following command to list all current Steam sources lists in your /etc/apt/sources.list.d repository:
ls /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam*This command will display the Steam sources lists present in your /etc/apt/sources.list.d directory.
Remove Steam Extra Sources Lists
You might see three files. At the beginning of this guide, you imported the steam.list, which is the correct one. The others are not necessarily incorrect but are redundant. While some users may think of using the beta version, it often lags behind the latest Steam stable version. Do not install Steam from beta unless an actual beta is available and announced.
In your terminal, run the following commands to remove the excess sources:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam-beta.list
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam-stable.listThese commands will remove the unnecessary Steam sources lists from your system.
If you accidentally delete all three, re-import the sources list from this guide at the beginning of the section.
Refresh APT Index
Next, run an APT update to ensure your package list works correctly now:
sudo apt updateThis command updates your system’s package information to reflect the removal of the extra Steam sources lists.
Launching Steam User Interface
CLI Method to Launch Steam
If you’re already working in your terminal, you can quickly launch Steam with the following command:
steamGUI Method to Launch Steam
While the terminal option is helpful for quick access, most users prefer launching Steam directly from the desktop. To do this, follow the steps below:
- Click on the “Activities” or “Applications” menu, depending on your Ubuntu desktop environment.
- Search for “Steam” in the search bar.
- Click on the “Steam” icon to launch the application.

First-time Setup with Steam
Install the Required Packages for Steam
When you launch Steam for the first time, a terminal window may appear, prompting you to install additional packages necessary for running the client. Follow the on-screen instructions and proceed with the installation.

Note: If you have enabled 32-bit support on your system, you might encounter two prompts asking you to install the required packages.
Download and Update Steam Components
Once launched, you will observe a series of automatic pop-up windows showing Steam downloading and updating its components. Now, all you need to do is sit back and wait for the process to finish. For most users, this update should take only a few minutes.

Log in or Create a New Steam Account
Once the updates finish, the Steam Launcher login window will greet you. You can sign in with your existing Steam account or create a new one if you do not already have one.
To create a new account, click the “Create a new account” button and follow the on-screen instructions, providing the necessary information to set up your account. If you are signing in with an existing account, enter your account credentials and click “Log in.”
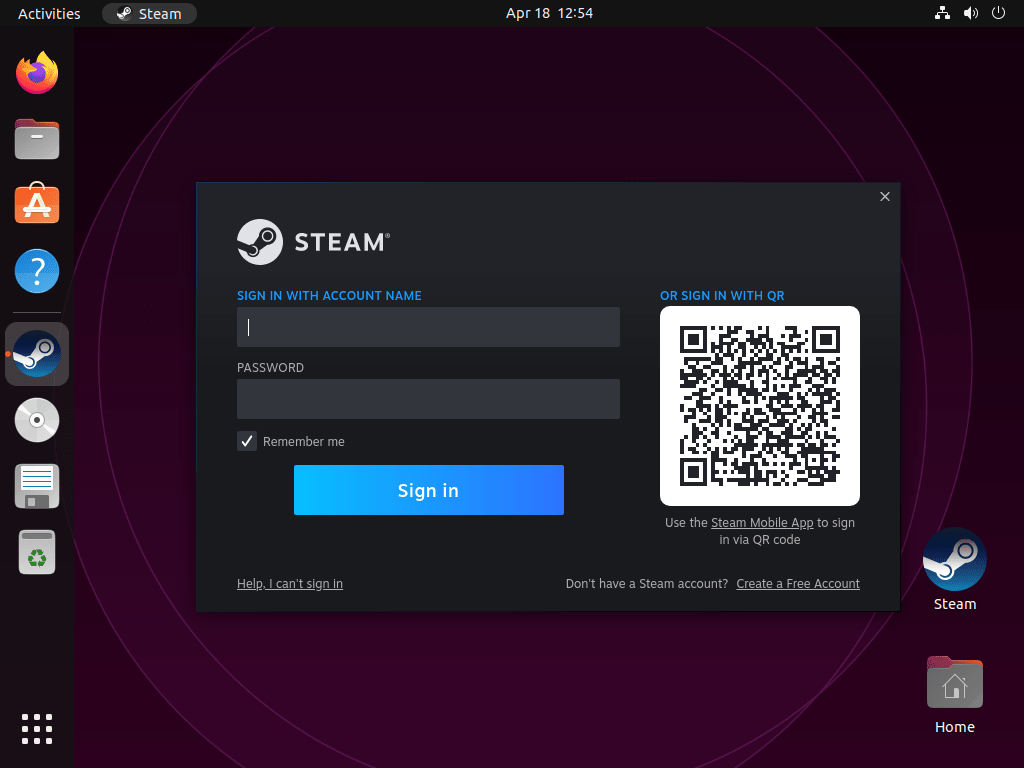
Enjoy Gaming on Steam with Ubuntu
Once logged in or registered, you have completed the Steam installation process and are ready to enjoy the platform’s vast games and features.
Browse the Steam store, discover new games, or search for your favorite titles. You can also socialize with other gamers, join communities, and participate in online multiplayer games. Steam offers a comprehensive gaming experience that caters to various interests and preferences.

