Deluge is a lightweight BitTorrent client designed for versatility, offering features suitable for both casual users and advanced network managers. Known for its low resource consumption, Deluge can run as a standalone desktop application or function as a daemon with the deluged package, enabling remote control through the deluge-web web interface or the deluge-console terminal client. Additionally, it supports plugins that expand its functionality, including encryption, speed limits, and IP filtering. Whether you need a simple torrent downloader or a headless server solution, Deluge’s modular design makes it an excellent choice for Ubuntu systems.
This guide walks you through installing Deluge on Ubuntu using four methods: the default APT repository for stability, the Deluge Team PPA for the latest development builds, Flatpak from Flathub for sandboxed installations, and the headless daemon setup for servers with web-based management. By the end, you will have a fully functional BitTorrent client configured on your system, complete with verification steps and removal instructions.
Choose Your Deluge Installation Method
Before proceeding, consider which installation method best suits your needs. The table below compares the available options:
| Method | Channel | Version | Updates | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT (Default) | Ubuntu Repos | Stable | Automatic via apt upgrade | Desktop users who prefer tested packages |
| APT (PPA) | Deluge Team PPA | Development | Automatic via apt upgrade | Users who want the latest features |
| Flatpak | Flathub | Latest stable | Via flatpak update | Users who prefer sandboxed applications |
| APT (Headless) | Ubuntu Repos | Stable | Automatic via apt upgrade | Headless servers with web interface access |
For most users, the default APT method is recommended because it provides stable, distribution-tested packages with automatic security updates. Only use the PPA if you specifically need the latest development features, and note that these builds may contain bugs.
This guide supports Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and 24.04 LTS installations. The Deluge Team PPA typically supports the two most recent LTS releases, while Flatpak remains compatible across all Ubuntu versions. Commands shown work identically on both supported LTS releases.
Method 1: Install Deluge with APT
Update Your Ubuntu System
Before installing Deluge, first ensure that your Ubuntu system is up-to-date. This helps prevent potential issues due to outdated packages or dependencies.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThe first part of this command refreshes your package index, while the second upgrades all installed packages to their latest versions.
Select Your APT Installation Option
There are two options for installing Deluge via APT: the default Ubuntu repository or the Deluge Team’s Personal Package Archive (PPA). Choose the option that best matches your needs.
Option 1: Install from Ubuntu Repository
For most users, the easiest method is installing Deluge from Ubuntu’s default repository. This approach ensures compatibility and stability with your distribution. To install the Deluge desktop client, run the following command:
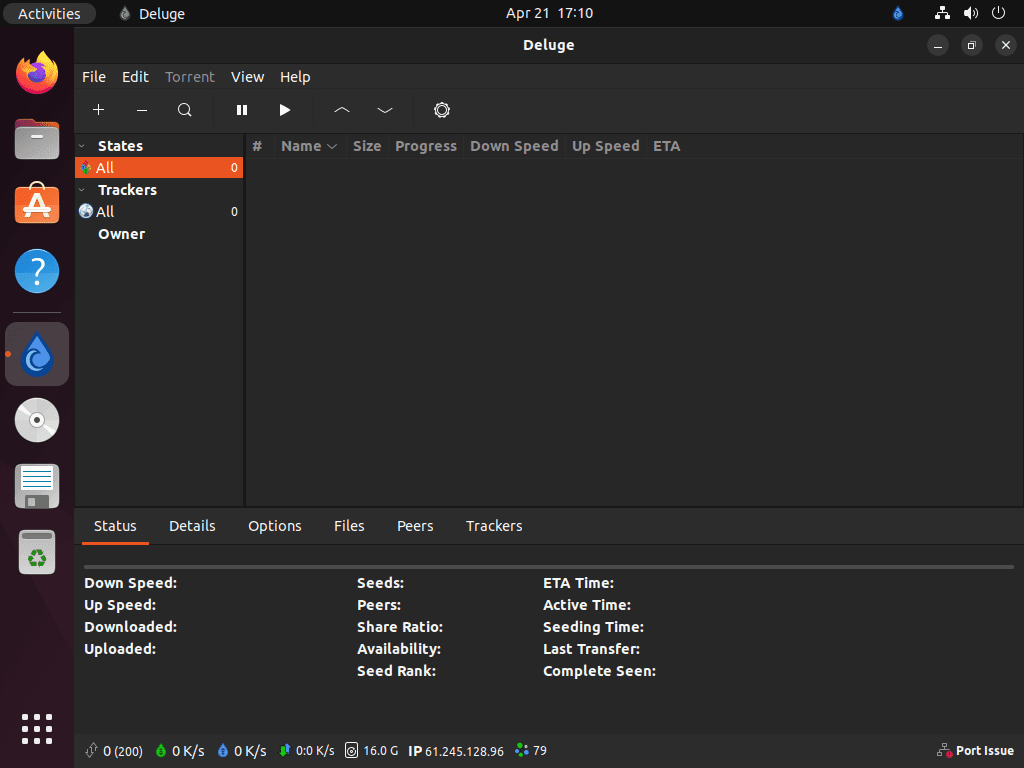
sudo apt install delugeThis command installs the Deluge GTK client along with its core dependencies including deluge-common and python3-libtorrent. Once installation completes, verify the installation by checking the installed version:
apt-cache policy delugeThe output confirms the installed version and its source repository. Note that the default repository version differs between Ubuntu releases: Ubuntu 24.04 provides Deluge 2.1.x while Ubuntu 22.04 includes Deluge 2.0.x. Both versions work identically for basic torrenting tasks.
