LibreWolf is a privacy-focused Firefox fork that removes telemetry, enables tracking protection by default, and includes uBlock Origin for ad blocking. Whether you need private browsing for research, daily web use without corporate data collection, or enhanced security for sensitive activities, LibreWolf provides these capabilities without sacrificing Firefox’s compatibility and performance. By the end of this guide, you will have LibreWolf installed on Linux Mint 22 or 21, verified it launches correctly, and understand how to keep it updated through automatic package management.
Choose Your LibreWolf Installation Method
LibreWolf is available through two installation channels on Linux Mint: the official repository via extrepo, and Flatpak from Flathub. The extrepo method integrates with your system’s package manager for automatic updates alongside other system packages, while Flatpak provides sandboxed isolation with application-level update control.
| Method | Channel | Version | Updates | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extrepo | LibreWolf Official | Latest stable | Automatic via APT upgrades | Most users who prefer native package management |
| Flatpak | Flathub | Latest stable | Automatic via Flatpak updates | Users who prefer sandboxed applications with container isolation |
For most users, the extrepo method is recommended because it provides automatic security updates through your existing system package manager and requires minimal maintenance. Flatpak is an excellent alternative if you prefer application sandboxing or already use Flatpak for other software.
These instructions support Linux Mint 22.x and 21.x. The extrepo method works identically across both versions since it automatically configures the repository for you. Flatpak is pre-installed with Flathub enabled by default on Linux Mint, making it ready to use without additional setup.
Install LibreWolf on Linux Mint via Extrepo (Recommended)
Step 1: Update Linux Mint Package Lists
Update your package list to ensure you install the latest available version:
sudo apt updateStep 2: Install Extrepo Repository Management Tool
Extrepo simplifies repository management by automatically handling GPG keys and repository configuration. Install it first:
sudo apt install extrepoVerify the installation:
extrepo --versionExpected output:
extrepo version 1.0
Step 3: Enable the LibreWolf Repository with Extrepo
