qBittorrent stands out as a reliable torrent client for those prioritizing security and efficiency. This guide will detail the installation process for qBittorrent on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster and also cover the steps to set up qBittorrent-nox, the version equipped with WebUI.
Let’s quickly cover some fundamental differences between the qBittorrent installation methods:
qBittorrent Desktop Benefits:
- User-Friendly Interface: Offers a graphical interface that’s intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Clean Experience: Being open-source, it’s free from ads and unnecessary bundled software.
- Feature-Rich: Includes sequential downloading, bandwidth scheduling, and more.
qBittorrent-nox Benefits:
- Optimized for Headless Systems: Designed for minimal resource usage, ideal for constrained systems.
- Web Interface: Allows for operations via a web-based interface.
- Remote Management: Facilitates the management of servers and distant systems through its web interface.
qBittorrent’s commitment to transparency and security is evident in its open-source nature and active development. For those seeking a blend of functionality and user-friendliness in a torrent client, qBittorrent remains a top recommendation, backed by a community-driven approach that ensures it stays attuned to user requirements.
It is now moving on to the main article on installing the BitTorrent software.
Method 1: Install qBittorrent Desktop
In this section, we delve into installing the qBittorrent desktop client on your Debian system and initializing it for the first time. It is essential to keep your system up to date to avoid conflicts and ensure compatibility with the qBittorrent installation.
Update Debian Before qBittorrent Installation.
Updating the system package list and upgrading the installed packages ensures that you work with the latest software by running the following command:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgradeIf the upgrade involves updating many packages or the Linux kernel, it is wise to reboot the system for the changes to take effect.
sudo rebootInstall qBittorrent Desktop via APT Command
With an updated system, you are set to install qBittorrent. This versatile desktop client can be installed directly from Debian repositories. Execute the following command to install qBittorrent:
sudo apt install qbittorrentThis command will retrieve the latest qBittorrent package from the Debian repositories and install it on your system.
Launch qBittorrent Desktop Client