deluge:
Installed: 2.1.2~dev0+20240121-1
Candidate: 2.1.2~dev0+20240121-1
Version table:
*** 2.1.2~dev0+20240121-1 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble/universe amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
Option 2: Install from Deluge Team PPA
Ubuntu LTS releases sometimes lag behind new software releases due to their focus on system stability. As a result, you might prefer to install a more recent version of Deluge with new features and performance improvements.
Development Builds Warning: The deluge-team/develop PPA contains daily development builds from the git develop branch. These are not production-ready releases and may have bugs or cause data loss. Keeping backups is recommended if you choose this option.
First, install the software-properties-common package, which provides tools for managing PPAs:
sudo apt install software-properties-common -yNext, import the Deluge Team PPA into your system:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deluge-team/develop -yNow, update your package list to include the new PPA:
sudo apt updateFinally, install the Deluge BitTorrent client using the imported PPA:
sudo apt install delugeAfter installation, confirm the PPA version is installed by checking the package policy:
apt-cache policy delugedeluge:
Installed: 2.2.1~dev7883+6158d7b71-202508250248~ubuntu24.04.1
Candidate: 2.2.1~dev7883+6158d7b71-202508250248~ubuntu24.04.1
Version table:
*** 2.2.1~dev7883+6158d7b71-202508250248~ubuntu24.04.1 500
500 https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/deluge-team/develop/ubuntu noble/main amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
2.1.2~dev0+20240121-1 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble/universe amd64 Packages
The output shows both versions available: the PPA’s development build (installed) takes priority over the default repository version. The three-asterisk marker indicates the currently installed package.
Method 2: Install Deluge via Flatpak and Flathub
Flatpak provides an alternative installation method that offers sandboxed applications with automatic updates. Additionally, this method works across all Ubuntu versions and isolates Deluge from your system packages.
Flatpak is not pre-installed on Ubuntu. If you have not set it up yet, install it with
sudo apt install flatpakand restart your session before continuing. For detailed setup including the Flathub repository, follow our Flatpak installation guide for Ubuntu.
Enable Flathub Repository
First, add the Flathub repository if it is not already configured on your system:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoInstall Deluge from Flathub
Once Flathub is configured, install Deluge using the following command:
sudo flatpak install flathub org.deluge_torrent.deluge -yOnce installation completes, verify the installation by checking the application info:
flatpak info org.deluge_torrent.delugeDeluge - A fully-featured BitTorrent Client
ID: org.deluge_torrent.deluge
Ref: app/org.deluge_torrent.deluge/x86_64/stable
Arch: x86_64
Branch: stable
Origin: flathub
Version: 2.2.0
Method 3: Install Deluge Daemon for Headless Servers
For server environments without a graphical desktop, Deluge provides the deluged daemon and deluge-web web interface. This setup lets you manage torrents remotely through any web browser, making it ideal for headless Ubuntu servers, NAS appliances, or always-on seedboxes.
