Timeshift creates incremental snapshots of your Ubuntu filesystem, allowing you to roll back to an earlier state when system issues occur. Specifically, Timeshift proves invaluable when a kernel upgrade breaks your boot sequence, when package conflicts render applications unusable, or when you need to recover from accidental system file deletions. Additionally, it supports both RSYNC for ext4 filesystems and BTRFS mode for Btrfs snapshots.
This guide covers two installation methods: the default Ubuntu repository provides stable, production-ready releases, while the developer PPA offers daily development builds with newer features. For most users, the default repository version is recommended.
Ubuntu Version Compatibility: This guide supports Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and 24.04 LTS installations. The default repository method works on both versions, while the developer PPA may not provide packages for newer or older Ubuntu releases. Commands shown work identically on both supported LTS releases.
Update Ubuntu System Packages
Before installing new software, ensure your system packages are current. Run the following command in your terminal to refresh package lists and upgrade installed packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command performs two actions: sudo apt update refreshes your local software repositories, ensuring your system knows the latest versions. Following this, the sudo apt upgrade updates your system’s installed packages to their latest versions.
Install Timeshift on Ubuntu via APT
Ubuntu users can install Timeshift from the default repository for stability or add the developer PPA for the latest development builds. The following table compares these methods:
| Method | Channel | Version | Updates | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT (Default) | Ubuntu Repos | 21.09.1 (22.04) 24.01.1 (24.04) | Automatic via apt upgrade | Production systems |
| APT (PPA) | teejee2008 PPA | 25.07.7 (both) | Automatic via apt upgrade | Testing daily builds |
Option 1: Install Timeshift via Ubuntu Repository
The Ubuntu repository provides stable Timeshift releases tested for compatibility with your Ubuntu version. To install from the default repository, run the following command:
sudo apt install timeshiftOnce installation completes, verify Timeshift installed correctly by checking the version:
timeshift --versionExpected output on Ubuntu 22.04:
Timeshift v21.09.1 by Tony George (teejeetech@gmail.com)
Expected output on Ubuntu 24.04:
Timeshift v24.01.1 by Tony George (teejeetech@gmail.com)
Option 2: Install Timeshift via Developer PPA (Development Builds)
The teejee2008 PPA provides daily development builds of Timeshift. However, these builds include the latest features but may contain unstable code. The PPA description explicitly states these are “daily (development) builds” not stable releases. Therefore, for production systems, use the default repository method instead.
Development builds from this PPA may include breaking changes or bugs. Only use this method if you need bleeding-edge features and can tolerate potential instability. For most users, the default repository version provides adequate functionality with better stability.
To incorporate the PPA into your system’s software sources, use the following command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:teejee2008/timeshift -yThis command adds the teejee2008/timeshift PPA to your system’s list of software sources. Furthermore, the -y flag automatically confirms the addition of the PPA, saving you from an extra step.
Next, after adding the PPA, you must update your system’s software sources again. This ensures that the system recognizes the newly added PPA. To do this, run the following command:
sudo apt updateWith the PPA added and recognized, you can now install Timeshift:
sudo apt install timeshiftFinally, after installation, verify you received the PPA version by checking the version number:
timeshift --versionExpected output from the development PPA (both Ubuntu versions):
Timeshift v25.07.7 by Tony George (teejeetech@gmail.com)
As expected, the PPA version (25.07.7) is significantly newer than the default repository versions, reflecting its development build status.
Launch Timeshift Application
Launch Timeshift via CLI
For terminal users, you can launch Timeshift by running:
timeshiftLaunch Timeshift via GUI
Alternatively, for desktop users, you can access Timeshift through your application menu:
- Click Activities at the top left corner of your screen.
- Click Show Applications (grid icon at the bottom of the sidebar).
- Search for Timeshift and click the icon to launch.
Note that Timeshift requires root privileges and will prompt for your password.