Additional Steam Commands
Update Steam
Steam usually updates itself automatically, and Ubuntu desktop users may see notifications of available updates through the APT package manager. However, it’s a good idea to check for updates manually from time to time to ensure your Steam client stays up-to-date.
Run the following command in your terminal to check for available updates:
sudo apt updateTo apply the available updates, run the following command:
sudo apt upgradeRemove Steam
If you ever need to remove the Steam software from your Ubuntu system, follow these steps:
Run the following command in your terminal to uninstall Steam:
sudo apt remove steam*For users who installed the Steam APT repositories, remove the repository using the following command:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam.listLastly, if you added the Steam APT repository and imported the GPG key, use the following command to remove the imported GPG key:
sudo rm /usr/share/keyrings/steam-archive-keyring.gpgConclusion
With Steam installed on your Ubuntu system using the official APT repository mirror, you can enjoy seamless access to your game library and the latest updates directly from Steam. This method ensures that your Steam installation remains up-to-date with the latest features, security patches, and game releases. Regularly checking for updates through the repository will help maintain optimal performance, allowing you to fully enjoy your gaming experience on Ubuntu.


Newbie question: why go to all this trouble when Ubuntu 24.04.1 LTS has Steam in its App Center?
Does the App Center’s install of Steam have Proton included?
Hello, The method didn’t work for me on Ubuntu 24.04. However, using the Debian package provided on the official Steam website for download works. Thank you!
Starting with Ubuntu 24.04, you may encounter an issue where Steam fails to run, displaying an error that user namespaces need to be enabled. This problem is similar to what some users have experienced with Flatpak. The introduction of a new security feature in Ubuntu 24.04 has inadvertently caused complications for many users. As a result, most Electron-based applications that use sandboxing now require special adjustments to function properly.
While Valve is likely working on a long-term fix, you can temporarily resolve the issue by following these steps. Open your Terminal and execute the commands below:
sudo sysctl -w kernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_unconfined=0sudo sysctl -w kernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_userns=0
You’ll need to enter your root password when prompted. Once done, close the Terminal and try running Steam again. This fix not only resolves the Steam issue but also addresses other namespace-related problems with other software. However, be aware that this workaround reduces your system’s security, and you’ll need to reapply it after each reboot.
If you prefer a permanent solution, you can edit the sysctl.conf file located in /etc/. Add the following lines at the end of the file:
kernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_unconfined=0kernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_userns=0
Alternatively, you can automate this process by running the following command in the Terminal, which will append the necessary lines to the sysctl.conf file for you:
sudo sed -i '$ a\kernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_unconfined=0\nkernel.apparmor_restrict_unprivileged_userns=0' /etc/sysctl.confAfter saving the changes (whether manually or via the command), double-check that they were applied correctly, then run:
sudo service procps restartThis will make the changes persist between system boots, but it also represents a greater security risk.
While these steps will enable you to continue using Steam, it’s important to note that disabling these security features could leave your system vulnerable to potential threats. Use this solution at your discretion, as it disables a feature that many did not request in the first place.
Anecdotal, but I’d *not* use the Steam DEB, it caused weird keyboard behaviour on my (international) keyboard. More in point, the left CTRL died in all the games via Steam – and that’s not a insignificant key in most action games. 🙂
when calling this:
echo deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/steam.gpg] http://repo.steampowered.com/steam/ stable steam | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam.list
I get: ‘zsh: bad pattern: [arch=amd64’
does anyone know why ?
The error happens because zsh interprets square brackets [] differently compared to bash. To fix this, wrap the square brackets in single quotes like this:
echo 'deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/steam.gpg]' http://repo.steampowered.com/steam/ stable steam | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/steam.listThis should work in zsh without causing the error.