With qBittorrent successfully installed, it is time to launch the application. You can do this from the terminal by executing:
qbittorrentThis launches the qBittorrent client, and you are now ready to manage your torrents.
You can launch qBittorrent from your system’s application menu if you prefer graphical interfaces. To do this, follow these steps:
Activities > Show Applications > qBittorrent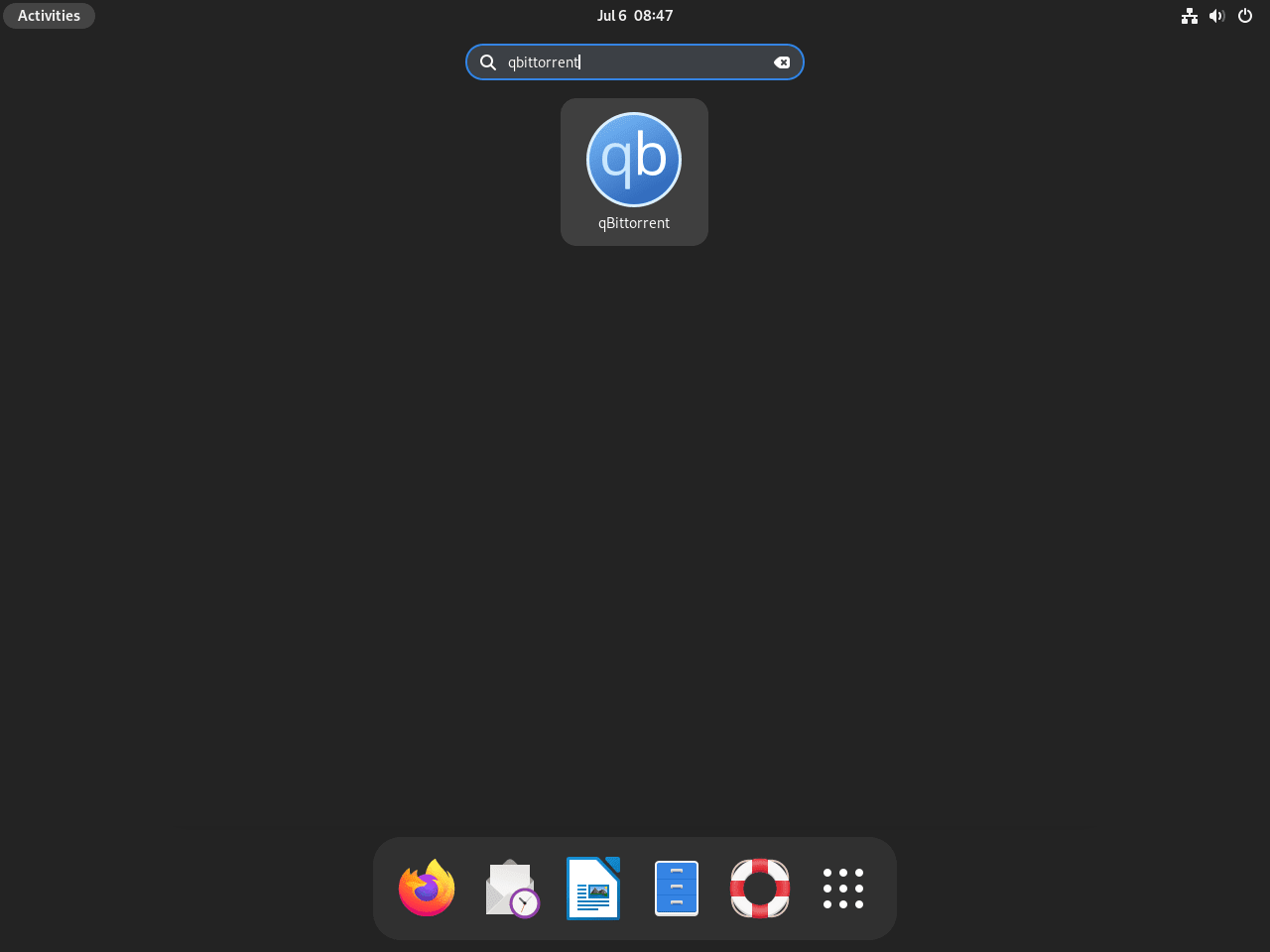
Read Legal Notice From qBittorrent
A legal notice will appear when you launch qBittorrent for the first time. This notice helps protect qBittorrent from legal issues related to torrent sharing. After you agree to the notice, the main window of qBittorrent will open, and you can start using the software.
Method 2: Install qBittorrent-nox (server / web-UI)
In this section, we focus on installing qBittorrent-nox, which is particularly beneficial for running qBittorrent on a headless Debian server or remotely accessed desktop. The WebUI interface enables efficient management of qBittorrent via a web browser.
Install qBittorrent-nox via APT Command
Begin by installing qBittorrent-nox with the command below. It’s tailored for headless systems, and the Web interface can be accessed at the default location http://localhost:8080.
sudo apt install qbittorrent-noxCreate a Dedicated System User and Group for qBittorrent
For enhanced security, qBittorrent-nox should run as an unprivileged user. Creating a systemd service unit facilitates this, as it operates in the background and initializes at system boot.
Execute the following command to create a user and group for qBittorrent-nox:
sudo adduser --system --group qbittorrent-noxThe --system flag specifies that this is a system user, which doesn’t have the full capabilities of a regular user.
Add Your Username to the qBittorrent-nox Group
To grant your user account the necessary permissions, add it to the qbittorrent-nox group:
sudo adduser your-username qbittorrent-noxReplace your-username with your actual username.
Create a Systemd Service File for qBittorrent-nox
Create a new systemd service file to define how the qBittorrent-nox service should run:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/qbittorrent-nox.serviceEnter the following content into the file:
[Unit]
Description=qBittorrent Command Line Client
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=qbittorrent-nox
Group=qbittorrent-nox
UMask=007
ExecStart=/usr/bin/qbittorrent-nox -d --webui-port=8080
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetSave and close the file by pressing CTRL+O followed by CTRL+X.