Create Snapshots Using Timeshift
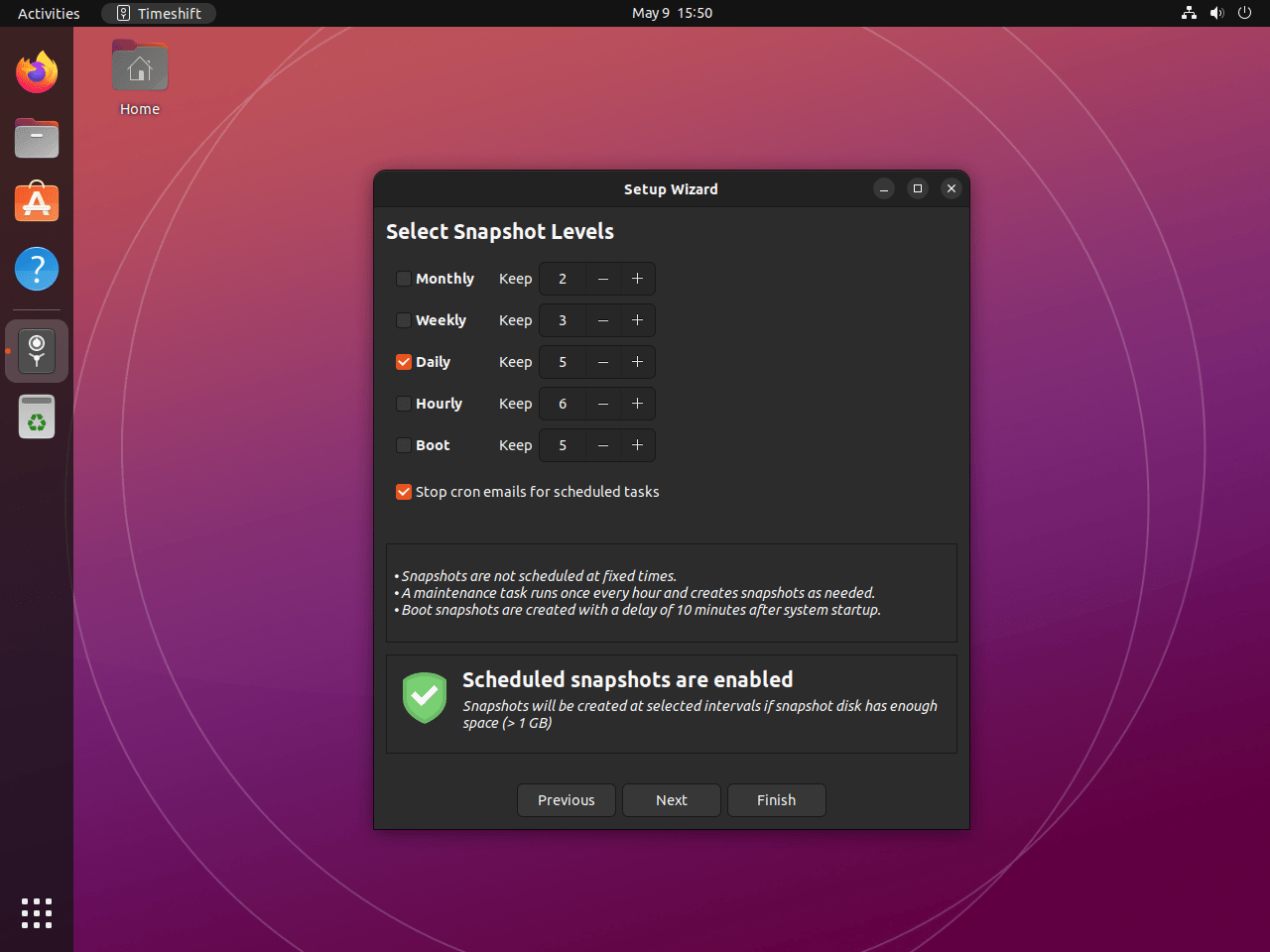
Timeshift snapshots capture your system state at a specific point in time. Consequently, the snapshot wizard walks you through configuration, snapshot creation, and schedule setup.
Configure Snapshot Settings
Before creating your first snapshot, configure Timeshift’s snapshot type and storage location. First, choose between RSYNC mode (for ext4 filesystems) or BTRFS mode (for Btrfs filesystems). Then, select which files to include in snapshots—typically system files only, excluding user home directories. Additionally, ensure adequate storage space for your snapshots; a full system snapshot typically requires 5-10 GB depending on installed packages.