Use extrepo to enable the official LibreWolf repository. This command automatically downloads the GPG key and creates the repository configuration:
sudo extrepo enable librewolfExtrepo creates a DEB822-format repository file at /etc/apt/sources.list.d/extrepo_librewolf.sources and handles GPG key verification automatically.
Step 4: Update Package Lists and Install LibreWolf
Update your package list to recognize the new repository:
sudo apt updateInstall LibreWolf:
sudo apt install librewolfVerify the installation:
which librewolfExpected output:
/usr/bin/librewolf
Install LibreWolf on Linux Mint via Flatpak
Step 1: Verify Flatpak and Flathub Configuration
Linux Mint comes with Flatpak pre-installed and Flathub enabled by default. Verify your setup:
flatpak --versionExpected output:
Flatpak 1.14.x
Confirm Flathub is enabled:
flatpak remotesExpected output:
flathub system https://flathub.org/repo/
Step 2: Install LibreWolf via Flatpak
Install LibreWolf from Flathub:
flatpak install flathub io.gitlab.librewolf-community -yVerify the installation:
flatpak list | grep -i librewolfExpected output:
LibreWolf io.gitlab.librewolf-community 147.0-1 stable system
Launch LibreWolf on Linux Mint
Launch LibreWolf from Terminal
Launch LibreWolf from the command line. For the extrepo/APT installation:
librewolfFor the Flatpak installation:
flatpak run io.gitlab.librewolf-communityLaunch LibreWolf from Applications Menu
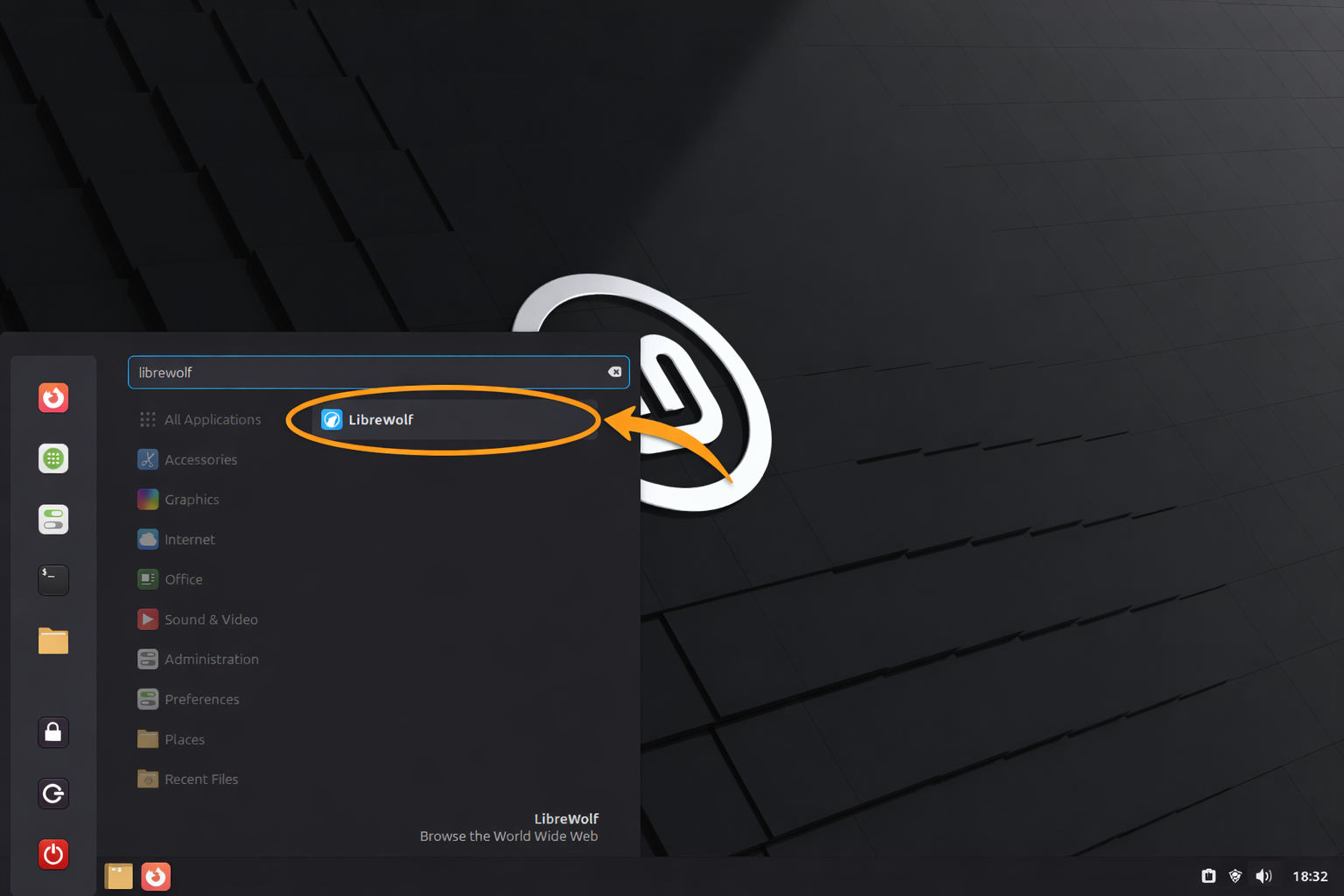
Locate LibreWolf in your Applications Menu under Internet or use the system search:
Taskbar > Internet > LibreWolf
Configure LibreWolf for First Use
Understand Default Privacy Settings
LibreWolf applies strict privacy defaults that may break some websites. The browser blocks third-party cookies, fingerprinting scripts, and cross-site trackers by default. If a site fails to load correctly, check the shield icon in the address bar and temporarily disable protections for that site. Use about:config to fine-tune settings, but note that changes persist across updates.
Change the Default Search Engine
LibreWolf sets DuckDuckGo as the default search engine. To change it, open Settings → Search and select from available privacy-focused engines (Startpage, Searx, Qwant). Adding Google or Bing requires manual configuration through the search engine manager. Privacy-focused engines won’t track your searches but may return fewer localized results.