Reload the Systemd Daemon
To activate the new service, reload the systemd daemon:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadStart and Enable qBittorrent-nox
Now, start the qBittorrent-nox service and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl start qbittorrent-nox
sudo systemctl enable qbittorrent-noxsudo systemctl enable qbittorrent-noxIt’s a good practice to check the status to ensure the service is running smoothly:
systemctl status qbittorrent-nox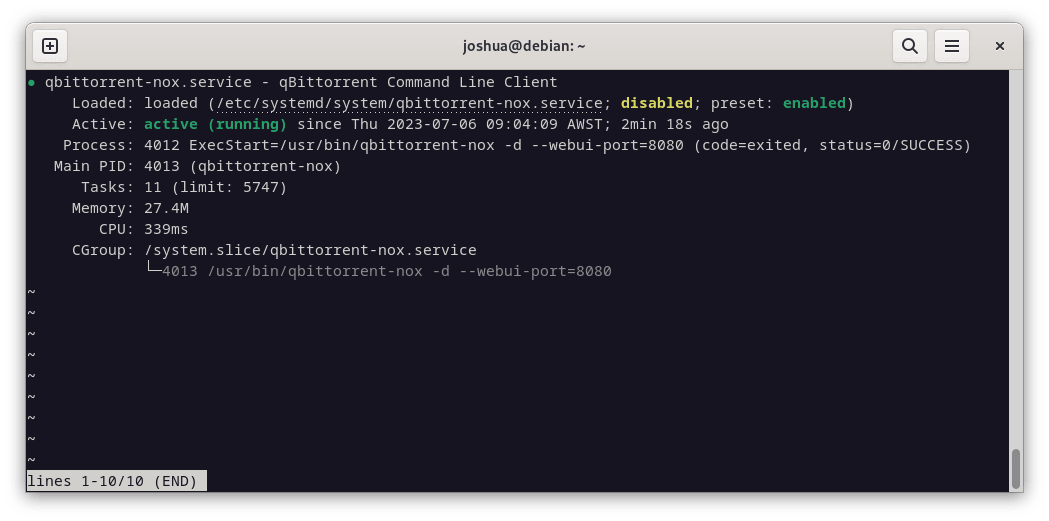
If you find an error, the most common issue is the qbittorrent-nox service cannot create the required directories. To fix this, run the following commands:
sudo mkdir /home/qbittorrent-nox
sudo chown qbittorrent-nox:qbittorrent-nox /home/qbittorrent-nox
sudo usermod -d /home/qbittorrent-nox qbittorrent-noxThen start or restart the service:
sudo systemctl start qbittorrent-noxAccess qBittorrent Web UI
Access the qBittorrent Web UI through a browser by entering your server’s internal IP address followed by the port number (8080), like 192.168.55.156:8080. If running locally, use 127.0.0.1:8080.