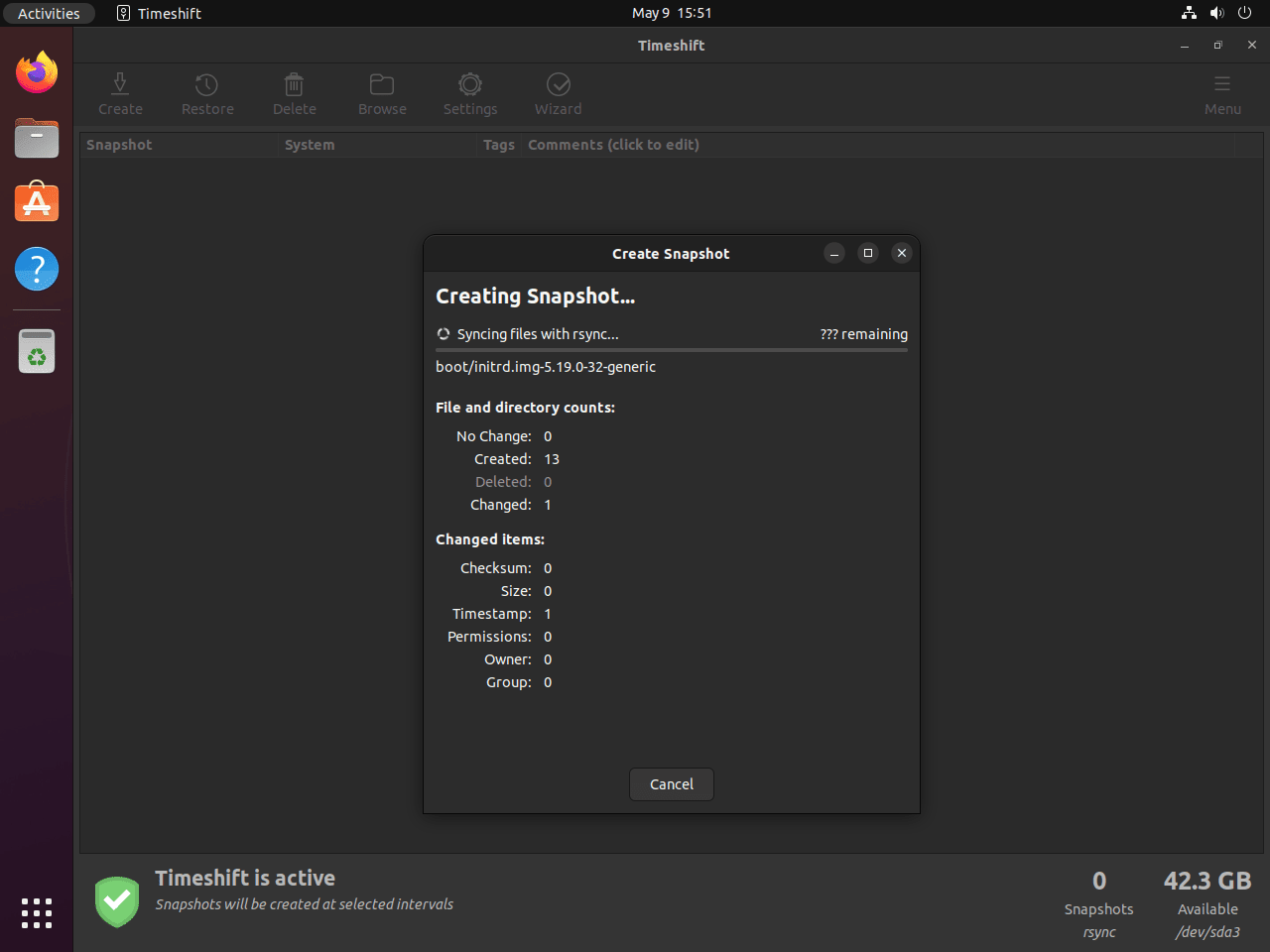
Create Manual Snapshot
After configuring your preferences, click the Create button to generate your first snapshot. The snapshot process duration depends on your system size and selected files, and Timeshift displays progress in real-time. Once complete, your snapshot appears in the main window with a timestamp and description.
Manage Existing Snapshots
Timeshift lists all snapshots with timestamps and sizes. From here, you can click any snapshot to view details, restore your system to that point, or delete old snapshots to free disk space. Additionally, configure automatic snapshot schedules (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly) in the settings to maintain system backups without manual intervention.
Manage Timeshift Snapshots from the Command Line
Timeshift also includes a command-line interface for automation and remote management. The following commands cover the most common operations.