Install Additional Extensions
LibreWolf includes uBlock Origin for ad blocking. Add privacy-focused extensions from Firefox Add-ons, but avoid extensions that require telemetry or extensive permissions. Recommended additions include Privacy Badger for tracking protection and Decentraleyes for local CDN resource serving. Check extension compatibility at about:addons after installation.
Update LibreWolf on Linux Mint
Update Extrepo Installation
LibreWolf updates automatically through your system’s package manager. To manually update:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeUpdate Flatpak Installation
Update all Flatpak applications including LibreWolf:
flatpak updateFor more details on managing Flatpak updates, see our guide to upgrading Flatpak on Linux Mint.
Troubleshooting LibreWolf on Linux Mint
Repository Update Fails with GPG Error
If sudo apt update shows GPG signature errors for the LibreWolf repository, verify the repository configuration:
sudo extrepo update librewolfThis refreshes the repository metadata and GPG keys. If the error persists, disable and re-enable the repository:
sudo extrepo disable librewolf
sudo extrepo enable librewolf
sudo apt updateLibreWolf Won’t Launch After Installation
Verify LibreWolf is properly installed by checking the executable path:
which librewolfExpected output: /usr/bin/librewolf
If the command returns nothing, reinstall LibreWolf. For Flatpak installations, verify the application ID:
flatpak list | grep -i librewolfIf missing, reinstall: flatpak install flathub io.gitlab.librewolf-community -y
Profile Migration from Firefox
LibreWolf can import Firefox profiles, but the feature may not work automatically. Manually copy your Firefox profile:
cp -r ~/.mozilla/firefox/*.default-release ~/.config/librewolf/librewolf/Launch LibreWolf and open about:profiles to select the migrated profile. Some Firefox-specific extensions may not work in LibreWolf due to telemetry dependencies.
Remove LibreWolf Browser From Linux Mint
Remove Extrepo Installation
Remove the LibreWolf package:
sudo apt remove librewolfDisable the LibreWolf repository:
sudo extrepo disable librewolfRemove unused dependencies:
sudo apt autoremoveVerify the repository was disabled:
ls /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ | grep librewolfNo output means the repository configuration was removed successfully.
Remove Flatpak Installation
Uninstall LibreWolf from Flatpak:
flatpak uninstall io.gitlab.librewolf-communityRemove unused Flatpak dependencies:
flatpak uninstall --unusedRemove User Data (Optional)
LibreWolf stores profiles, cache, and settings in your home directory. This data persists after uninstallation.
Removing these directories deletes all browsing history, bookmarks, extensions, and preferences. Back up any data you want to keep before proceeding.
Remove LibreWolf user data:
rm -rf ~/.config/librewolfRemove cache files:
rm -rf ~/.cache/librewolfFrequently Asked Questions
LibreWolf disables Digital Rights Management (DRM) by default for privacy. To play protected content, go to Settings > General > Digital Rights Management (DRM) Content and enable “Play DRM-protected content”.
Yes. While LibreWolf removes telemetry, it retains Firefox Sync support. You can enable it in the settings to sync your data with a Mozilla account, just like in standard Firefox.
Use Extrepo (APT) if you want LibreWolf to integrate with your system and update alongside other system packages. Use Flatpak if you prefer a sandboxed environment with stronger isolation from the rest of your system.
Conclusion
LibreWolf is now installed on your Linux Mint system using either extrepo or Flatpak. The extrepo method integrates with your system’s package manager for automatic updates, while Flatpak provides sandboxed isolation. Keep LibreWolf updated through your chosen installation method to receive security patches and new features. The browser’s telemetry removal and built-in tracking protection work immediately without additional configuration. When you need to uninstall LibreWolf, follow the removal instructions for your installation method and optionally clean user data directories. For stronger privacy with Tor network routing, see our guide to installing Tor Browser on Linux Mint.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>