Install Deluge Daemon and Web Interface
To begin, install both the Deluge daemon and web interface packages:
sudo apt install deluged deluge-webThis installs the headless daemon (deluged) that handles all torrent operations and the web interface (deluge-web) that provides browser-based management. Both packages include systemd service files for automatic startup.
Enable and Start Deluge Services
The Deluge daemon runs as a dedicated system user (debian-deluged) created during package installation. To enable the services, run the following commands:
sudo systemctl enable --now deluged
sudo systemctl enable --now deluge-webNext, verify both services are running:
systemctl status deluged deluge-web● deluged.service - Deluge Bittorrent Client Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/deluged.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2024-12-15 06:15:00 UTC; 5s ago
● deluge-web.service - Deluge Bittorrent Client Web Interface
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/deluge-web.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2024-12-15 06:15:01 UTC; 4s ago
Access Deluge Web UI
The Deluge web interface runs on port 8112 by default. Access it through your browser using the server’s IP address:
http://your-server-ip:8112
If accessing from a remote machine, ensure your firewall allows traffic on port 8112. Ubuntu users with UFW can open the port with:
sudo ufw allow 8112/tcpThe default web interface password is
deluge. Change this immediately after first login through Preferences > Interface > Password. The web interface will prompt you to connect to the local daemon on first access.
View Daemon Logs
If you encounter issues, check the daemon logs for troubleshooting:
sudo journalctl -u deluged -n 50 --no-pagerSimilarly, for the web interface logs:
sudo journalctl -u deluge-web -n 50 --no-pagerLaunch Deluge Desktop Client
After successfully installing Deluge, you can launch the application using either the terminal or the graphical application menu.
Launch Deluge from Terminal
If you prefer using the terminal, launch Deluge with the command that matches your installation method:
APT installation:
delugeFlatpak installation:
flatpak run org.deluge_torrent.delugeLaunch Deluge from Applications Menu
Alternatively, open the Activities overview by pressing the Super key, type “Deluge” in the search bar, and click the Deluge icon to launch the application. To add Deluge to your favorites for quick access, right-click the icon and select “Add to Favorites.”
Manage Deluge
This section covers essential commands for managing the Deluge BitTorrent client on Ubuntu Linux. Specifically, it includes updating and removing the application.
Update Deluge
Deluge updates are typically included in system updates. However, if notifications fail to appear, you can manually check for updates using the terminal.
APT installation:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeFlatpak installation:
sudo flatpak updateRemove Deluge
If you no longer need Deluge, follow the removal instructions that match your installation method.
Remove APT Installation
First, remove the Deluge package:
sudo apt remove delugeNext, remove any orphaned dependencies that were installed with Deluge:
sudo apt autoremoveAdditionally, if you installed from the PPA, remove the Deluge Team repository:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:deluge-team/develop -yRemoving the PPA ensures that your package list no longer includes development builds from the Deluge Team repository.
Remove Headless Server Installation
If you installed the daemon and web interface for headless operation, first stop and disable the services:
sudo systemctl disable --now deluged deluge-webThen remove the server packages:
sudo apt remove deluged deluge-web
sudo apt autoremoveRemove Flatpak Installation
sudo flatpak uninstall org.deluge_torrent.delugeAfter removal, clean up unused Flatpak runtimes:
sudo flatpak uninstall --unusedRemove User Configuration Data
Warning: The following command permanently deletes your Deluge configuration, including torrent data, settings, and plugin configurations. If you want to keep any data, back it up first.
To completely remove Deluge configuration files from your home directory, run the following command:
rm -rf ~/.config/delugeSimilarly, for Flatpak installations, also remove the sandboxed data directory:
rm -rf ~/.var/app/org.deluge_torrent.delugeFinally, for headless server installations, the daemon configuration is stored in a system directory owned by the debian-deluged user:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/delugedConclusion
You now have Deluge installed on your Ubuntu system using your preferred method. The default APT repository provides stable, tested packages suitable for most desktop users. The Deluge Team PPA offers the latest development features, though with potential stability trade-offs. Flatpak provides a sandboxed installation that stays up-to-date independently of your system packages. For server environments, the headless daemon with web interface enables remote management from any browser. Whichever method you chose, Deluge is ready to handle your torrenting needs with its plugin system, remote access capabilities, and modular architecture.
For alternative BitTorrent clients on Ubuntu, consider exploring qBittorrent or KTorrent, which offer similar functionality with different interfaces.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>