Check Timeshift Status
To view current snapshot configuration and existing snapshots, run:
sudo timeshift --statusThis command displays snapshot mode (RSYNC/BTRFS), storage location, and lists existing snapshots with their timestamps and sizes. For example, you should see output similar to:
Timeshift v24.01.1 by Tony George (teejeetech@gmail.com) Device : /dev/sda1 UUID : abc123-def456-ghi789 Path : /timeshift Mode : RSYNC Status : 1 snapshots, 15.2 GB on disk
Create Snapshot via CLI
To create a manual snapshot from the command line, use:
sudo timeshift --createThe snapshot creation process displays progress as files are copied. Upon completion, you’ll see output similar to:
Creating new snapshot... Saving to device: /dev/sda1, mounted at: /run/timeshift/backup Syncing files with rsync... Created snapshot: 2024-12-08_15-00-01 Snapshot saved successfully (5 min 23 sec)
Restore Snapshot via CLI
To restore your system to a previous snapshot, use the tag identifier:
sudo timeshift --restore --snapshot-tag <tag>Replace <tag> with the snapshot identifier from timeshift --list output. Subsequently, Timeshift prompts for confirmation before restoring to prevent accidental system changes.
Delete Snapshot via CLI
To remove old snapshots and free disk space, run:
sudo timeshift --delete --snapshot-tag <tag>Replace <tag> with the snapshot identifier. Note that deleting snapshots is permanent and cannot be undone.
Update Timeshift
Keep Timeshift updated through the standard Ubuntu update process:
Update Timeshift via APT
Timeshift updates automatically when you run the standard system update command. To check for updates and apply them:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeAs a result, this updates package lists and upgrades all installed packages to their latest available versions.
Remove Timeshift
If you no longer need Timeshift, remove it using APT. The removal process differs slightly depending on whether you used the PPA.
Remove Timeshift Package
First, remove Timeshift regardless of installation method:
sudo apt remove timeshiftThis removes the Timeshift package but preserves configuration files. For a complete removal including configuration files, use purge instead:
sudo apt purge timeshift
sudo apt autoremove -yRemove Developer PPA (If Used)
If you installed Timeshift from the teejee2008 PPA, also remove the PPA after uninstalling the package:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:teejee2008/timeshift -ySubsequently, after removing the PPA, update your package lists:
sudo apt updateFinally, verify Timeshift was removed successfully:
apt-cache policy timeshiftAs a result, the output should show the package is no longer installed:
timeshift:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 24.01.1-1build2
Version table:
24.01.1-1build2 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble/universe amd64 Packages
Removing Timeshift does not delete existing snapshots. If you want to reclaim disk space, manually delete snapshot directories (typically stored in
/timeshifton your backup partition or your configured location) before uninstalling Timeshift.
Troubleshooting Common Timeshift Issues
The following solutions address common Timeshift problems encountered on Ubuntu systems.
Timeshift Fails to Create Snapshot with “No Space Left” Error
Error message:
E: Error creating snapshot: No space left on device
Diagnostic: Check available disk space on your snapshot storage location:
df -hLook for your snapshot partition in the output. If the “Use%” column shows 100% or nearly full, that’s causing the error:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 100G 95G 5.0G 95% / /dev/sdb1 500G 480G 20G 96% /timeshift
Solution: Delete old snapshots or change snapshot location to a drive with more space. To do this, open Timeshift GUI, go to Settings, and either remove old snapshots or reconfigure the snapshot storage location to a larger partition.
PPA Version Shows Same Version as Repository After Installation
Diagnostic: Verify which repository provides your Timeshift package:
apt-cache policy timeshiftSolution: If the PPA is not listed or shows lower priority, ensure you ran sudo apt update after adding the PPA. Then reinstall Timeshift:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install --reinstall timeshiftTimeshift GUI Won’t Launch or Crashes on Startup
Diagnostic: Run Timeshift from terminal to see error messages:
sudo timeshift-gtkSolution: If you see dependency errors, reinstall Timeshift and its GTK dependencies:
sudo apt install --reinstall timeshift libgtk-3-0Verification: Finally, confirm Timeshift launches without errors. The application window should open and display your snapshot configuration.
Conclusion
You now have Timeshift installed and can protect your Ubuntu system with incremental snapshots. The default repository provides stable versions suitable for production use, while the developer PPA offers bleeding-edge features for users comfortable with development builds. Remember to configure automatic snapshot schedules and verify snapshots complete successfully. Additionally, use timeshift --status to check snapshot health and timeshift --create before major system changes. For restoration needs, boot from a live USB and use Timeshift’s restore function to recover your system. Next, explore automated security updates with Unattended Upgrades or strengthen system security with UFW firewall configuration.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>