Remember, the default username is admin, and the password is adminadmin.
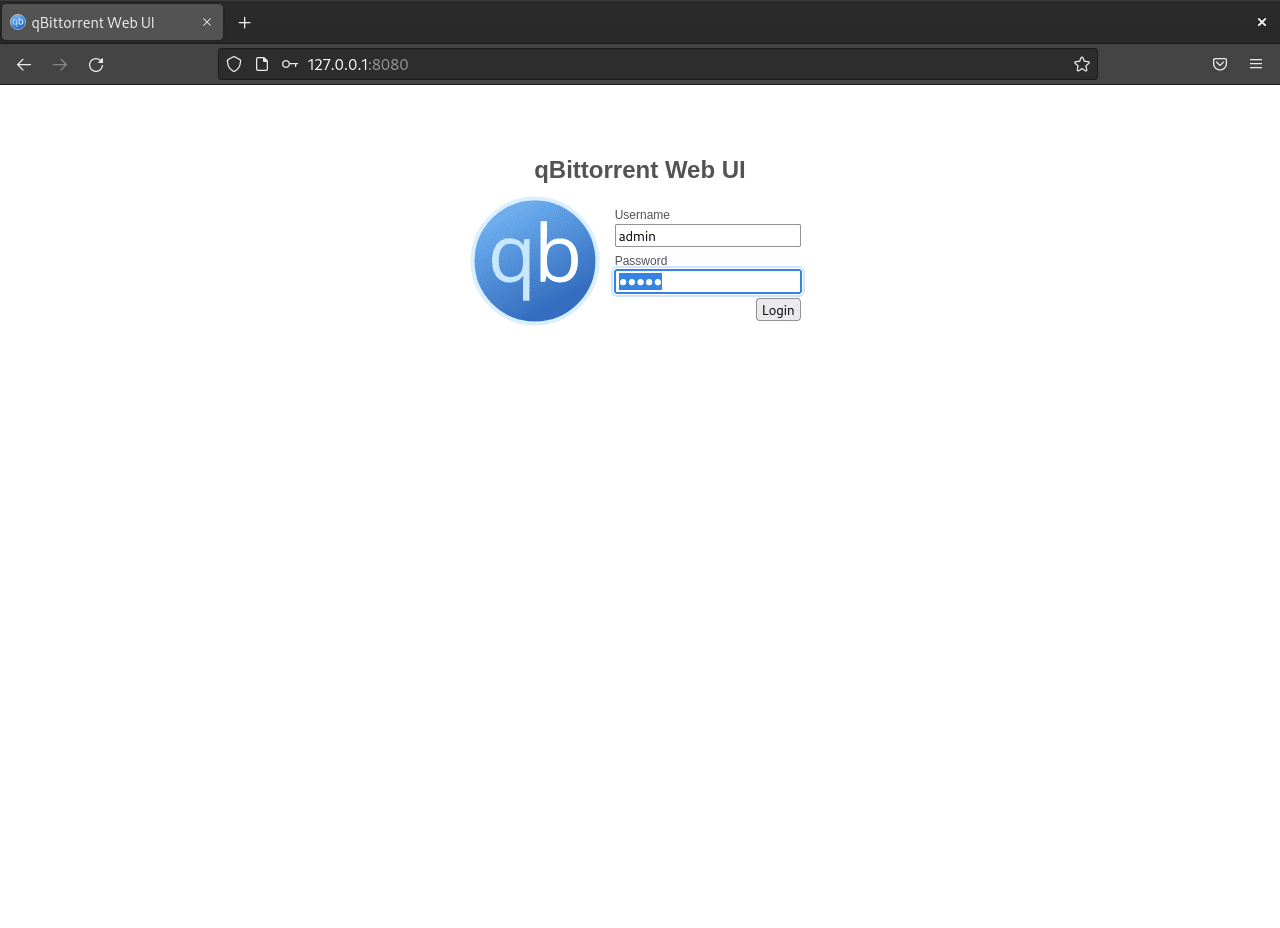
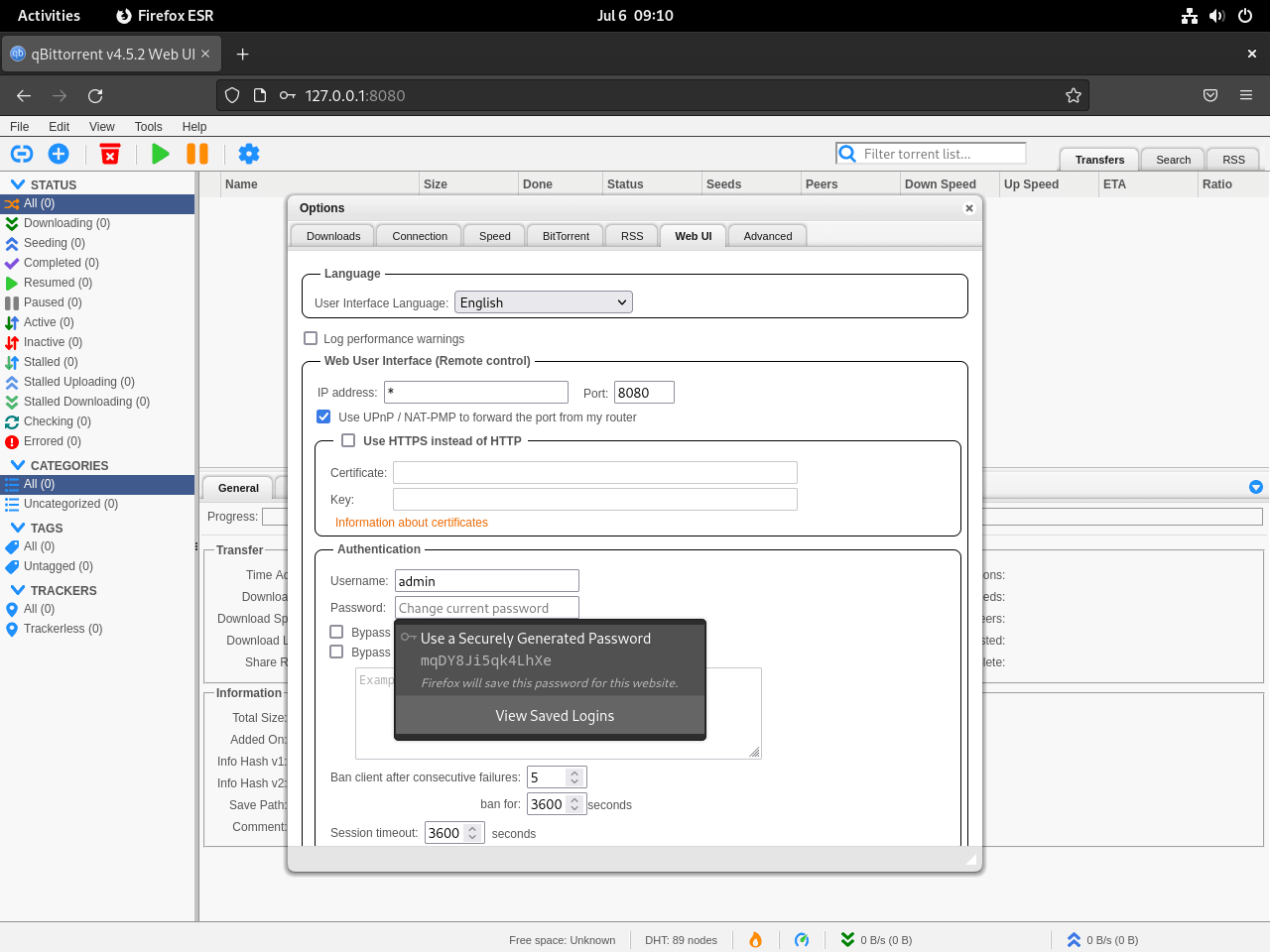
It’s paramount to change the default login credentials for security purposes. Navigate through Tools > Options > Web UI > Authentication in the Web UI. Here, you can set a custom username and password.
This step ensures that your qBittorrent Web UI is secure and accessible only to individuals with the proper credentials.
Additional Commands For qBittorrent
Update qBittorrent or qBittorrent-nox
To check for updates for qBittorrent or qBittorrent-nox, use the command below:
sudo apt updateYou should proceed with the upgrade if an update is available for qBittorrent or qBittorrent-nox with the following command:
sudo apt upgradeRemove qBittorrent or qBittorrent-nox
There could be various reasons for wanting to uninstall qBittorrent or qBittorrent-nox, such as system resource management or switching to an alternative application. Whatever the reason, follow this simple process.
To uninstall qBittorrent, enter the following command:
sudo apt remove qbittorrentIf you have installed qBittorrent-nox, which is the headless variant, you can remove it by using the following command:
sudo apt remove qbittorrent-noxConclusion
In this guide, we walked through the comprehensive steps to install and manage qBittorrent on Debian versions 10, 11, and 12. We delved into the specifics of setting up qBittorrent-nox, which is ideal for servers and remote configurations. Additionally, we highlighted establishing a systemd service, ensuring that qBittorrent-nox operates seamlessly in the background and initializes upon system startup. Key steps such as adding your user to the qBittorrent-nox group, configuring the systemd service file, and accessing the Web UI were also detailed.
For optimal security, it’s imperative to regularly update the qBittorrent package to benefit from the latest patches and enhancements. To bolster safety, modify the default credentials for the Web UI. By adhering to these guidelines, you can achieve a secure and efficient qBittorrent setup on your Debian platform.


Thank you so much!!
Great guide! it was all straightfoward
THANK YOU A LOT for the fix when qbitorrent-nox won’t start, I’ve been stuck on this for far too long!!!!